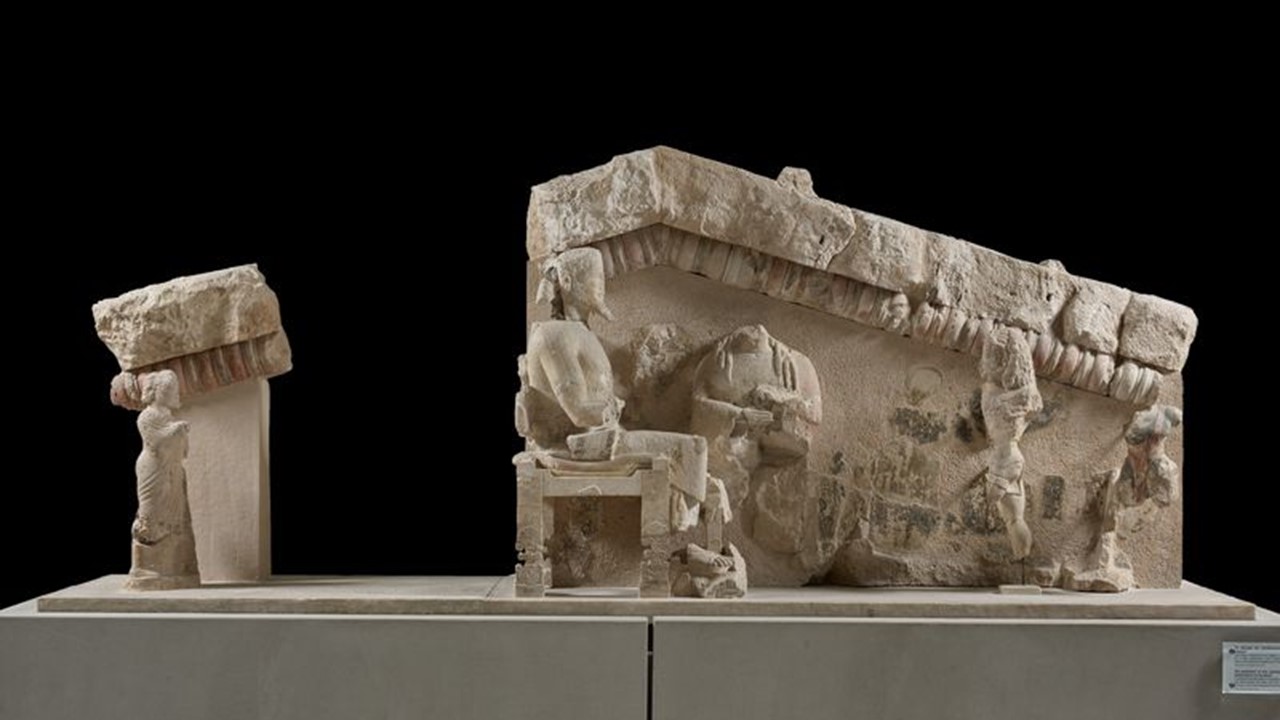
https://www.theacropolismuseum.gr/en/apotheosis-deification-herakles-pediment
I will sing of Herakles, the son of Zeus and much the mightiest of men on earth. Alcmena bare him in Thebes, the city of lovely dances, when the dark-clouded Son of Cronos had lain with her. Once he used to wander over unmeasured tracts of land and sea [5] at the bidding of King Eurystheus, and himself did many deeds of violence and endured many; but now he lives happily in the glorious home of snowy Olympus, and has neat-ankled Hebe for his wife. Hail, lord, son of Zeus’ Give me success and prosperity… writes the anonymous poet of Homeric Hymn 15… and The Apotheosis of Herakles in the Acropolis Museum comes to my mind. https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.01.0138%3Ahymn%3D15
Let’s answer some questions about The Apotheosis of Herakles in the Acropolis Museum…
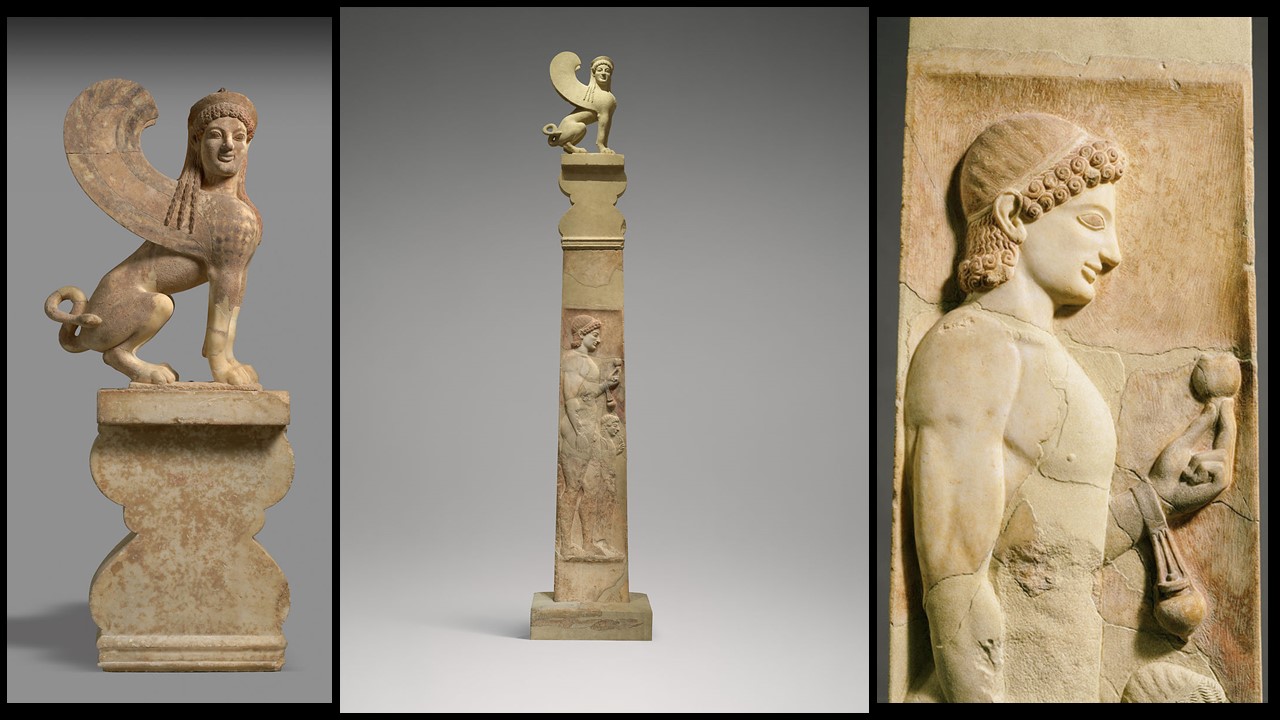
