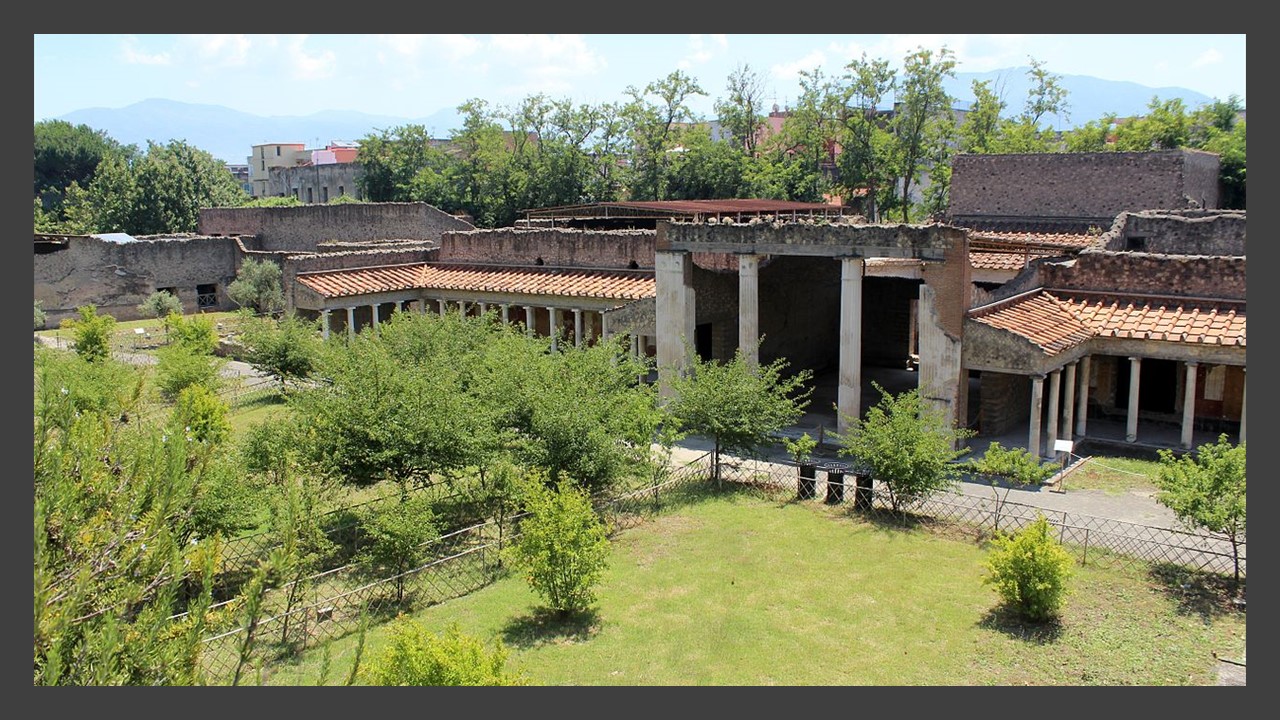
A traveller cruising by boat in the Bay of Naples during the 1st century AD would have marvelled at the continuous chain of private villas lining the coast. Although evidence of these villas survives to the present day, our knowledge is mostly fragmentary due to the fact that many are buried beneath Vesuvius’s ashes, modern estates or have been swallowed by the sea. Travellers would have been amazed by the opulence of the architectural features exhibited in these structures: porticoes, panoramic exedras, artificial or natural grottos, galleries, nymphaea, and piscinae. Travellers would have been equally amazed by the diverse interior designs and luxurious materials used by the artists. Villa Poppaea, in the ancient Roman town of Oplontis (Torre Annunziata between Naples and Sorrento, in Southern Italy) was one such extraordinary Villa…
https://jeanclaudegolvin.com/oplontis/
