Isabella d’Este, Marquise of Mantua (1474–1539), 1534/36 Oil on Canvas, 101.9 × 64 cm, Kunsthistorisches Museum Vienna, Austria https://tiziansfrauenbild.khm.at/en/
In a well-known passage in De pictura, Alberti describes the principal power of portraits, and even painting in general, as follows: Painting possesses a truly divine power in that it does not only make the absent present, as they say of friendship, but it also represents the dead to the living many centuries later […] Through painting, the faces of the dead go on living for a very long time. Does Titian’s Portrait of Isabella d’Este possess a truly divine power in presenting the true likeness of the Marchioness of Mantua? https://scholarlypublications.universiteitleiden.nl/access/item%3A2889008/view page 125
Titian’s renowned painting of Isabella d’Este, commonly referred to as La Bella (The Beautiful), was created in 1534 when Isabella herself was approximately 60 years old. Notably, the Marchioness of Mantua did not directly sit for Titian’s brush; instead, she dispatched a portrait of herself executed by Francesco Francia (now lost) in 1511 to provide a reference for her likeness. Titian, the accomplished Venetian master, concluded his Portrait in 1536, earning Isabella’s delight with the outcome. In a letter to the Mantuan ambassador in Venice, she acknowledged… The portrait by Titian’s hand captures such a pleasing essence that we are prompted to question whether, during the age he depicts us, we ever possessed the beauty it encapsulates.
Titian’s Portrait of Isabella d’Este is currently housed in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna. It portrays Isabella as a young and exquisite woman, dressed in elegant attire, with a sophisticated hairstyle and adorned with jewels. The portrait may not be an accurate portrayal of Isabella turning sixty, but it effectively captures the regal poise and demeanor that defined the Marchioness of Mantua.
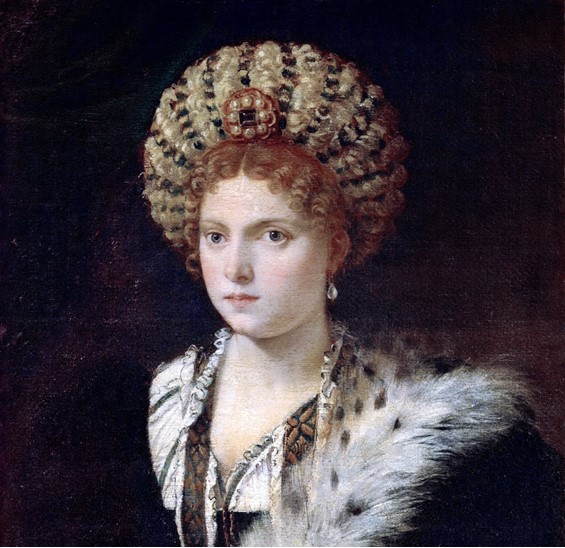

