October, 1878, oil on canvas, 180.7 x 196.0 cm, National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne, Australia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/October_(painting)#/media/File:Jules_Bastien-Lepage_-_October_-_Google_Art_Project.jpg
October is the treasurer of the year, / And all the months pay bounty to her store; / The fields and orchards still their tribute bear, / And fill her brimming coffers more and more… The painting October by Jules Bastien-Lepage fills October’s brimming coffers with… ordinary potatoes, and back-breaking labor. Yet, there is such dignity in Bastien-Lepage’s presentation of this unassuming composition, that I would like to explore it more… https://www.poemhunter.com/poem/october-39/comments/
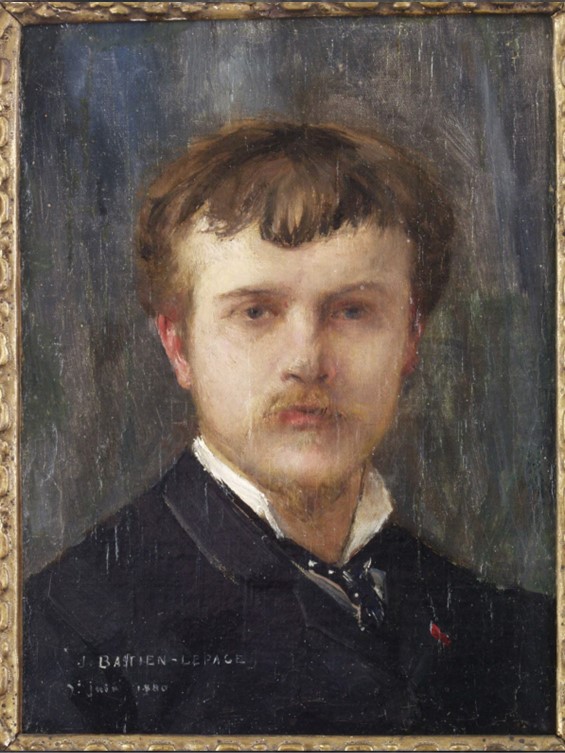

Self-portrait at 32 years old, 1880, oil on canvas, 31×25 cm, Musée Bastien-Lepage, Clos Raymond, France
https://www.vosgesmatin.fr/art-et-culture/2019/05/12/autoportrait
Bastien-Lepage produced a collection of deeply personal artworks, firmly establishing his position within the Naturalism movement’s historical timeline. His oeuvre is focused on three main areas of art, namely, depicting realistic genre themes, creating rural landscapes, and fashioning truthful portraits. The sincerity portrayed in his paintings gained him a loyal following not only in France but also across Europe. Beauty, I am convinced, Jules Bastien-Lepage once said, is the exact truth: neither to the right nor to the left, but in the middle! https://www.theartstory.org/artist/bastien-lepage-jules/
The artist was born (November 1, 1848) in Damvillers, France, and showed an early talent for art. He studied at the École des Beaux-Arts in Paris, where he was influenced by the works of the Barbizon School painters, particularly Jean-Baptiste Corot and Gustave Courbet. Bastien-Lepage’s style combined elements of Realism with a focus on capturing the effects of light and atmosphere. His approach to painting often involved working directly from nature, capturing the effects of light and the nuances of everyday life. His subjects included landscapes, portraits, and genre scenes, all characterized by meticulous attention to detail and a sense of honesty and seriousness.
Unfortunately, Jules Bastien-Lepage’s career was cut short when he died at the age of thirty-six. His work, however, had a significant impact on the development of Naturalism and influenced many artists who followed. Today, regarded as an important figure in the history of 19th-century French art, Bastien-Lepage is respected for the sincerity, and the dignity with which he depicted the Meuse region in which he grew up, and the workers and peasants who his brush rendered! https://www.theartstory.org/artist/bastien-lepage-jules/
For the Paris Salon Bastien-Lepage created and exhibited a pair of Harvest Scenes that marked a new direction in his career as a painter. The earlier of the two works, The Haymakers, (today, in the Musée d’Orsay), exhibited at the Salon in 1878, shows two weary haymakers resting in the summer heat. The second painting, exhibited at the Paris Salon of 1879, and titled October or The Potato Harvest, (today, in the National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne, Australia) is an account of the bleak autumnal potato harvest, set in a bare, featureless landscape. Both paintings, powerfully rendered, and careful studies of life in the fields, had a considerable influence on the art scene of the time. Both paintings created a new trend in art, and, without intention on Bastien-Lepage’s part, the painter of the Meusian peasants became the head of an Art School. https://www.ngv.vic.gov.au/explore/collection/work/3768/
October or The Potato Harvest was an 1879 Salon success. Carried out on a large canvas, the painting indicates Bastien-Lepage’s ambitious artistic program but also bespeaks his confidence in his own technical virtuosity. The artist presents its theme in a solemn key, with warm yet sober colours, and an exquisite understanding of the country in the late summer. It was powerfully executed, full of vigor, serenity, and the ability to combine the high ‘finish’ expected of a conventional academic picture with the looser brushwork associated with the Impressionists. https://www.ngv.vic.gov.au/explore/collection/work/3768/

October (detail), 1878, oil on canvas, 180.7 x 196.0 cm, National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne, Australia
https://www.flickr.com/photos/eoskins/19429557290
The Salon audience noticed the painting’s artistic power, and the Russian painter Vasily Surikov upon seeing it in Paris wrote to his colleague Pavel Chistyakov… I want to talk about those few works that have true dignity. Take Bastien-Lepage’s picture of a Woman Picking Potatoes. The face is both painted and written as living. Everything is written in the air. Reflexes, color, everything is so whole, unbroken, that it is a miracle. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/October_(painting)
For a PowerPoint on the artistic oeuvre of Jules Bastien-Lepage, please… Check HERE!
Interesting to read is the book Jules Bastien-Lepage and His Art. A Memoir. Written by the artist’s friend Andre Theuriet, the entire book is free and online at… https://archive.org/details/julesbastienlepa00theu/page/50/mode/2up