“Villa A of Oplontis, attributed by some to Poppaea the second wife of emperor Nero, was, strictly speaking, a maritime villa. It commanded a panoramic view from the top of a sheer cliff more than 14 m high that overlooked the ancient shoreline. To the south the view ranged from the limestone cliffs of the faraglioni (tall formations that resemble lighthouses) of Rovigliano, the islet near the port of Pompeii at the mouth of the Sarno River, to the length of the coast of the Sirens as far as Capri. To the west the superimposition of various layers of lava that created the Capo Oncino promontory during the Middle Ages had not completely concealed the Neapolitan and Phlegraean coast.” https://quod.lib.umich.edu/cgi/t/text/text-idx?c=acls;idno=heb90048.0001.001;rgn=div1;view=text;cc=acls;node=heb90048.0001.001:18
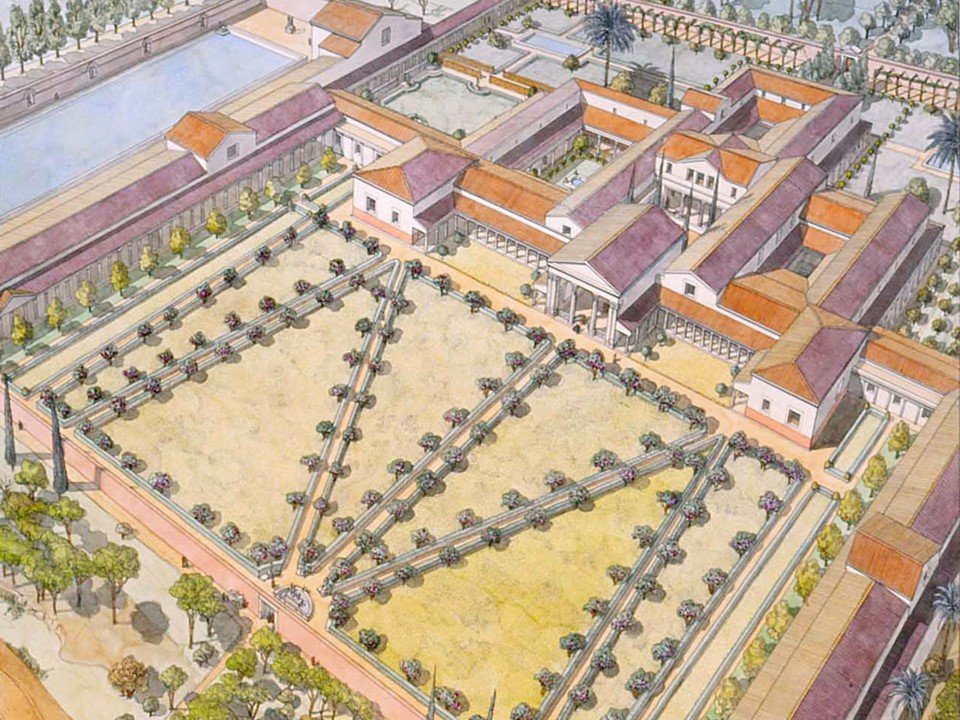
Villa Poppaea, built on a plateau, fourteen meters above sea level, took advantage of all the scenic pleasures of the Bay of Naples. Rooms were in such a way organized so that its residents and their guests would be able to enjoy the open air and the dramatic view of the sea in an environment of the utmost luxury. Please allow me to explain why Villa Poppaea was, for me, worth exploring…
