Christos Laskaris captures the essence of Spring in his evocative poem: ‘Διάβαζα ένα ποίημα για την άνοιξη / όταν την είδα / να έρχεται από μακριά: / μισή γυναίκα, / μισή όνειρο. / Κατέβαινε το μονοπάτι κάτω / στεφανωμένη / με άνθη κερασιάς. / Τότε κατάλαβα τι δύναμη έχουν τα ποιήματα. (I was reading a poem about Spring / when I saw her from afar: / half woman, / half dream. / She was going down the path / wreathed / with cherry blossoms. / That was when I understood the power poems hold.). These lines illustrate the transformative power of poetry, where words bloom into vivid imagery, evoking the ephemeral beauty and vitality of the season. As I reflected on Laskaris’s portrayal of Spring as ‘half woman, half dream,’ I was reminded of a small textile piece in the MET collection, a decorative artwork depicting the Personification of Spring. This intricate piece, adorned with motifs of blossoming flowers and a graceful figure, parallels the poem’s vision, embodying renewal and beauty in a tangible form. Together, the poem and the artwork highlight, I humbly believe, Spring’s timeless allure and its ability to inspire across art forms, reminding us of the season’s power to awaken imagination and connect us to the essence of life. https://e-keimena.gr/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=510:poihmata-gia-thn-anoiksh&catid=149:poihmata-anoiksh&Itemid=54
Searching for information on Early Christian Textiles, I came across two booklets I would like to share… and acting more like a Curator rather than a Teacher, I present you Textiles of Late Antiquity, a 1995 Metropolitan Museum of Art Publication, and Woven Interiors: Furnishing Early Medieval Egypt, an Exhibition Catalogue of 2020, organized by the George Washington University Museum, The Textile Museum, and Dumbarton Oaks Research Library and Collection. https://www.metmuseum.org/art/metpublications/Textiles_of_Late_Antiquity and https://museum.gwu.edu/woven-interiors-furnishing-early-medieval-egypt
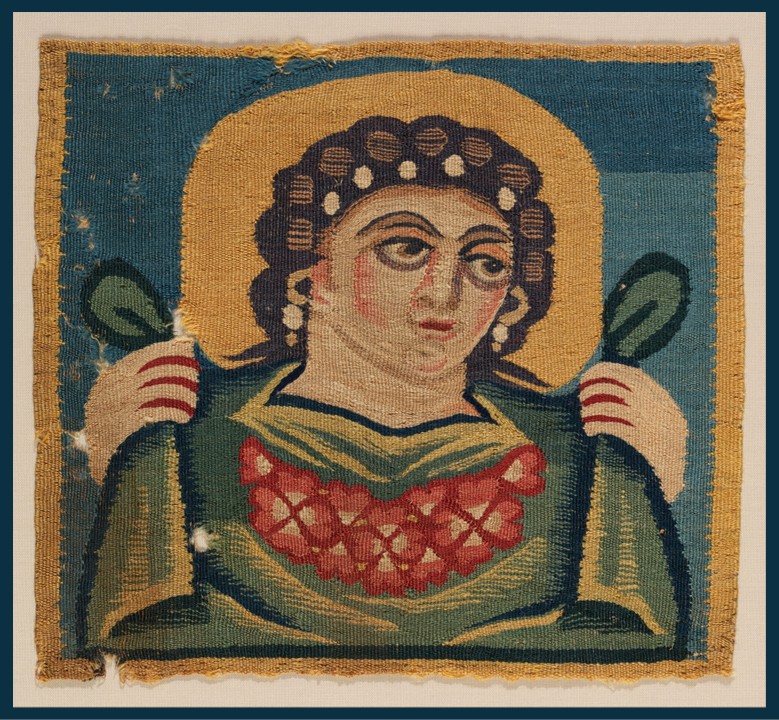
