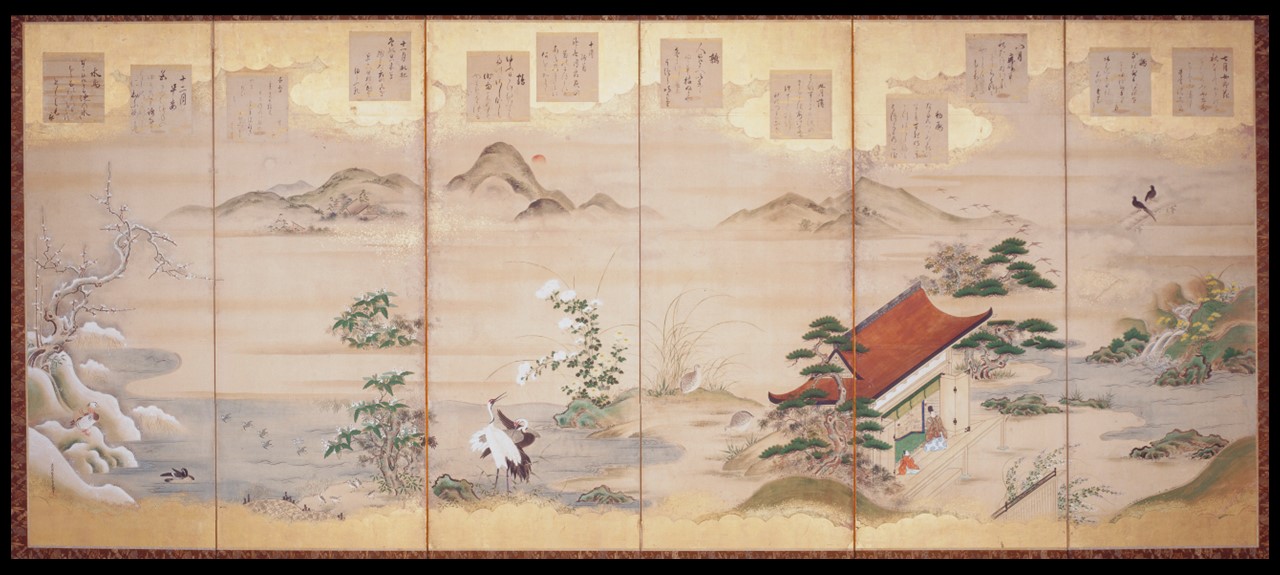
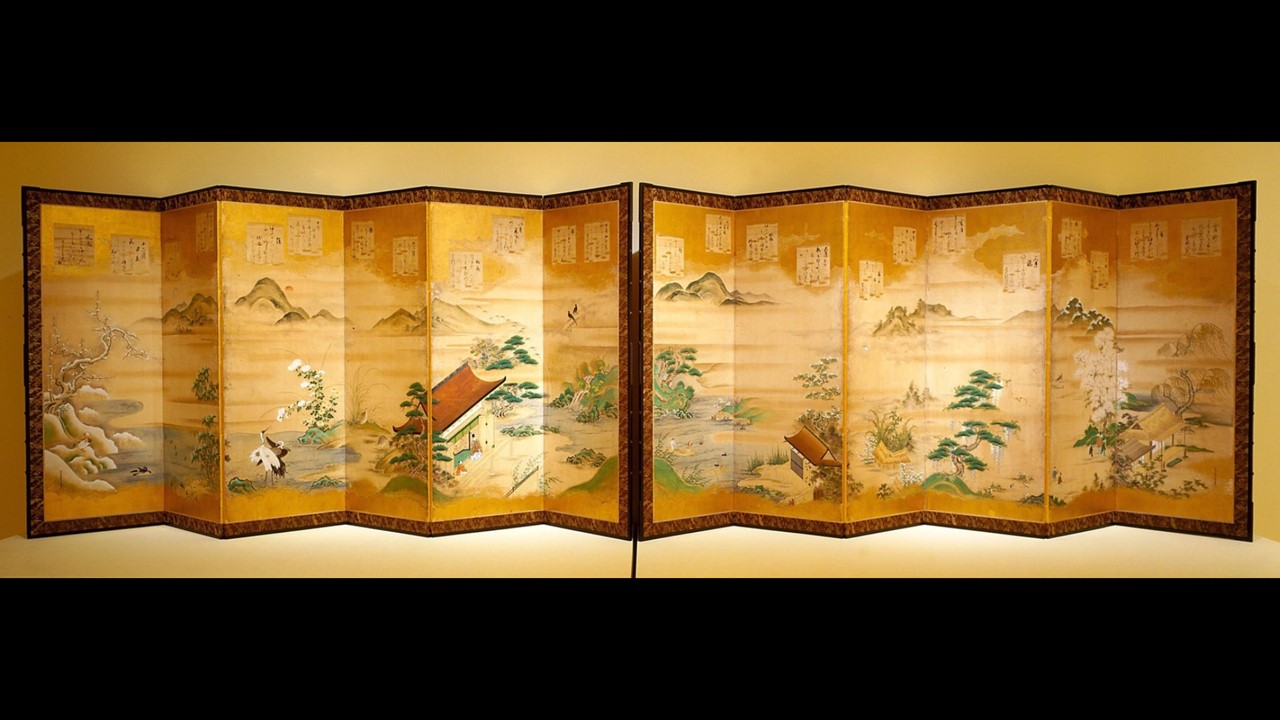
Teika’s Poems for the Twelve Months, Edo period (1603-1868), 1646-1710, ink, color and gold leaf on paper, six-fold screen, 170.18x 61.92 cm (each panel), Indianapolis Museum of Art, USA
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Tosa_Mitsunari_-_Teika%27s_Poems_for_the_Twelve_Months_-_2000.9_-_Indianapolis_Museum_of_Art.jpg
Before my eyes / the snowflakes fall upon the icy pond / piling up like the years gone by / like the layered feather coats of the oshi… wrote Fujiwara Teika back in 1214. Many years later Fujiwara Teika’s Poems for the Twelve Months presented by Tosa Mitsunari delight us with their elegance and beauty! http://collection.imamuseum.org/artwork/55793/
Who is Fujiwara Teika? Fujiwara Sadaie, also called Teika, or Fujiwara Teika, (born 1162, Japan—died Sept. 26, 1241, Kyōto), is one of the greatest poets of his age and Japan’s most influential poetic theorists and critics until modern times. The son of a great poet, Shunzei (or Toshinari, 1114–1204), Teika surpassed his father’s literary legacy and raised his family in political importance. His literary talent attracted the attention of retired emperor Go-Toba (1180–1239), who appointed him, in 1205, one of the compilers of the eighth Imperial anthology Shin kokinshū (c. 1205, “New Collection of Ancient and Modern Times”), and in 1232, sole compiler of the ninth anthology, Shin chokusenshū (1235; “New Imperial Collection”). This is a great accomplishment and honour. https://www.britannica.com/biography/Fujiwara-Sadaie