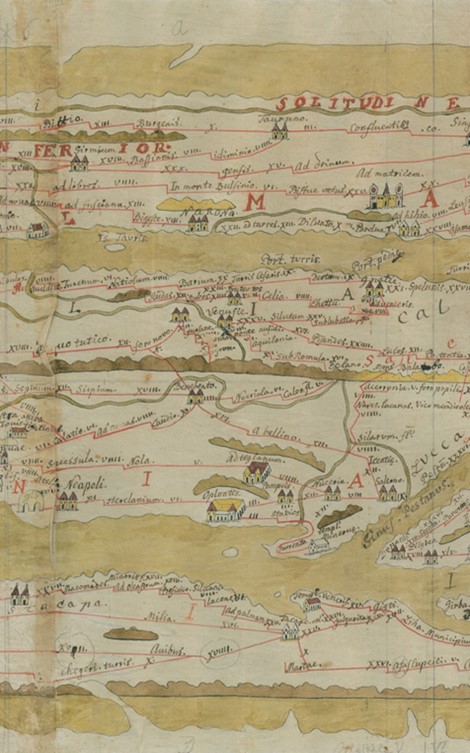
Tabula Peutingeriana, a unique twelfth-century copy of a fourth-century Roman map, marks Oplontis, the area where Villa Poppaea was discovered, as a large square building fronting the sea with twin, gabled, entrances. Interestingly, this is the only Roman reference to a site named Oplontis available to scholars. The name Oplontis is an intriguing mystery! https://quod.lib.umich.edu/cgi/t/text/text-idx?c=acls;idno=heb90048.0001.001;rgn=div1;view=text;cc=acls;node=heb90048.0001.001:20
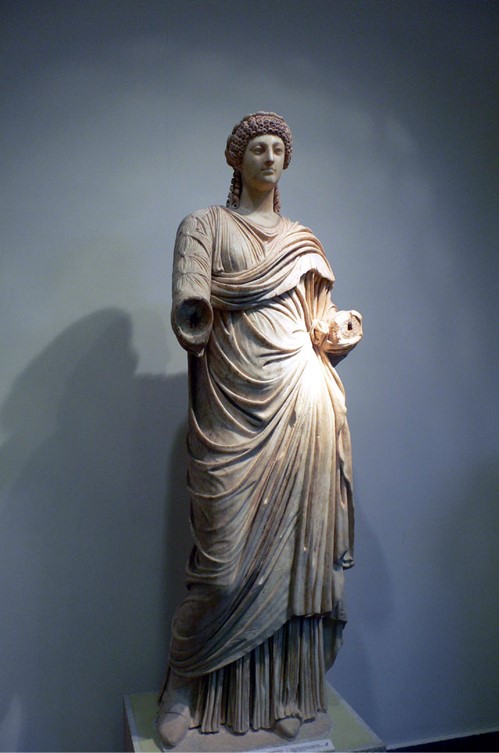

https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Poppaea_Olimpia.jpg
The luxurious Villa Maritime in Oplontis is believed to have been one of the residences of Poppaea Sabina, the second wife of Emperor Nero. Poppaea Sabina, born in nearby Pompeii, was the grand-daughter of Gaius Poppaeus Sabinus, Imperial Proconsul of Greece and the daughter of Poppaea Sabina the Elder, a celebrated Roman matron praised by Tacitus for her wealth and loveliness.
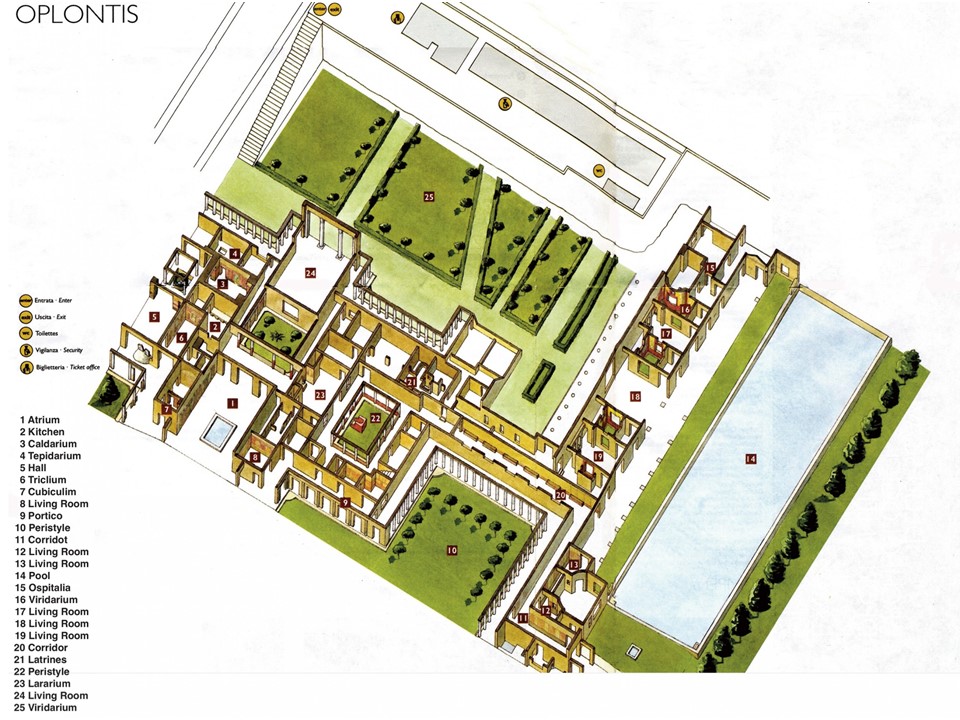