What is a Pediment and how important Pediments were they for Greek Temple Architecture? According to the Encyclopedia Britannica… Pediment, in architecture, is a triangular gable forming the end of the roof slope over a portico (the area, with a roof supported by columns, leading to the entrance of a building). For ancient Greek architecture, the two pediments featured on the two narrow sides of their temples were very important. They served as the ‘crowning feature’ of the whole structure. The triangular wall surface of the pediment, called the tympanum, was often decorated with sculptural compositions. Last but not least, Pediments were always crowned by a raking, or slanted, cornice. https://www.britannica.com/technology/pediment-architecture
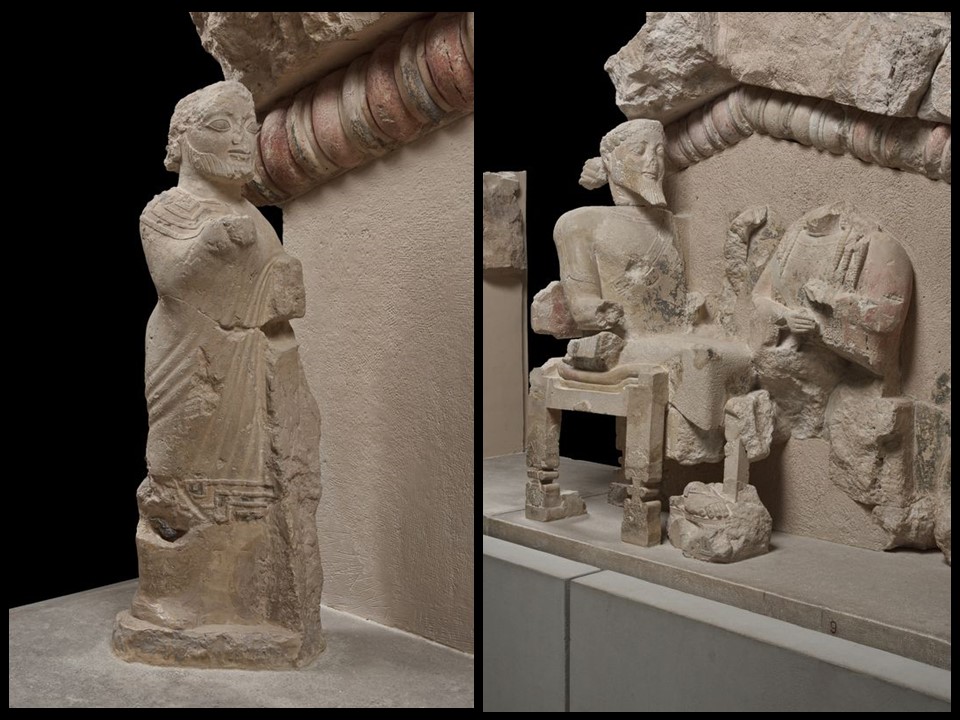
Where, and When, did the Apotheosis of Herakles Pediment was discovered? The Apotheosis of Herakles pediment was discovered, during the 1888 excavation period, buried, east and southeast of the Parthenon, in the Acropolis of Athens.
Was the Apotheosis of Herakles Pediment part of the Acropolis Perserschutt? Yes! The Perserschutt consists of numerous remains of statues vandalized by the Achaemenids during the