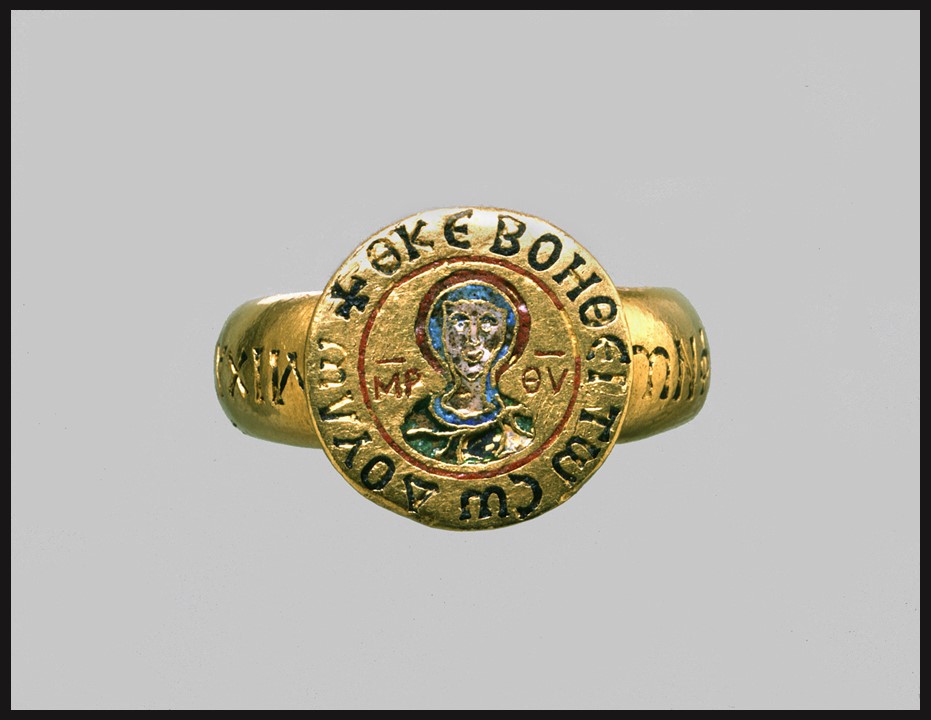
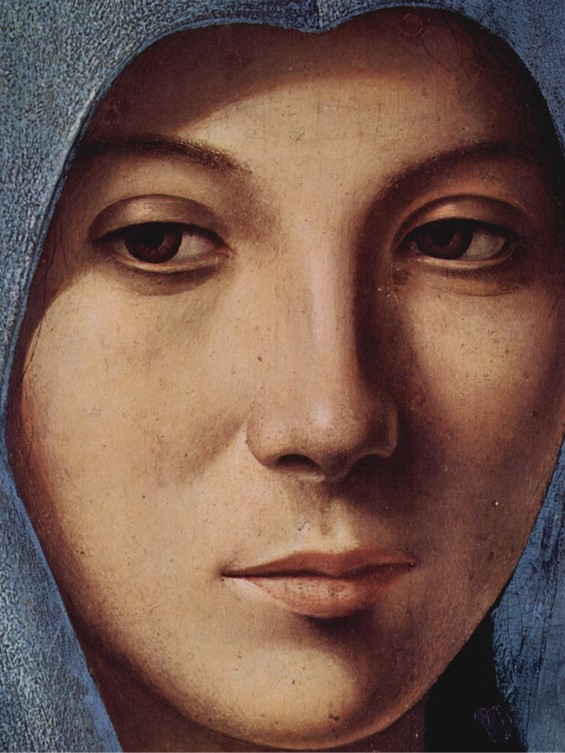
“The house of Angelus, which had thus found greatness so suddenly and unexpectedly thrust upon it, was neither old nor particularly distinguished.” Writes John Julius Norwich on page 156 of his book on Byzantium – The Decline and Fall… and continues “…for of all the families who at one time or another wore the imperial crown of Byzantium, the Angeli were the worst. Their supremacy was mercifully short: the three Angelus Emperors – Isaac II, Alexius III and Alexius IV – reigned, from first to last, a mere nineteen years. But each was in his own way disastrous, and together they were responsible for the greatest catastrophe that Constantinople was ever to suffer until its final fall.” The Ring of Michael Stryphnos in the Byzantine Collection of the Dumbarton Oaks Museum reminds me of one such catastrophic decision taken by Emperor Alexius III Angelus and its disastrous outcome.