Villa Poppaea, uninhabited and under reconstruction at the time of Vesuvius’s eruption, was a massive residence of more than one hundred rooms and thirteen gardens. Construction started in the 50s BC, while renovations and extensions occurred regularly until the 79 AD volcanic eruption. This sumptuous villa was probably the model house for many of the smaller and less opulent houses built in the area at the same time. The oldest part of the house developed around the atrium, with a number of private or public rooms to serve its purpose for leisure and formalities. By 54 AD, the house extended to the east, with the addition of peristyles with collonaded porticoes extending out from the building’s core, an immense swimming pool and formal gardens. http://pompeiisites.org/en/oplontis-en-2/villa-poppaea/
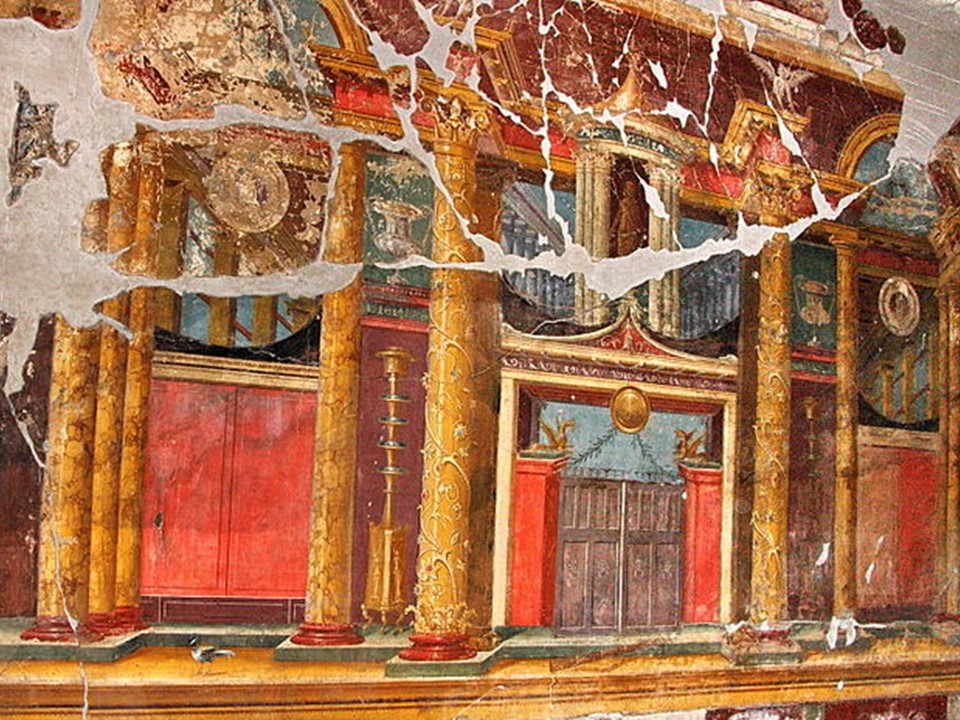

The 4th reason why Villa Poppaea was, for me, worth exploring, is its interior decoration… please bear with me as I will discuss the Villa’s frescoes in Villa Poppaea, Part II.
For a PowerPoint on Villa Poppaea, please… Check HERE!
