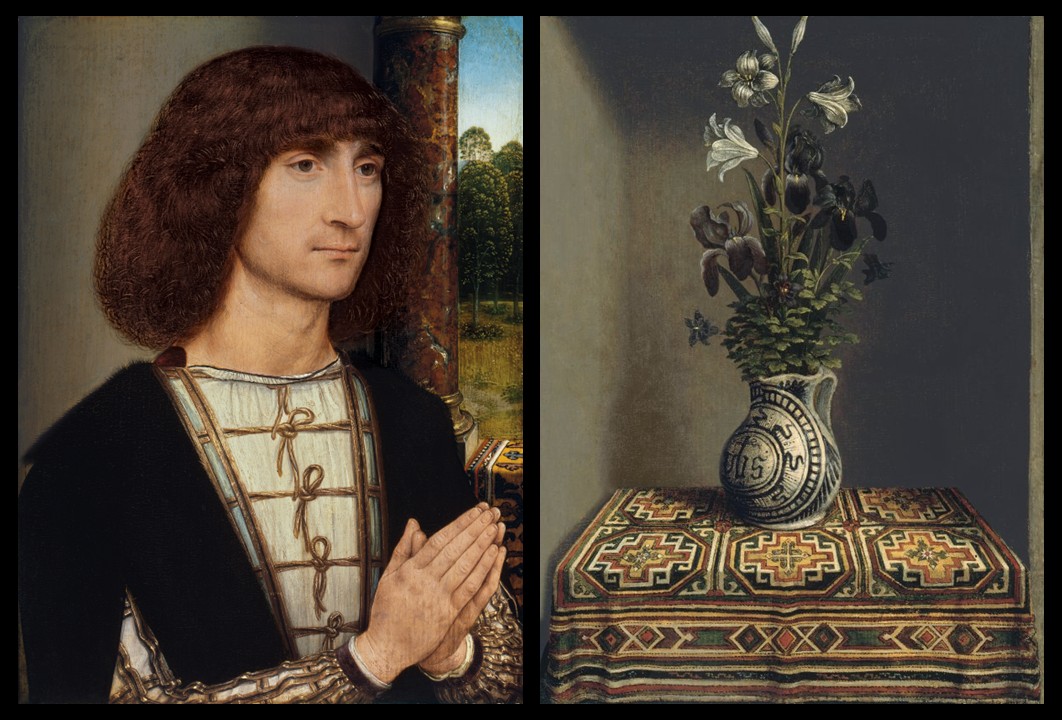
Portrait of a young man praying (obverse) and Flowers in a Jug (verso), ca. 1485, Oil on Panel, 29.2 x 22.5 cm, Museo Nacional Thyssen-Bornemisza, Madrid, Spain https://www.museothyssen.org/coleccion/artistas/memling-hans/retrato-hombre-joven-orante-anverso and https://www.museothyssen.org/coleccion/artistas/memling-hans/florero-reverso
Hans Memling, a prominent Flemish artist of the 15th century, holds a significant place in the Thyssen-Bornemisza National Museum’s collection in Madrid. Known for his refined and emotive style that bridges the Gothic and early Renaissance, Memling’s works exemplify the sophisticated use of colour, meticulous detail, and spiritual depth characteristic of Early Netherlandish painting. The museum houses the double-sided painting of the Portrait of a Young Man Praying and Flowers in a Jug, which demonstrates the artist’s ability to convey sacred narratives with clarity and grace. Memling’s contribution to the collection enriches its representation of Northern Renaissance art, offering visitors a glimpse into the devotional and artistic sensibilities of his era.
Hans Memling, born in Seligenstadt near Frankfurt around 1435, was a German painter who became a leading figure in the Early Netherlandish school. By 1465, he had relocated to Bruges, where he obtained citizenship and established a successful workshop. Memling’s early training is believed to have been under Rogier van der Weyden in Brussels, which significantly influenced his artistic development. Throughout his career, Memling received numerous commissions from both local patrons and international clients, particularly from the Italian community in Bruges. He remained active in Bruges until his death in 1494.
The artist’s work is characterized by its refined elegance and serene compositions, often reflecting the influence of his mentor, Rogier van der Weyden. He was instrumental in popularizing the use of landscape backgrounds in portraiture, enhancing the naturalism and depth of his paintings. His portraits are noted for their meticulous attention to detail and the harmonious depiction of his subjects. Among his notable works are the Triptych of the Last Judgment (1467–1471) housed in the National Museum in Gdańsk, and the Diptych of Maarten van Nieuwenhove (1487) in the Memling Museum in Bruges. Memling’s art had a lasting impact on the development of Northern Renaissance painting, influencing artists such as Gerard David and Juan de Flandes.
Memling’s aesthetic is distinguished by his delicate balance between realism and idealization, a hallmark of Early Netherlandish painting. His works exhibit extraordinary attention to detail, from the intricate patterns of textiles to the soft rendering of skin tones and facial features. His use of colour is particularly notable, with a palette that combines rich, jewel-like tones with subtle gradations to create a sense of luminosity and depth. He masterfully employed oil paints to achieve smooth transitions and fine details, enhancing the lifelike quality of his figures. The tranquil expressions and poised gestures of his subjects contribute to the serene and contemplative mood that defines much of his oeuvre. Furthermore, his incorporation of detailed landscapes as backgrounds—featuring rolling hills, distant towns, and serene skies—imbued his compositions with a sense of expansiveness and connection to the natural world. Memling’s ability to blend spiritual gravitas with human intimacy made his works deeply appealing to both religious and secular patrons, securing his reputation as a preeminent painter of his time.