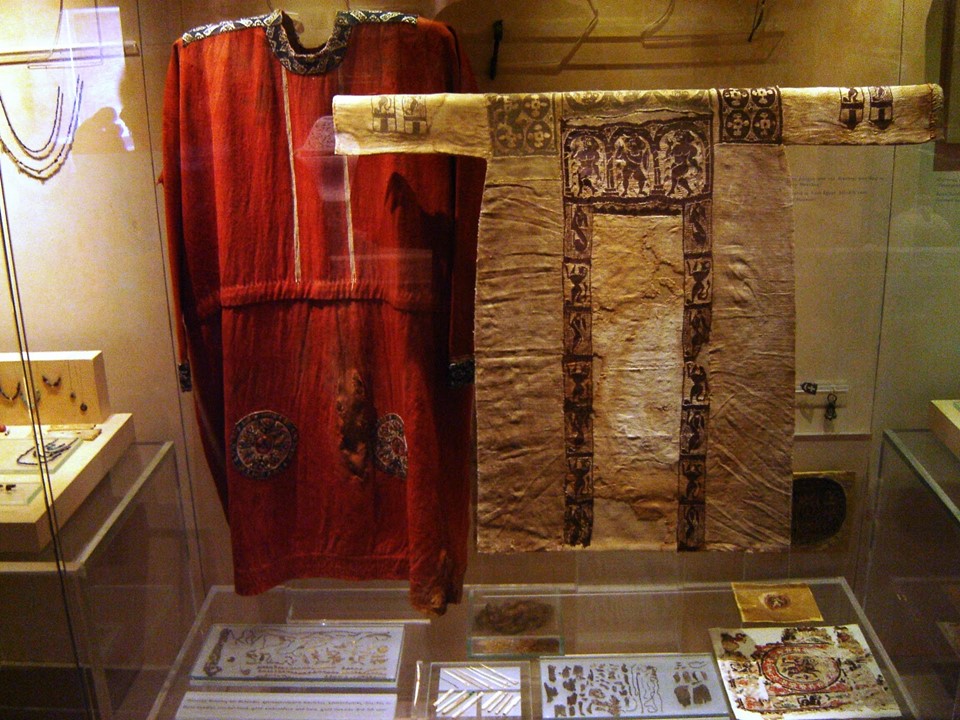
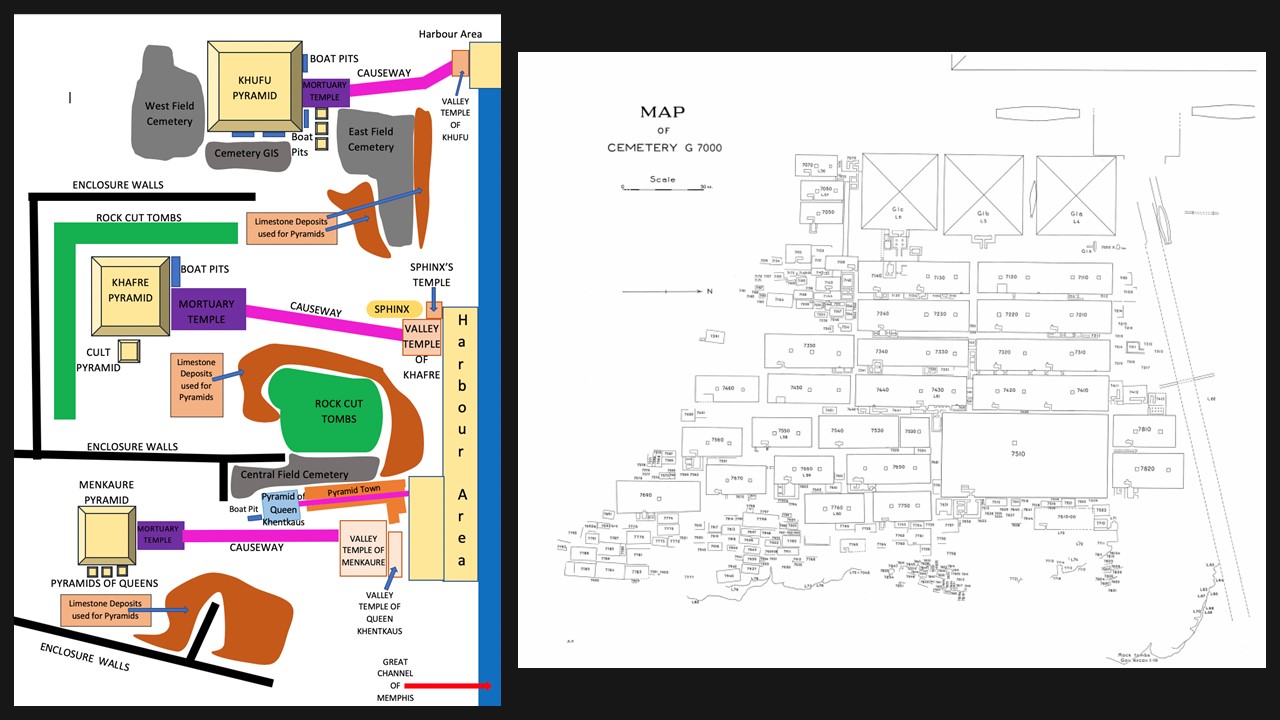
This small tapestry panel from Egypt in the Metropolitan Museum in New York City, identified as: Tabula (Square) with the Head of Spring. is a remarkable example of Coptic textile art from the Early Christian period. It was originally an appliqué on a larger textile, likely part of a set adorning a garment. Woven from linen and wool, the piece measures just a few centimeters across but is rich in detail and vibrant in colour. The central figure is a personification of Spring, adorned with a wreath of pink blossoms that symbolize the season’s renewal and fertility. The figure is depicted in a frontal pose, dressed in flowing robes with intricate floral patterns that demonstrate Spring’s association with nature’s abundance, and the skill of the weaver. The panel’s relatively well-preserved state is a testament to Egypt’s hot, dry climate, which has safeguarded textiles that would have otherwise been lost to time.
Aesthetically, the panel is a harmonious blend of naturalistic detail and stylized design, characteristic of Coptic art. The vibrant colour palette, dominated by earthy tones and soft pinks, reflects the organic materials used in its creation and emphasizes the figure’s connection to nature. The composition is balanced, with the central figure drawing the viewer’s eye while the centrally placed floral elements create a sense of movement and vitality. The weaving technique, combining fine detail with bold forms, showcases the artistic and technical sophistication of the Coptic weavers. Symbolically, the personification of Spring embodies themes of renewal, prosperity, and the cycle of life, which held deep significance in both pagan and early Christian contexts. This small yet exquisite piece thus serves as both a functional decorative element and a meaningful cultural artifact, bridging artistic tradition and symbolic expression.
For a Student Activity inspired by the MET textile with the Personification of Spring, please… Check HERE!