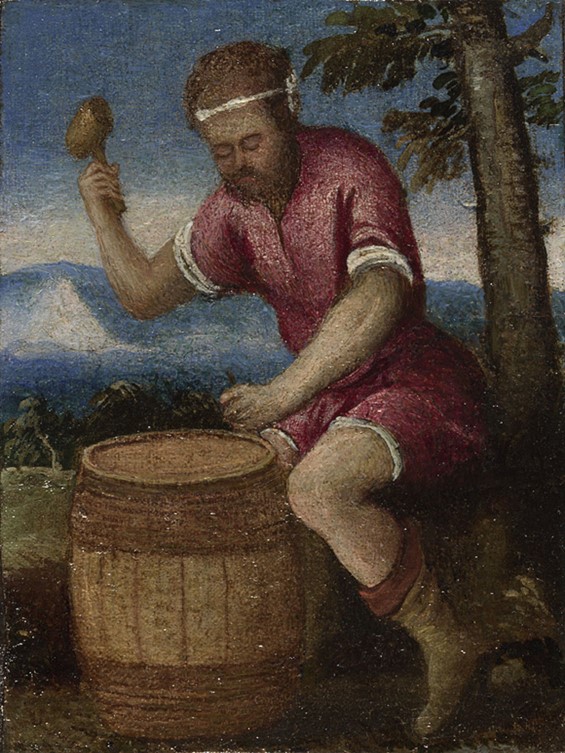
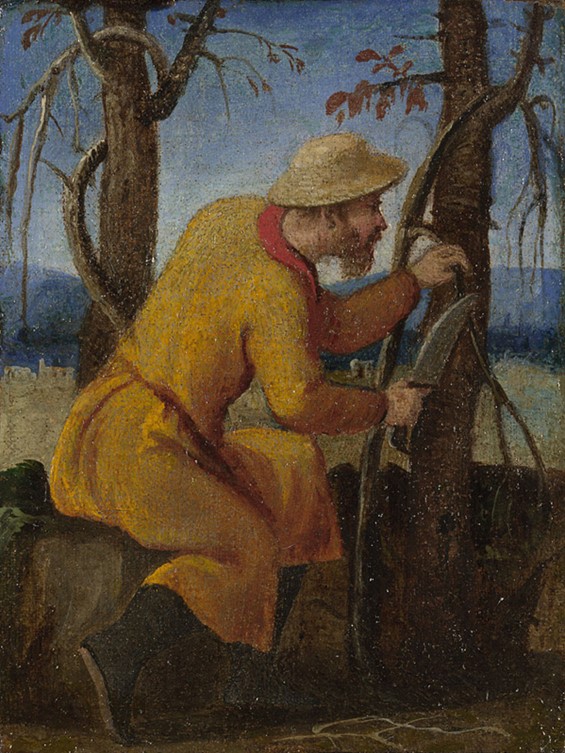
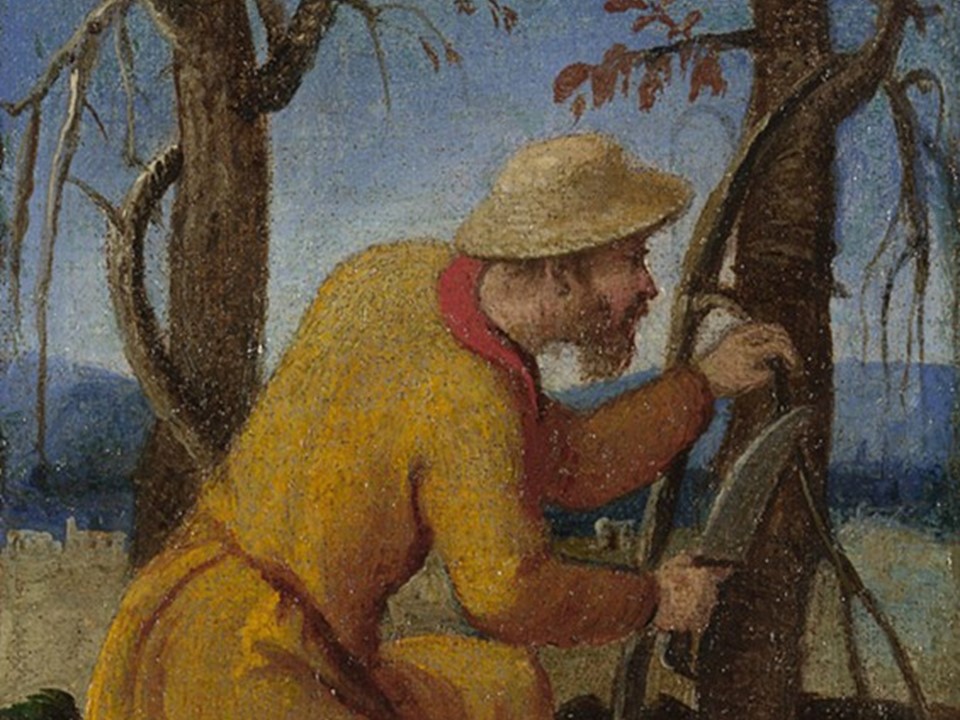
The Labours of the Months: April, about 1580, oil on canvas, 13.6 x 10.6 cm, National Gallery, London
https://www.nationalgallery.org.uk/paintings/italian-venetian-the-labours-of-the-months-january#painting-group-info
Whan that Aprill with his shoures soote: When April with its sweet-smelling showers / The droghte of March hath perced to the roote, Has pierced the drought of March to the root, / And bathed every veyne in swich licour And bathed every vein (of the plants) in such liquid / Of which vertu engendred is the flour; By the power of which the flower is created; / Whan Zephirus eek with his sweete breeth When the West Wind also with its sweet breath, / Inspired hath in every holt and heeth In every holt and heath, has breathed life into / The tendre croppes, and the yonge sonne The tender crops, and the young sun / Hath in the Ram his half cours yronne, Has run its half course in Aries, / And smale foweles maken melodye, And small fowls make melody, / That slepen al the nyght with open ye Those that sleep all the night with open eyes / (So priketh hem Nature in hir corages), (So Nature incites them in their hearts)… Geoffrey Chaucer first line for The Canterbury Tales refers to April… for The Labours of the Months: April cer/gp-aloud.htm
In London, at the National Gallery there are 12 small pictures, “painted on canvas and then each glued to a wooden panel. It is possible that they were made to decorate the recessed panels of a pair of doors. The paintings seem to have been planned in pairs with the figures facing each other and are currently displayed in two frames in groups of six. They show the ‘labours of the months’ – the rural activities that take place each month throughout the year.” This set of painted Doors combines simplicity in execution and extravagance in visual effect! https://www.nationalgallery.org.uk/paintings/italian-venetian-the-labours-of-the-months-january#painting-group-info