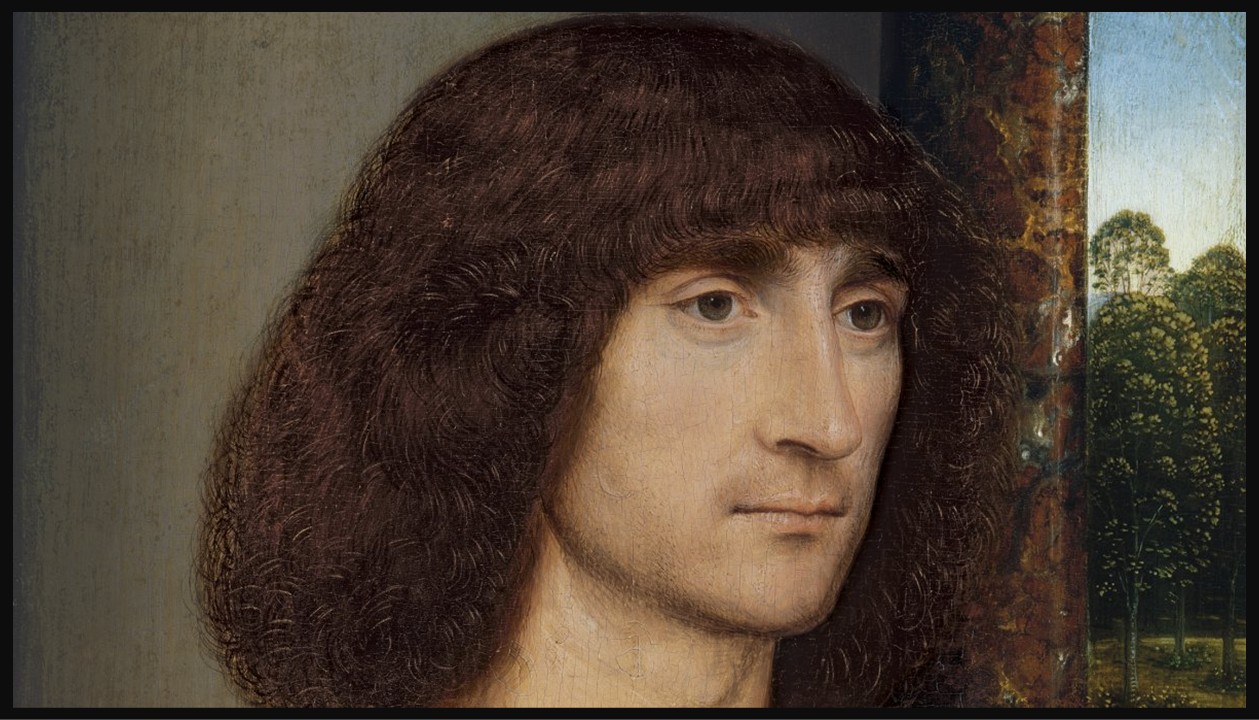


Portrait of a young man praying (obverse) and Flowers in a Jug (verso) (details), ca. 1485, Oil on Panel, 29.2 x 22.5 cm, Museo Nacional Thyssen-Bornemisza, Madrid, Spain https://www.museothyssen.org/coleccion/artistas/memling-hans/retrato-hombre-joven-orante-anverso and https://www.museothyssen.org/coleccion/artistas/memling-hans/florero-reverso
The Thyssen-Bornemisza double-sided painting, created around 1485, features the Portrait of a Young Man Praying on the obverse and Flowers in a Jug on the verso. The portrait depicts an unidentified young man in a devout posture, suggesting that the panel was originally part of a triptych. In such an arrangement, the central panel would likely have featured the Virgin and Child, with a female counterpart to the young man on the opposite wing. The subject’s attire and hairstyle indicate he may have been an Italian patron, reflecting Memling’s connections with the Italian community in Bruges. The meticulous attention to detail and serene expression exemplifies Memling’s refined portraiture style.
On the reverse side, Flowers in a Jug, the artist presents one of the earliest known independent still lifes. The composition includes symbolic elements: lilies representing the Virgin Mary’s purity and a jug adorned with Christ’s monogram, alluding to the Holy Family. This panel likely served as one of the exterior wings of the triptych, with the other wing possibly featuring a complementary still life or the couple’s emblem. Memling’s inclusion of such detailed still life elements highlights his innovative approach and contributes to the rich symbolism characteristic of his work.
For a PowerPoint Presentation of Hans Memling’s oeuvre, please… Check HERE!
Bibliography: https://www.museothyssen.org/coleccion/artistas/memling-hans/retrato-hombre-joven-orante-anverso and https://www.museothyssen.org/coleccion/artistas/memling-hans/florero-reverso