Agnus Dei, 1635 – 1640, Oil on Canvas, 37.3×62 cm, Prado Museum, Spain https://www.museodelprado.es/en/the-collection/art-work/agnus-dei/795b841a-ec81-4d10-bd8b-0c7a870e327b
The term Agnus Dei carries significance in both Christian liturgy and art, emanating from Latin to mean Lamb of God. Its usage and implications span religious, cultural, and historical contexts. The connection between Agnus Dei and Easter is central to Christian symbolism and deeply interwoven with the themes of sacrifice, redemption, and renewal inherent in the Easter celebration. The painting of Agnus Dei by Francisco de Zurbarán, is I believe one of the finest examples.
In Christian art, the Agnus Dei symbolizes Jesus’ sacrificial death and resurrection. This symbol is often depicted as a lamb carrying a cross or with a halo around its head, sometimes holding a flag, representing victory over death. This imagery has been a significant motif in Christian iconography since the early centuries of Christianity, appearing in mosaics, sculptures, paintings, and liturgical objects.
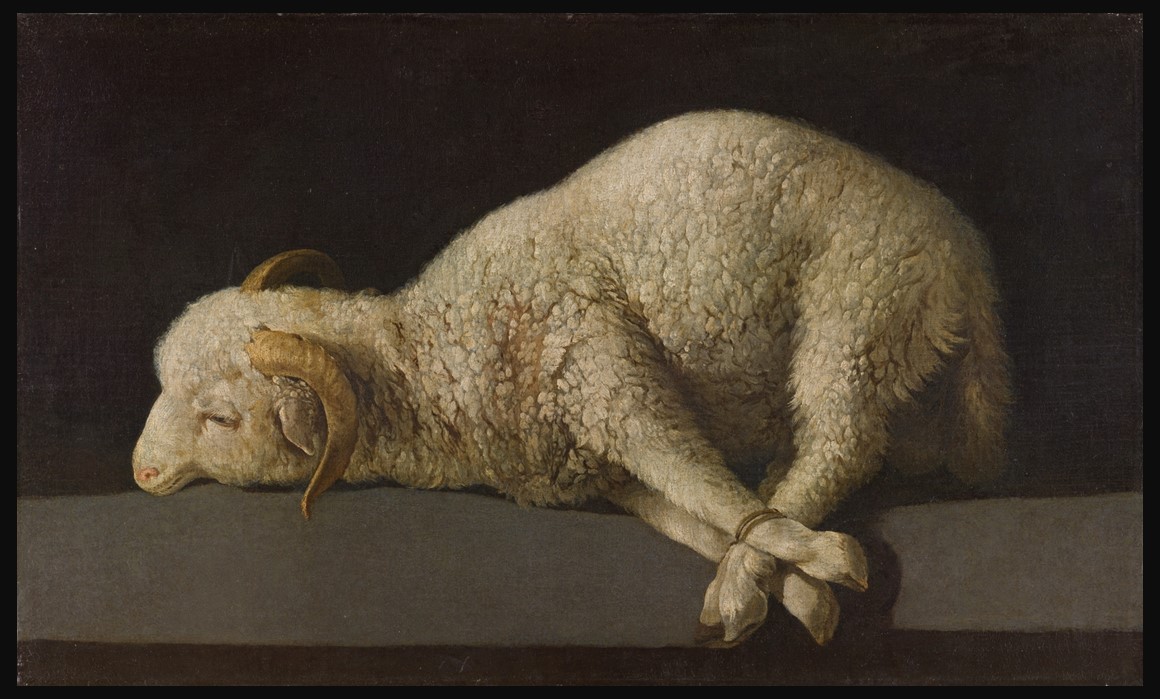
Francisco de Zurbarán, a Spanish painter of the Baroque period, is renowned for his deeply religious works that often depict monastic life, still lifes, and themes of Christian mysticism with a dramatic interplay of light and shadow. Zurbarán’s painting titled Agnus Dei, dating from around 1635-1640 is a fine example of his style. In this work, the artist presents a bound merino lamb between eight and twelve months old, lying on its side positioned against a dark, undefined background on top of a grey table. The lamb is presented with a remarkable degree of realism, from the texture of its wool to the serene expression on its face, despite the foreboding sense of its imminent sacrifice. This powerful image serves as a direct visual representation of the Lamb of God as referenced in Christian theology, symbolizing Jesus Christ’s sacrifice for the sins of humanity.
The elements of Zurbarán’s painting, the bound state of the lamb, and the overall somber tone evoke the Passion of Christ. The lamb, an innocent creature, becomes a poignant symbol of Christ’s submission to the crucifixion and his role as the sacrificial lamb who takes away the sins of the world. The use of chiaroscuro, or the contrast between light and dark, highlights the purity and innocence of the lamb, making it stand out against the dark background, which adds to the painting’s emotional depth and spiritual solemnity.
Zurbarán’s focus on this theme aligns with the Counter-Reformation period’s emphasis on religious renewal and the visual expression of Catholic doctrine. His works are celebrated for their ability to convey profound religious concepts with intense emotional weight and a deep sense of piety. Through his depiction of the Agnus Dei, Zurbarán invites contemplation on themes of innocence, sacrifice, and redemption, providing a visual meditation on the Christian faith and the mystery of Christ’s sacrificial love.
Francisco de Zurbarán’s engagement with the Agnus Dei theme extended beyond a singular masterpiece, manifesting in no fewer than six paintings, each with its iconographic nuances, highly sought after, presumably by private patrons. The allure of these pieces was such that in 1724, Antonio Palomino, both painter and writer, recounted the pride of an art aficionado in Seville who treasured a Zurbarán lamb, “painted from life,” more than a hundred actual sheep. The presented Museo del Prado example stands out as the epitome of Zurbarán’s artistry, marrying unparalleled technical skill, vivid descriptiveness, and poignant expressiveness with a layer of emotional depth considered unmatched by its counterparts. Art historians concur that this version emerged in the finest moment of Zurbarán’s creative period, specifically pinpointed to between 1635 and 1640, showcasing the artist at the pinnacle of his powers.
Francisco de Zurbarán (1598–1664), hailed from Fuente de Cantos, Extremadura, is an important figure of the Spanish Baroque period. As a painter, Zurbaráns is known for his profound religiosity, meticulous attention to detail, and masterful use of chiaroscuro. His artistic journey blossomed in Seville, where he established his workshop and became a pivotal figure in the city’s vibrant art scene, often being referred to as the ‘Spanish Caravaggio’ due to his dramatic interplay of light and shadow. His oeuvre predominantly explores themes of Christian mysticism and monastic life, with works that depict saints, martyrs, and biblical narratives imbued with a stark realism and emotional depth. Among his most celebrated works are the series for the Monastery of Guadalupe, the altarpieces for the San Pablo El Real, and his poignant renditions of the Agnus Dei. Zurbarán’s ability to blend spiritual intensity with lifelike representation won him the admiration of his contemporaries and a significant commission from King Philip IV. Despite facing financial difficulties in his later years, Zurbarán’s legacy endured, influencing not only the trajectory of Spanish art but also leaving a lasting impact on the broader tapestry of Baroque painting.
For a PowerPoint Presentation of 10 Masterpieces by Francisco de Zurbarán, please… Check HERE!