terrible years of the second Persian invasion… Ten years after the Battle of Marathon (490 BC), the Persians returned to Greece and after their victory at the Battle of Thermopylae, in September of 480 BC, they entered Athens. The small number of Athenians who had barricaded themselves on the Acropolis, hoping that the Wooden Walls of the Delphic Oracle would protect them, were eventually defeated, and Xerxes ordered Athens to be torched. Those Persians who had come up first betook themselves to the gates, which they opened, and slew the suppliants; and when they had laid all the Athenians low, they plundered the temple and burnt the whole of the Acropolis. (Herodotus VIII.53). Months later, after the victory at Salamis, and the Battle of Plateae in 479 BC, the Athenians returned to their city… they respectfully buried the mutilated sacred statues of the Archaic period on the Acropolis (these remains are called Perserschutt) and proceeded with reorganizing their civic and private lives… waiting for the right time to rebuild their Acropolis. https://www.khanacademy.org/humanities/special-topics-art-history/arches-at-risk-cultural-heritage-education-series/xa0148fd6a60f2ff6:ruins-reconstruction-and-renewal/a/destruction-memory-and-monuments-the-many-lives-of-the-parthenon
Which Acropolis building did the Apotheosis architectural sculptures decorate? Archaeologists are not categorically certain. According to the Acropolis Museum experts, the pediment probably decorated one of the small buildings, referred to as “oikemata”, on the Archaic Acropolis. Some scholars, however, suggest these remains were once part of the pediment of the Hekatompedon, a building that stood on the site now occupied by the Parthenon. https://www.theacropolismuseum.gr/en/apotheosis-deification-herakles-pediment

https://www.theacropolismuseum.gr/en/apotheosis-deification-herakles-pediment

https://www.theacropolismuseum.gr/en/apotheosis-deification-herakles-pediment
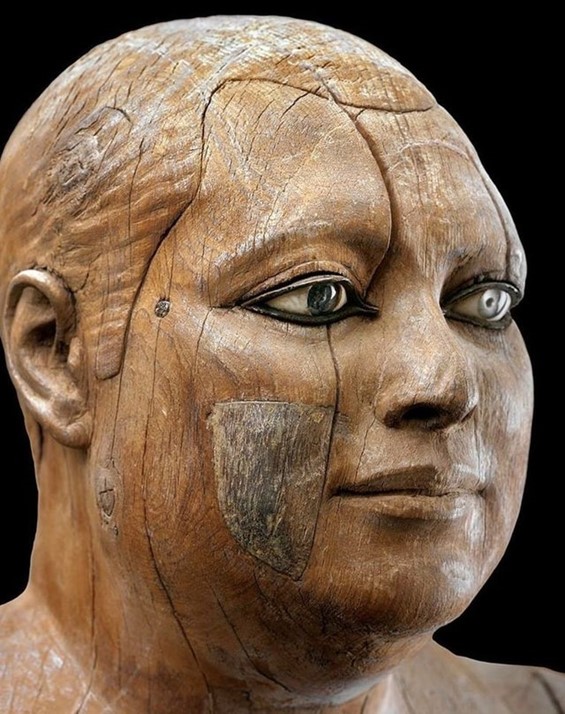
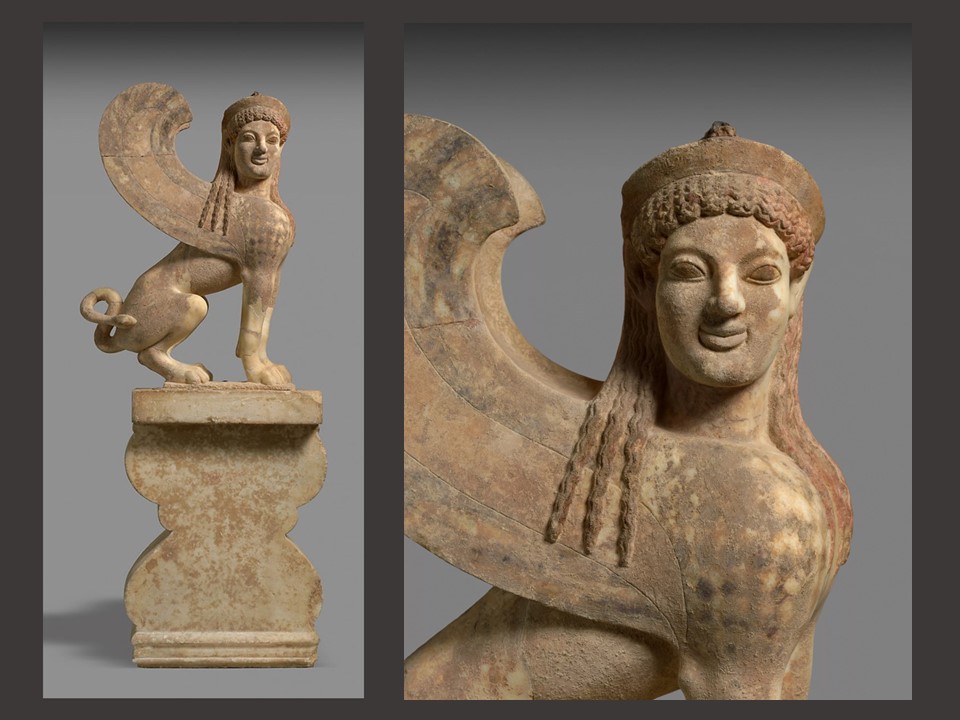
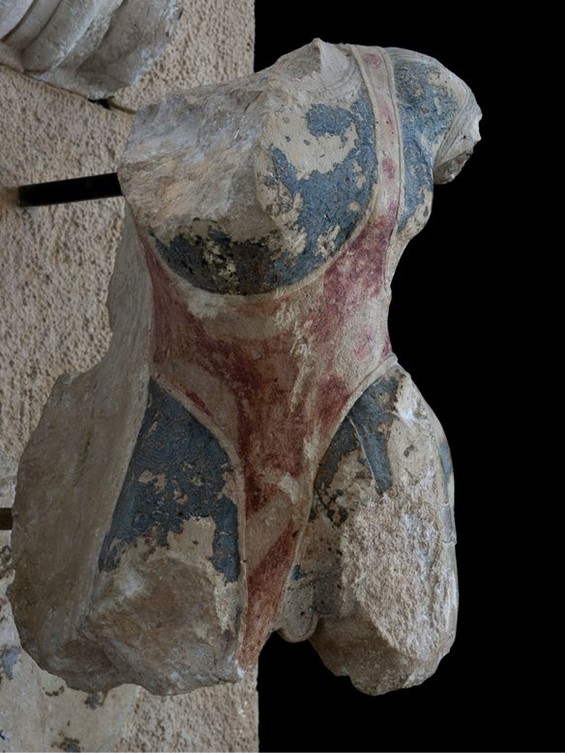
