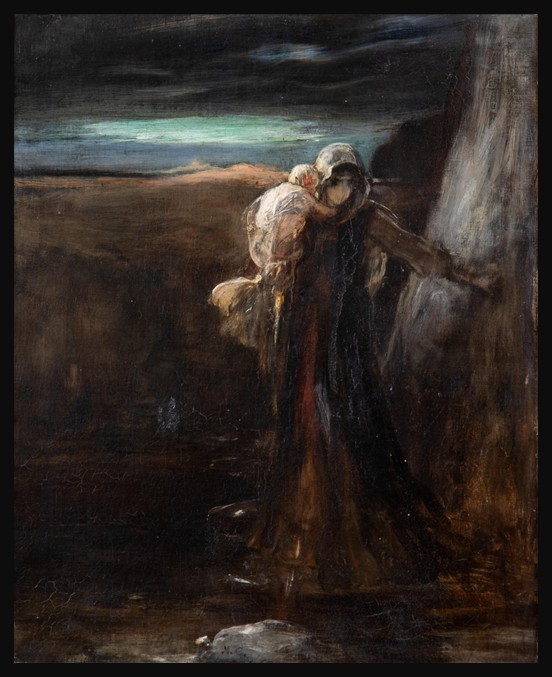
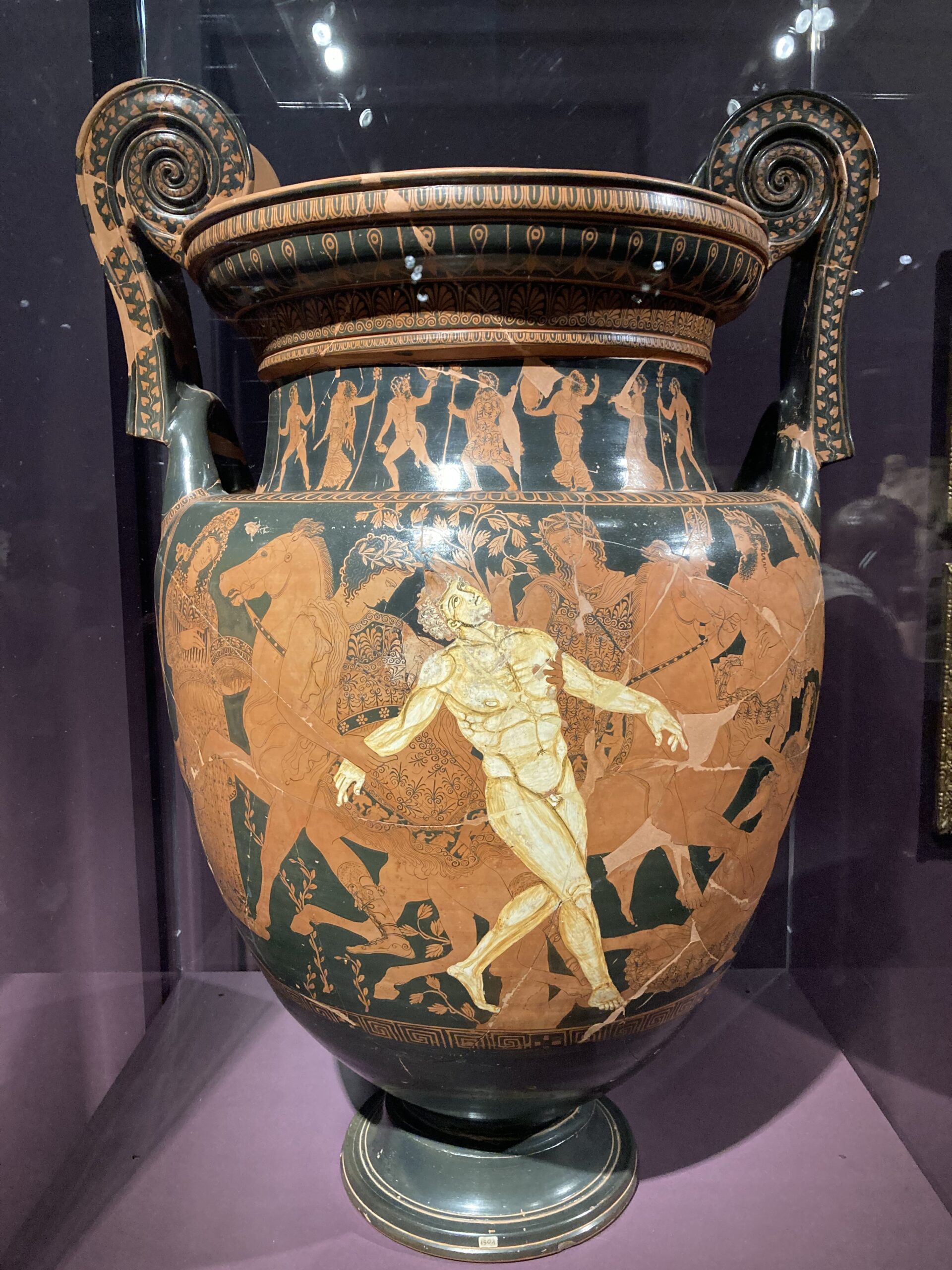
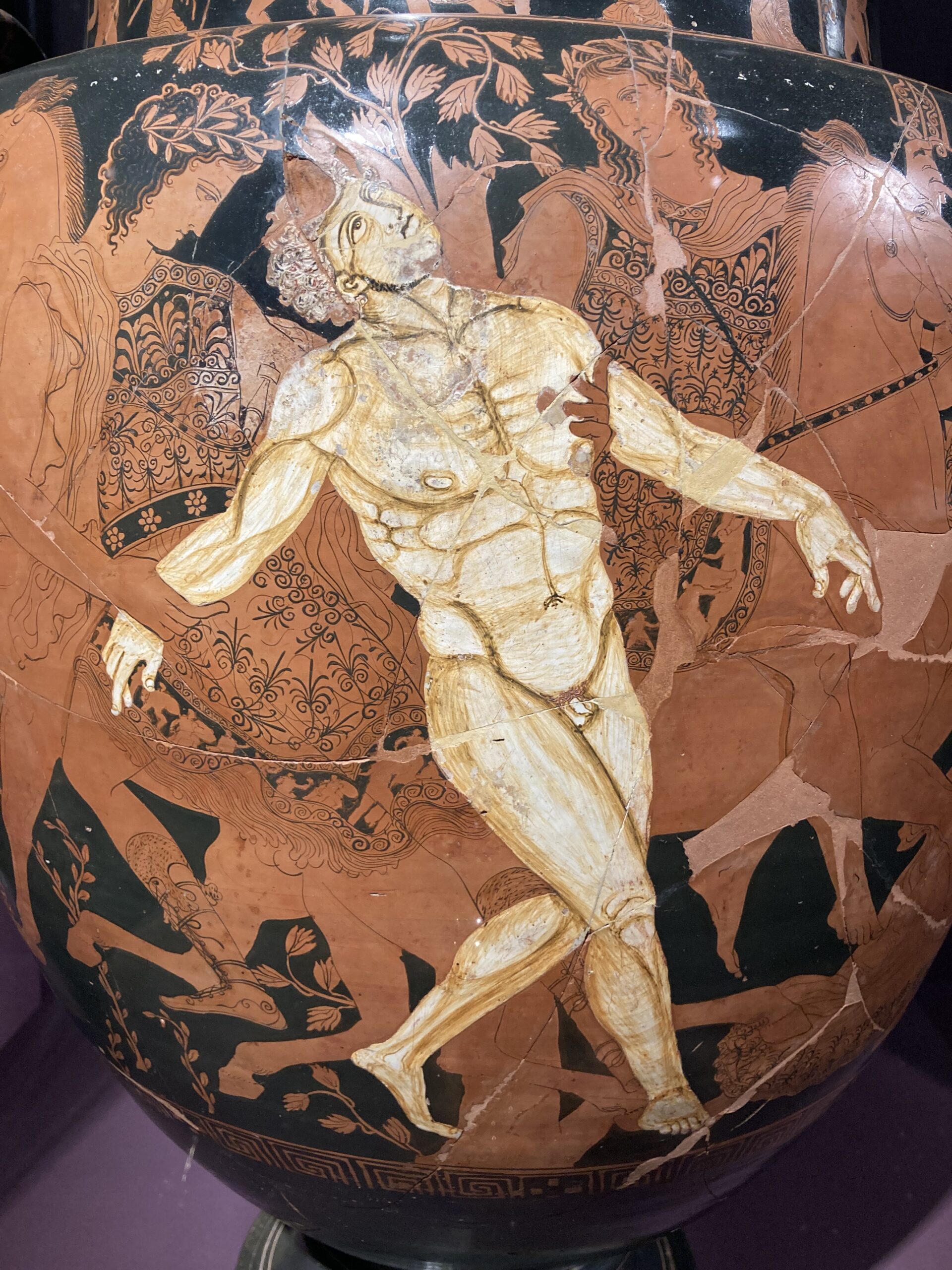
Fuite après le massacre de Psara (Flight after the Massacre of Psara), c. 1896, Oil on Canvas, 37,5 x 30,5 cm, Private Collection https://www.bonhams.com/auction/29818/lot/4/nicholaos-gysis-1842-1901-fuite-apres-le-massacre-de-psara/
Nikolaos Gyzis’ poignant painting Fuite après le massacre de Psara (Flight after the Massacre of Psara) captures the haunting aftermath of one of the most devastating events of the Greek War of Independence. The destruction of Psara in 1824 by Ottoman forces marked a tragic moment in Greek history, leaving the island in ruins and its people displaced. Gyzis, deeply inspired by his homeland’s struggles, translates this historical trauma into an evocative visual narrative of despair and resilience. His painting resonates with Dionysios Solomos’ immortal lines: Στῶν Ψαρῶν τὴν ὁλόμαυρη ράχη / Περπατῶντας ἡ Δόξα μονάχη. / Μελετᾷ τὰ λαμπρὰ παλληκάρια, / Καὶ ‘ς τὴν κόμη στεφάνι φορεῖ / Γινομένο ἀπὸ λίγα χορτάρια / Ποῦ εἰχαν μείνῃ ‘ς τὴν ἔρημη γῆ. (On the all-black ridge of Psara / Glory walks by herself taking in / the bright young men on the war field / the crown of her hair wound / from the last few grasses left / on the desolate earth. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Destruction_of_Psara)
One of the most renowned Greek painters of the 19th century, Nikolaos Gyzis was born on the Cycladic island of Tinos, known for its rich artistic tradition. Coming from humble beginnings, Gyzis pursued art education at the School of Arts in Athens before continuing his studies at the prestigious Academy of Fine Arts in Munich, where he later became a professor. Settling in Munich, Gyzis emerged