Isabella d’Este, Marquise of Mantua (detail), 1534/36, Oil on Canvas, 101.9 × 64 cm, Kunsthistorisches Museum Vienna, Austria https://www.khanacademy.org/humanities/renaissance-reformation/high-ren-florence-rome/late-renaissance-venice/a/titian-isabella-deste-isabella-in-black
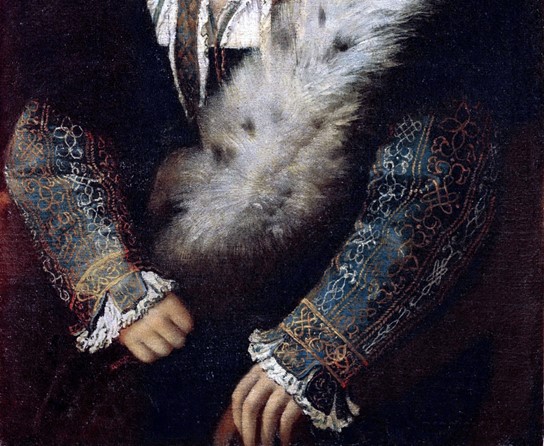

Isabella d’Este, Marquise of Mantua (detail), 1534/36, Oil on Canvas, 101.9 × 64 cm, Kunsthistorisches Museum Vienna, Austria https://www.khanacademy.org/humanities/renaissance-reformation/high-ren-florence-rome/late-renaissance-venice/a/titian-isabella-deste-isabella-in-black
In the painting, Isabella is portrayed in a three-quarter profile, with her gaze slightly averted from the viewer. She is adorned in a sumptuous gown that combines shades of blue and black, intricately embellished with the fantasie dei vinci pattern, which serves as a testament to her position as a prominent noblewoman of her era. The hues of her attire are both dark and vivid, and the fashionable accessories that Isabella wears, pearl earrings and a fur shawl gracefully draped over her shoulder, have been meticulously rendered. These details not only reflect Isabella’s significance but also highlight Titian’s expertise in capturing textures and fabrics. https://scholarlypublications.universiteitleiden.nl/access/item%3A2889008/view pp.22-23
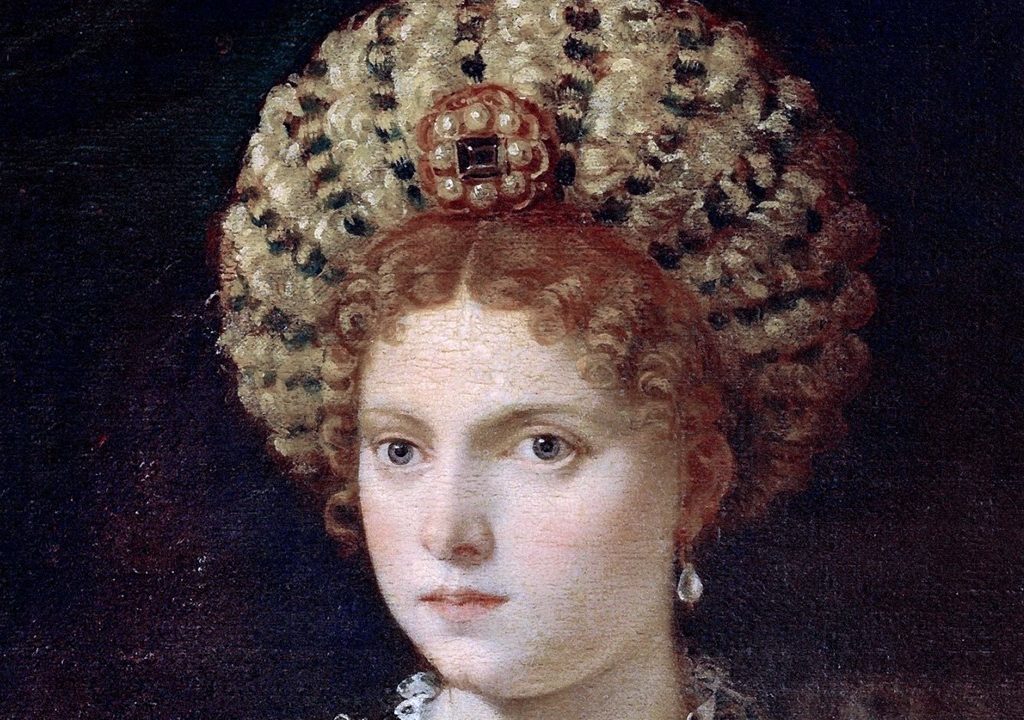

Isabella d’Este, Marquise of Mantua (detail), 1534/36, Oil on Canvas, 101.9 × 64 cm, Kunsthistorisches Museum Vienna, Austria https://www.khanacademy.org/humanities/renaissance-reformation/high-ren-florence-rome/late-renaissance-venice/a/titian-isabella-deste-isabella-in-black
1 am particularly drawn to the elegant arrangement of Isabella’s hair. The Marchioness wears a captivating bulbous headdress featuring a sizable brooch adorned with eight pearls encircling a gem. Isabella was a famous fashionista. The bulbous headdress (known as zazara at the time) was designed by Isabella herself, and the Titian painting served her own trendsetting fashion put on display. What a magnificent way to emphasize her majestic presence!