How important, artistically, is the Apotheosis Pediment? These pedimental sculptures are of high quality. Of particular interest are the heads that have been preserved, that of Zeus and especially that of Heracles with finely worked details of his facial features and hair. The garments worn by the figures are equally attractively rendered, as is Zeus’s throne with palmettes on the legs, and the skin of the lion, whose head, with incised curls on the mane, covers Heracles’ head like a hood. https://www.latsis-foundation.org/content/elib/book_8/acropolis_en.pdf page 30-31
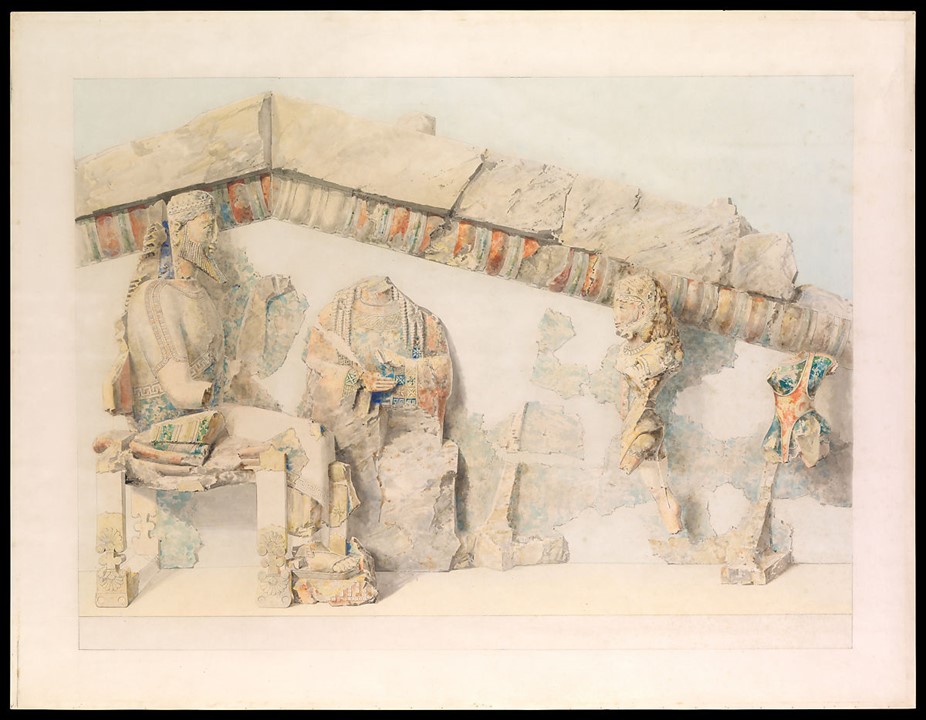

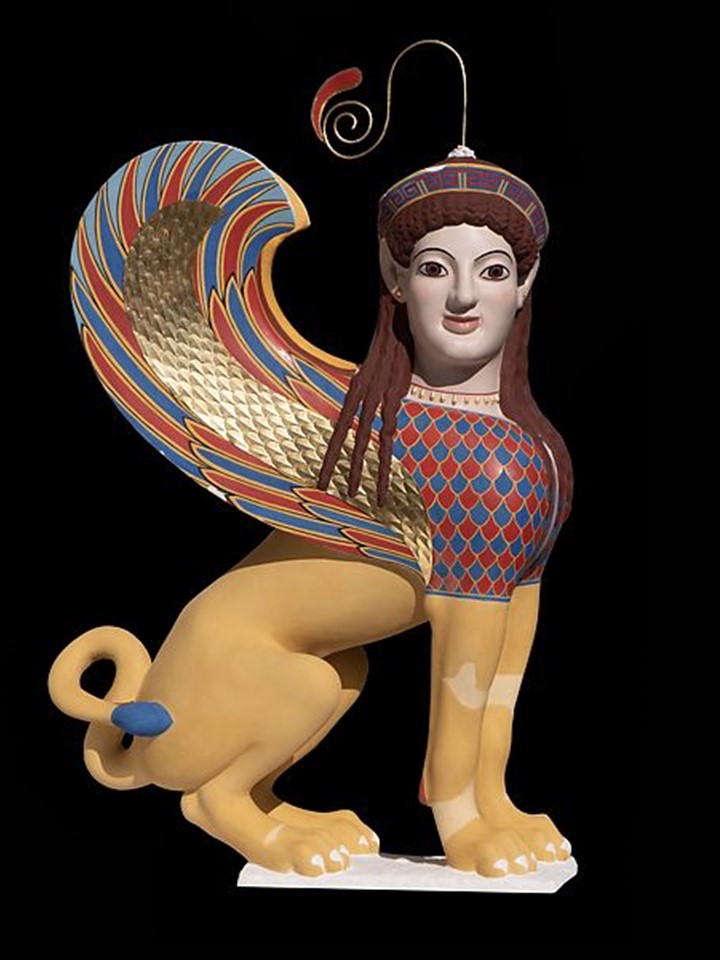
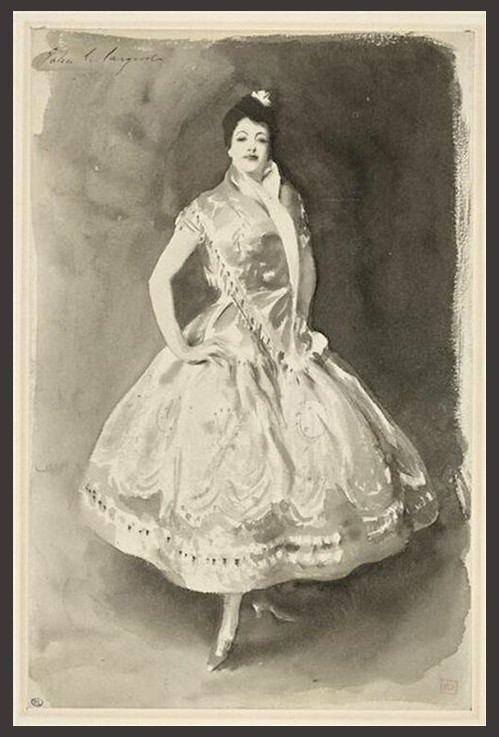
Apotheosis (Deification) of Herakles Pediment, 1919, Watercolor and graphite on paper, L. 110.5 cm, H. 85.1 cm, the MET, NY, USA https://www.metmuseum.org/art/collection/search/625053?&exhibitionId=0&oid=625053&pkgids=773
How is Émile Gilliéron père related to The Apotheosis of Herakles Pediment? In a letter addressed to Gisela M. A. Richter, curator of the Metropolitan Museum in New York, dated October 29, 1918, Emile Gilliéron père informs the noted archaeologist and art historian, that he has executed, at the Acropolis of Athens, four watercolors that may interest the Museum. One of these watercolours is the Apotheosis of Herakles. Gilliéron, recognized as a skilled archaeological draftsman, worked for the Deutsches Archäologisches Institut (DAI) in the Acropolis, Heinrich Schliemann at Mycenae, and Sir Arthur Evans at Knossos, where Gilliéron father and son served for thirty years as draftsmen, restorers, and advisers. The watercolour of the Apotheosis Pediment is of the utmost importance. It documents the vibrant colours the Archaic artist used, red, blue, black, green, and yellow, at the time of their discovery, before they were altered by prolonged exposure to the elements. The Gilliéron watercolour is exhibited at the MET, NY Exhibition Chroma: Ancient Sculpture in Color (Through 26, 2023). https://www.metmuseum.org/art/metpublications/Watercolors_of_the_Acropolis_Emile_Gillieron_in_Athens
For a PowerPoint on Gilliéron’s Watercolours of the Acropolis architectural sculptures, please… Check HERE!