The painting that may represent “sweet-smelling” April, shows a cooper making a wooden barrel. “He raises his mallet ready to strike the tool in his other hand. The work must be physically hard as he has tied a band of white cloth around his forehead to keep the sweat out of his eyes. The barrel will be used to store wine made from the grapes we see being pressed in September.” https://www.nationalgallery.org.uk/paintings/italian-venetian-the-labours-of-the-months-april
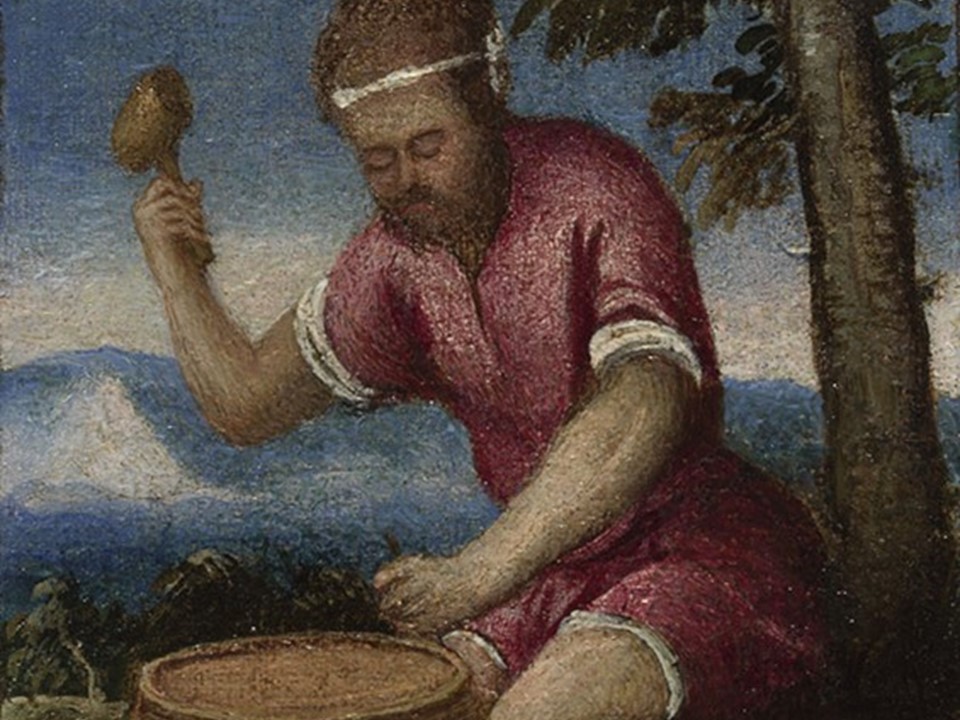

The Labours of the Months: April, about 1580, oil on canvas, 13.6 x 10.6 cm, National Gallery, London
https://www.nationalgallery.org.uk/paintings/italian-venetian-the-labours-of-the-months-january#painting-group-info
Coopers were important craftsmen during the Middle Ages and the Renaissance. They created wooden barrels to store wine, spirits and salted meats, buckets to draw and carry water, wooden bowls and plates for daily use, pails, churns and tubs for various agricultural or home-industry needs. Coopers, like the one depicted in the small London painting, were respected and valued Renaissance professionals.
Depicting the Labours of the Months was a popular artistic theme that was frequently used in the decoration of Cathedrals and Churches, Castles and Palaces, Psalters, Breviaries and Books of Hours across Europe during the Medieval and Early Renaissance period. Each month, depicting popular activities of peasants or/and the gentry throughout the year were sometimes paired with the Signs of the Zodiac circle. They would be either simple and small in size or large and elaborate, crafted in stone, wood, stained glass, painted in murals or often enough, painted in parchment. Many great Monuments and Libraries in Europe display fine examples of such artefacts for art lovers to enjoy. http://www.livingfield.co.uk/ages/labours-of-the-months/
For a PowerPoint on The Labours of the Months at the National Gallery in London, please… Check HERE!