
https://www.britishmuseum.org/collection/object/H_1984-0501-1
…it was becoming clear that Constantine was determined to put an end to Diocletian’s disastrous division of the Empire and to rule it alone. From 320, in defiance of recent tradition, he did not even include an easterner as one of the two annually elected Consuls, naming instead himself and his younger son; in 321 both his sons were named. The same year he began to gather together a huge war fleet, and to enlarge and deepen the harbour of Thessaloniki in readiness for its reception… writes John Julius Norwich in Byzantium, The Early Centuries, (pp. 47-48) and I think of the Gold Coin Pendant of Constantine the Great in the British Museum that commemorates the 321 Consulship and the ten years ahead that will change our world!
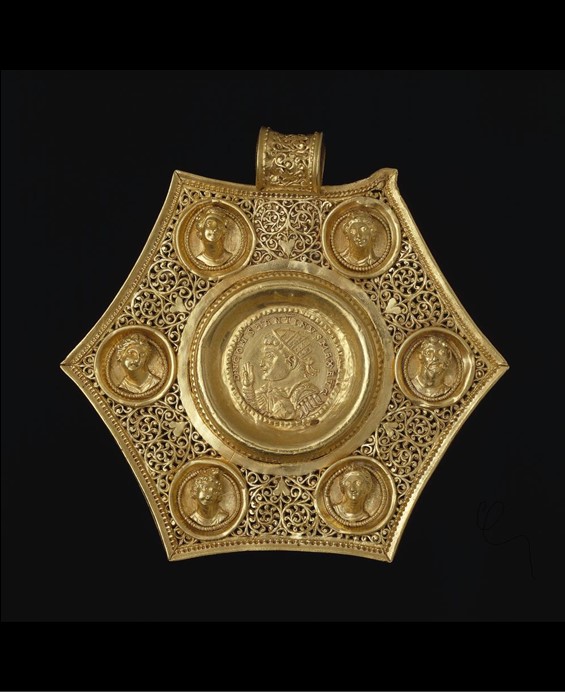
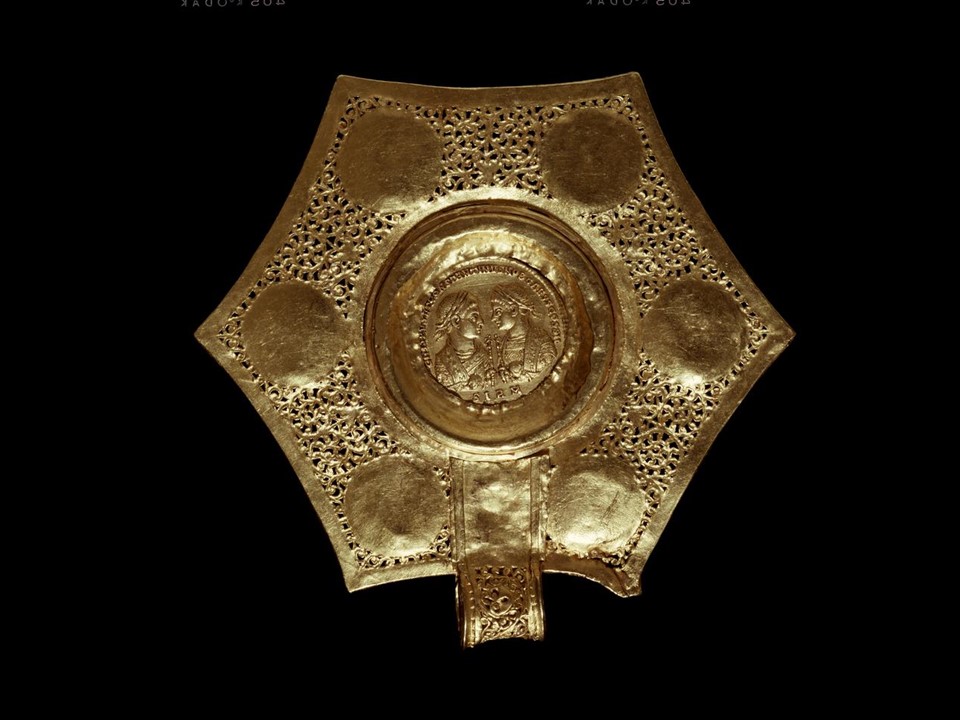
The British Museum Gold Coin Pendant of Constantine the Great is indeed spectacular! It is one of four or five similar Pendants, part of an impressive necklace, a very popular jewelry design of the Late Roman and Early Byzantine periods. Coin-set pendants were often of hexagonal shape, with a golden coin (solidus) placed in the center, and intricate pierced work, opus interrasile, for further ornamentation. https://www.britishmuseum.org/collectio n/object/H_1984-0501-1
https://www.britishmuseum.org/collection/object/H_1984-0501-1
According to the British Museum experts “…In the centre of the pendant is a double solidus of Constantine the Great. On the obverse, (depicted is) a bust of Constantine… wearing a radiate diadem and cuirass and paludamentum, (with his) right hand upraised (while) around the bust, a Latin inscription reads D N CONSTANTINVS MAX AVG. On the reverse, (depicted are) two confronted laureate busts of Constantine II and Crispus, both wearing imperial costume and holding eagle-topped sceptres. Around and below them, a Latin inscription reads CRISPVS ET CONSTANTINVS NOB CAESS COSS II. In each angle of the hexagon (the artist of the pendant created) a bust in high relief: from top left moving clockwise (a) female bust with elaborate coiffure (is depicted) looking to (the) right, (then a) female bust (is depicted) looking to (the) left. (A) bearded bust (follows) looking to (to the) left, (a)female bust looking to (the) left (as well), (a) bust of Attis (follows) wearing (a) Phrygian cap looking to (the) right (and finally a) female bust (is depicted) looking to (the) right. Each bust is framed by a circlet of beaded gold wire and a plain collar of gold sheet. The interstices between the busts are decorated in opus interrasile, the design comprising a heart-shaped motif in plain reserved gold from which emanate two vegetal scrolls which in turn form a larger open-work heart; running scroll tendrils fill the spaces between the collars and inner and outer borders; the scroll tendril design is less skilfully replicated on the suspension loop.” An inscription in Latin, SIRM, confirms that the Medallion was minted in Sirmium. https://www.britishmuseum.org/collection/object/H_1984-0501-1
For a Student Activity, please… check Here!