as a prominent figure in the Munich School, a movement characterized by its academic rigor and emphasis on naturalism and realism. Throughout his illustrious career, he received numerous awards and honors, cementing his reputation both in Greece and abroad. Despite his strong ties to Germany, Gyzis maintained a deep connection to his Greek heritage, often incorporating national themes into his work. His artistic journey reflects not only technical mastery but also a continuous quest for innovation and transcendence of academic traditions.
The artist’s oeuvre is a testament to his technical brilliance and profound spirituality. While his early works focused on detailed genre scenes, captivating portraits, and luminous still lifes, his later creations reveal a shift toward idealism and symbolism. Gyzis masterfully blended his solid academic foundation with a deep sense of imagination, allowing his works to transcend mere realistic depiction. His paintings often explored themes of human emotion, faith, and metaphysical ideas, with works such as Eros and the Painter and The Secret School exemplifying this evolution. The vibrant interplay of light and shadow in his compositions enhances the emotional depth of his pieces, while his careful attention to detail showcases his skill as a draftsman. In his final years, Gyzis embraced symbolic elements, imbuing his art with a spiritual and allegorical quality that left a lasting impact on Greek art and established him as a pioneer of modern Greek painting.
Nikolaos Gyzis’ Fuite après le massacre de Psara (Flight after the Massacre of Psara), c. 1896, is a powerful tribute to the resilience of the human spirit amid devastation. The painting portrays a young mother fleeing the ruins of Psara with her infant, embodying both personal and collective grief after the island’s brutal destruction by Ottoman forces in 1824. The composition showcases Gyzis’ mastery in balancing emotional depth with painterly elegance. The tall, sculptural figure of the mother, with her dark silhouette rooted in Byzantine “Mother and Child” iconography, radiates solemnity and strength. Her infant, rendered in a luminous patch of white against the earthy palette, symbolizes hope and purity amidst the despair. Through warm, dynamic brushstrokes and restrained detail, Gyzis achieves a composition of timeless grandeur, blending intimate storytelling with a symbolic meditation on survival, motherhood, and the enduring connection to homeland.
This painting draws thematic and stylistic parallels with Gyzis’ renowned works, such as Tama (Offering) and After the Destruction of Psara (1896). Like these masterpieces, Fuite après le massacre de Psara transcends its historical context to evoke universal ideals of nationhood and freedom. The absence of idealization lends the work an authenticity that heightens its emotional impact, while the romantic disposition and economy of detail reflect Gyzis’ concern with purely pictorial issues. The work’s dramatic contrasts—between light and shadow, motion and stillness—further enhance its poetic quality. By elevating the plight of a single mother to a symbol of collective suffering and resilience, Gyzis transforms the painting into a poignant ode to sacrifice and the enduring human spirit, resonating deeply with themes of national pride and cultural identity.
For a PowerPoint Presentation on Nikolaos Gyzis’s oeuvre, please… Check HERE!
Bibliography: https://www.bonhams.com/auction/29818/lot/4/nicholaos-gysis-1842-1901-fuite-apres-le-massacre-de-psara/