Who is Tosa Mitsunari? Tosa Mitsusuke (1675–1710) was a Japanese artist of the Edo era. In 1696, as the 18th head of the Tosa school of painting, Mitshunari was appointed Official Court Painter with duties to serve the Emperor. He worked for the Imperial Official Bureau of Painting and managed to revive his family’s political and economic fortunes. In 1709, he did paintings of room partitions in the royal palace and in the Sento palace with Kano Tsunenobu. Mitsuoki was known for reintroducing the Yamato-e style and reviving the Tosa school of painting. He painted delicate bird-and-flower (kacho) paintings in the Chinese court manner and was especially noted for his precise depictions of quail. https://prabook.com/web/tosa.mitsuoki/3742785 and https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tosa_Mitsusuke

Teika’s Poems for the Twelve Months, Edo period (1603-1868), 1646-1710, ink, color and gold leaf on paper, six-fold screen, 170.18x 61.92 cm (each panel), Indianapolis Museum of Art,
https://www.artsy.net/artwork/tosa-mitsunari-teikas-poems-for-the-twelve-months
How are a poet and a painter connected in art? Japanese secular painting and poetry walk side by side. Poets composed verses about images in paintings and painters made works based on poems and inscribed them with erudite calligraphy, or pasted a poem in elegant characters onto the painting. The resulting synthesis exceeded the sum of the parts, creating many layers of meaning. http://collection.imamuseum.org/artwork/55793/
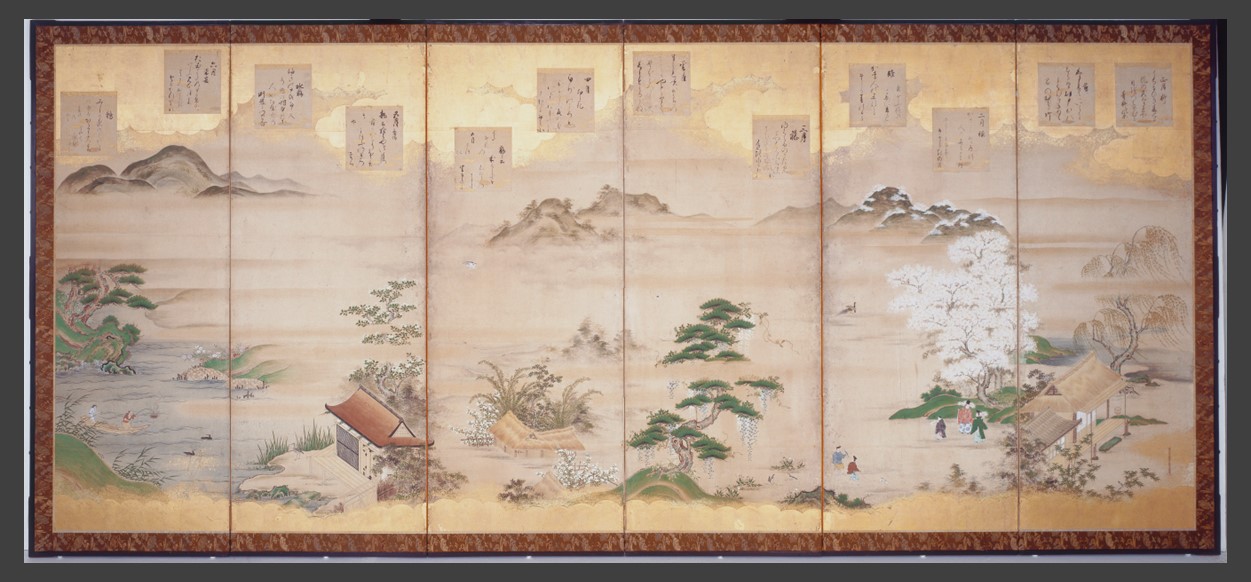

Teika’s Poems for the Twelve Months, Edo period (1603-1868), 1646-1710, ink, color and gold leaf on paper, six-fold screen, 170.18x 61.92 cm (each panel), Indianapolis Museum of Art,
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Tosa_Mitsunari_-_Teika%27s_Poems_for_the_Twelve_Months_-_2000.10_-_Indianapolis_Museum_of_Art.jpg
Are Fujiwara Teika’s Poems for the Twelve Months painted by Tosa Mitsunari in the Indianapolis Museum of Art Screen an example of artistic collaboration? Yes, the Indianapolis Screen is a perfect example. The pair of six-fold screens in the Indianapolis Museum masterfully combines landscape painting and poetic texts. The texts, poems by Fujiwara Teika, subtly express emotions through metaphors of nature. The imagery, a typical landscape by Tosa Mitsunari, celebrates the changing aspect of nature. The depicted months are numbered according to the lunar calendar, and the first month, presented in the first panel, roughly corresponds to February. http://collection.imamuseum.org/artwork/55793/
For a Student Activity inspired by the Indianapolis Museum Japanese Screens, please… Check, HERE!