https://vizantinaistorika.blogspot.com/2016/06/blog-post_30.html
The Early Christian Tunic refers to a garment style worn during the Late Roman/Early Christian period which generally spans from the 4th to the 7th century AD. This era is characterized by the transition from the classical Roman Empire to the Μedieval period, and it includes the later part of the Roman Empire and the Εarly Byzantine Empire. Tunics of that era evolved from the earlier Roman Τunics but had distinct features that reflected the changing cultural, social, and political landscape. My BLOG intends to present information on Two Early Christian Tunics in Thessaloniki, exhibited in the city’s amazing Museum of Byzantine Culture.
What exactly is an Early Christian Tunic? It is a simple, loose-fitting garment, worn by both women and men and often made from linen or wool. Tunics were generally loose-fitting garments, providing comfort and ease of movement. They had no sewing and were worn with the help of belts, buckles, and pins. Cutting and sewing are practices that experienced wider spread in the Mediterranean area after the 7th century. They had a T-shape or a tubular design, with a hole for the head and sometimes sleeves. The shape could vary, and some tunics were more form-fitting than others. The length of the Τunic could also vary. Some reached the knees, while others were longer, extending to the ankles. https://www.mbp.gr/exhibit/chitonas-2/
While some Τunics were plain, others were embellished with plain coloured bands or ‘ornaments’ of textile bands, roundels, or square panels. These bands (called clavi) were of different lengths and adorned the front and back parts of the garment at shoulder level, but sometimes the lower edge was also trimmed with a horizontal band that turned vertically upwards at right angles at each side. Tunics were also adorned with square panels or roundels (called orbiculi) on the shoulders and near their lower edge. Many times, clavi and orbiculi were garment ornaments, tapestry-woven separately, and then applied to the linen or woolen Tunic. https://www.jstor.org/stable/1522750?read-now=1#page_scan_tab_contents page 239
The clothing of the Early Christian period is often studied through archaeological findings, artistic representations, and references in historical texts. For the history of Early Christian garments and their decoration, Egypt is a treasure trove, due to its hot and dry climate. Egyptian textiles that have survived from this period are referred to as Coptic Textiles, an Arabic corruption of the Greek word ‘Aigyptos’, used to describe the Christianised Egyptians.
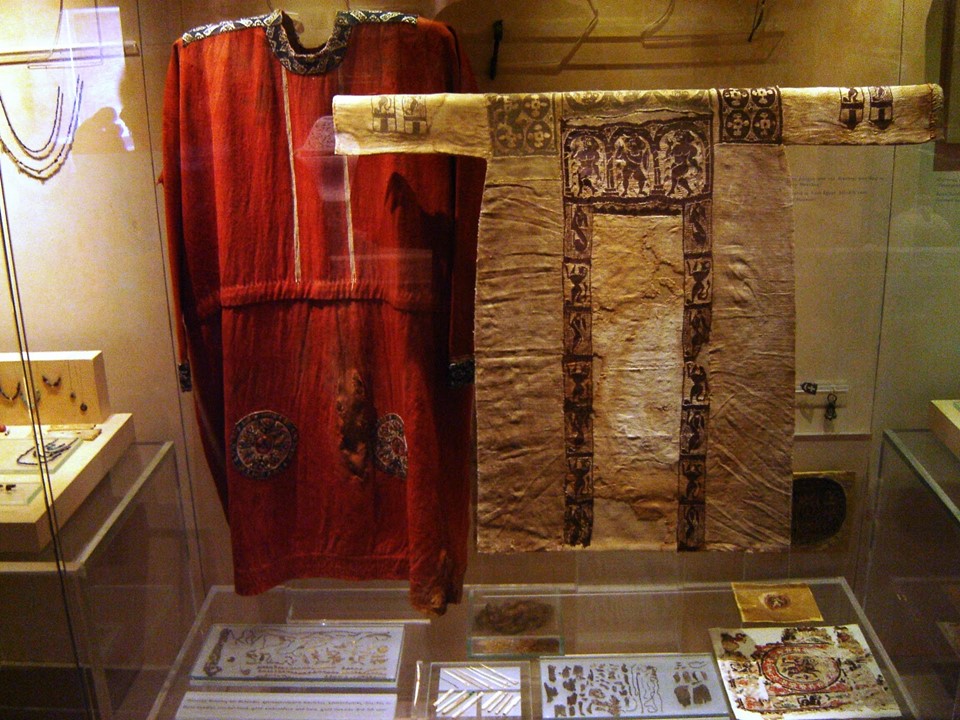
In the Museum of Byzantine Culture, in Thessaloniki, Greece, there are two Coptic Tunics (on permanent loan from the Benaki Museum) beautifully decorated with clavi and orbiculi.
One of the two Tunics has the natural color of linen and is adorned with purple-colored woven bands (clavi). Wide bands, for instance, embellish the upper part of the chest on both the front and back of the garment. These bands feature depictions of soldiers carrying shields under colonnades. A narrower band extends across the shoulders, displaying roundels with depictions of hares inside woven squares. Prominent features of the Tunic include two long vertical bands that start from the chest and extend to the hem. These bands are adorned alternately with running lions and hares, creating the impression of a hunt.
The second Tunic, multicoloured, and lively, is equally impressive. Made of linen, coloured a vibrant red, it is adorned with woven vertical white bands, thinner than usually fashionable, down to the waist. The rest of the Tunic’s ornamentation consists of bands for the neck area and the hem of each wrist, adorned with white geometric shapes against a black background for the neck, and white lozenge motifs against a black background for the cuffs. Finally, two discs (orbiculi) with stylized plant motifs in the same colour palette, are placed in the lower part of the Tunic. Noteworthy is the fact that at the height of the waist, there is a seam that covers a belt.
Both Tunics are displayed in the Museum’s 2nd Gallery, where aspects of Early Christian period city life are presented. This Exhibition, inaugurated on July 10th, 1998, is organized around the triclinium, that is the reception hall of a rich house in Thessaloniki. It presents issues that emphasize the role of the city as a fortified residential complex, its private and public life, professional activities, economic life, commerce, workshops, houses and their equipment (pottery and glass vessels), domestic activities (weaving, cooking) and objects for personal adornment. https://www.mbp.gr/en/permanentexhibitions/room-2-early-christian-city-and-dwelling/
For a Student Activity, inspired by the Coptic Tunics in Thessaloniki, please… Check HERE!