The ring itself is impressive and beautiful. The Dumbarton Oaks experts describe it as having “a heavy gold hoop and a circular bezel with the bust of the Virgin, inscribed in Greek, Mother of God, in cloisonne enamel.” The master jeweler used more enamel colours to brighten the ring up… pink for the face of the Mother of God, turquoise, green, red, and blue for the rest of the minuscule composition. “Around the beel is an enamelled inscription in Greek, Mother of God, help thy servant, which is continued on the hoop, Michael the Admiral Stryphnos. Michael Stryphnos has been identified as the Admiral of the Byzantine fleet under Emperor Alexius III Angelus (1195-1203). This beautiful, large, and enamelled gold ring, was probably given to Michael Stryphnos by Emperor Alexios III on the occasion of his appointment as the Megas Doux. Handbook of the Byzantine Collection – Dumbarton Oaks, page 72 https://books.google.gr/books?id=8IlFkJOPYx0C&pg=PA72&lpg=PA72&dq=Ring+of+Michael+Stryphnos&source=bl&ots=KCzeV2w8di&sig=ACfU3U3KMHNMlVldzFqjDg1td6XJXvazpg&hl=el&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjHxrO9x4TwAhVYgv0HHXMkBPIQ6AEwDnoECA8QAw#v=onepage&q=Ring%20of%20Michael%20Stryphnos&f=false
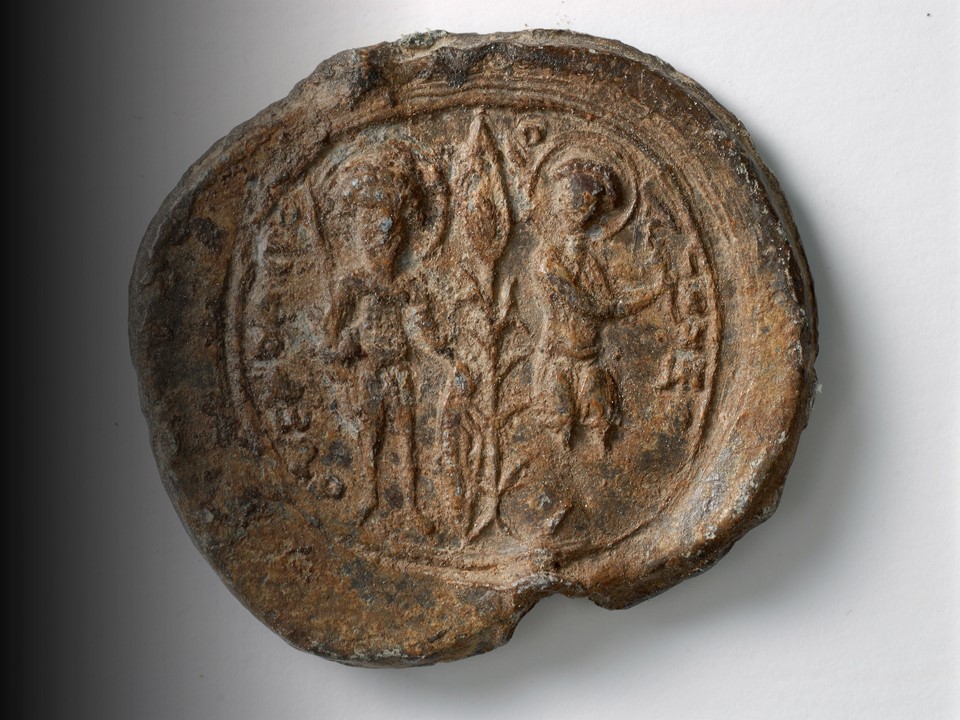

Michael Stryphnos is first recorded in Byzantine sources in 1192 as Sebastos and the head of the Vestiarion (the imperial treasury), under Emperor Isaac II Angelos. He then married Theodora, daughter of Andronikos Kamateros and the sister of the Empress Euphrosyne Doukaina, wife of Emperor Alexios III Angelos, the relationship with the Imperial family became closer and he became Megas Doux and the commander-in-chief of the Byzantine Navy. A lamentable choice for Alexios III because according to the historian Nikita Choniati, Stryphnos was “a man of Ring of Michael Stryphnos extraordinary rapacity and dishonesty of the rare.” Instead of fortifying the Byzantine navy, he used his position for personal gain. His actions “marked the effective end of the Byzantine fleet, which was, therefore, not able to resist the Fourth Crusade a few years later.” His position as Megas Doux, brought him to southern Greece as Governor of the area, visiting Athens ca. 1201-1202 AD. It was during this trip that the local Bishop, Michael Choniates, wrote a Eulogy in his honor and three interesting seals in the Dumbarton Oaks Collection survived time and destruction. https://amp.en.google-info.org/36817230/1/michael-stryphnos.html
For a Student Activity on the Ring of Michael Stryphnos, please… Check HERE!