Isabella’s expression is both serene and confident, befitting her reputation as a powerful and influential figure. Her gaze conveys a sense of introspection and sophistication, while the faint hint of a smile gracing her lips adds an air of subtle allure. The play of light and shadow in the painting adds depth and dimension to Isabella’s features, enhancing the overall realism of the portrait. Titian’s skillful use of chiaroscuro, a technique that contrasts light and dark tones, gives the portrait a lifelike quality and a sense of depth.
The background of the painting is relatively simple, allowing the focus to remain on Isabella’s presence and personality, her elegance, grace, and authority. Through meticulous attention to detail, refined use of color and light, and a keen understanding of portraiture, Titian created a lasting image that captures the essence of Isabella’s character and her place in history.
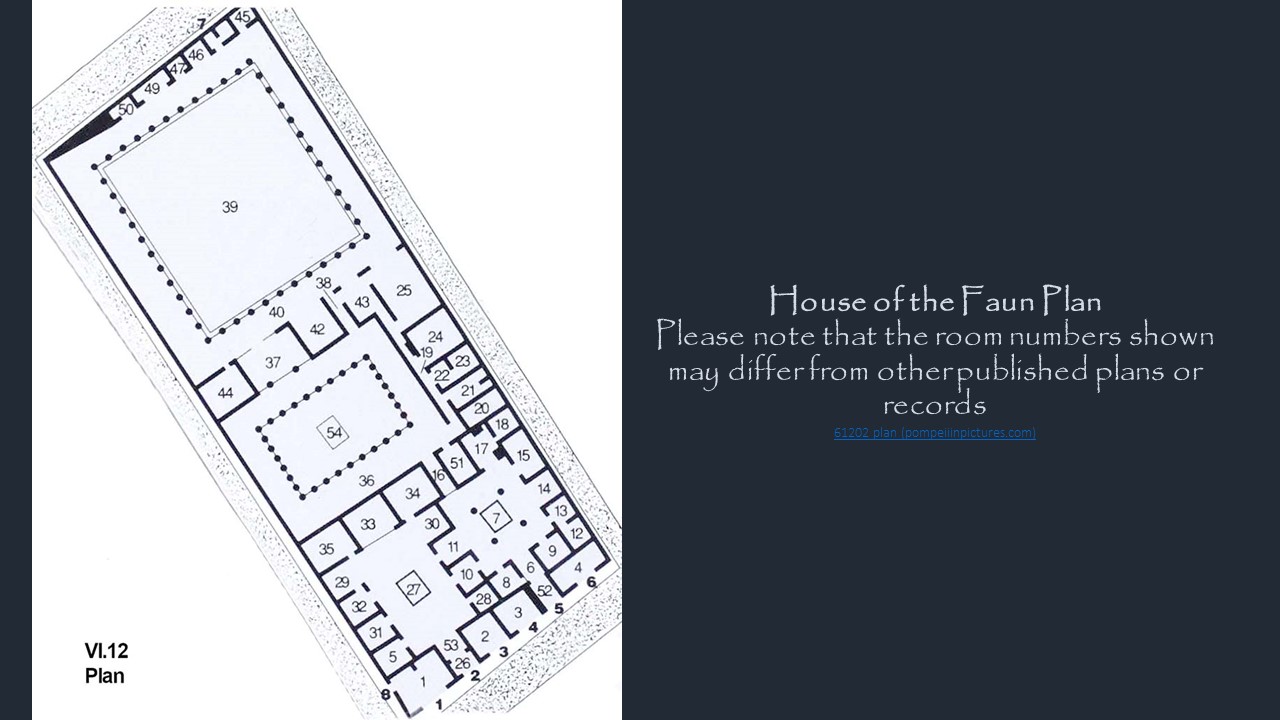
For a PowerPoint, titled 9 Portraits of Isabella d’Este, please… Check HERE!… Check HERE!
An Interesting Video about Isabella d’Este the Marchioness of Mantua during Early Renaissance Italy by World History Encyclopedia (8:09 min)