http://vizantinaistorika.blogspot.com/2014/03/blog-post_19.html
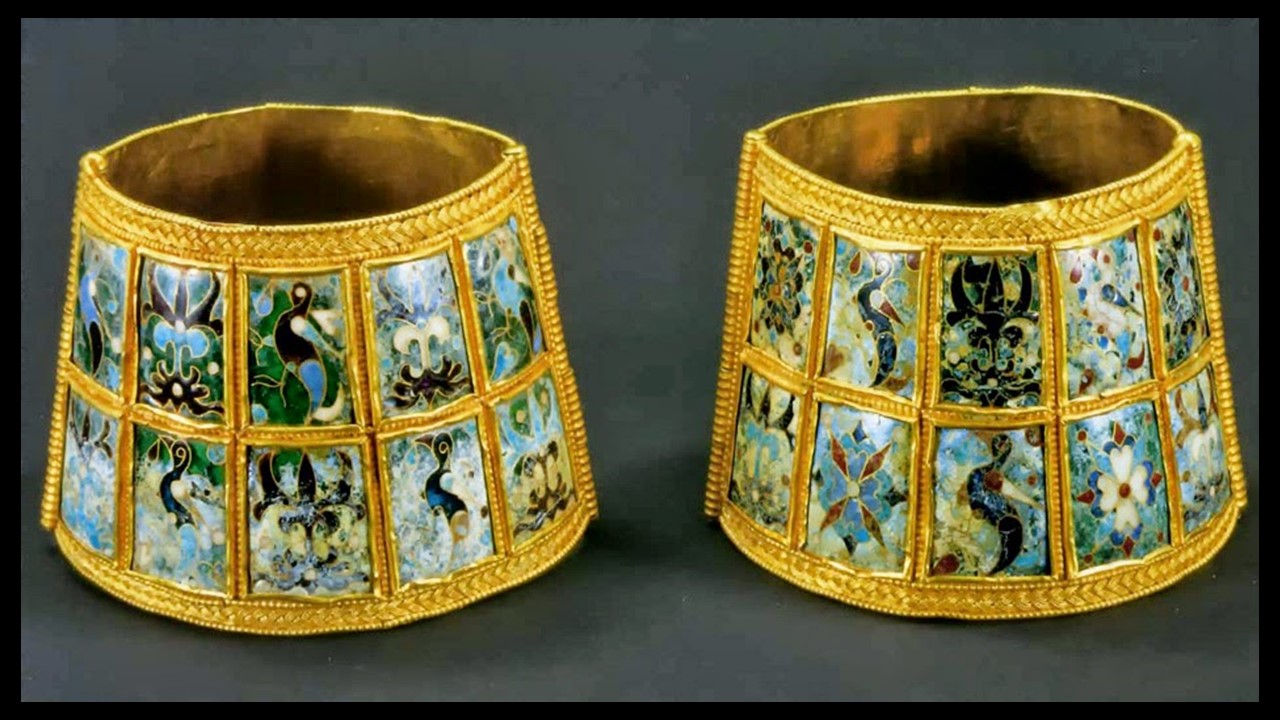
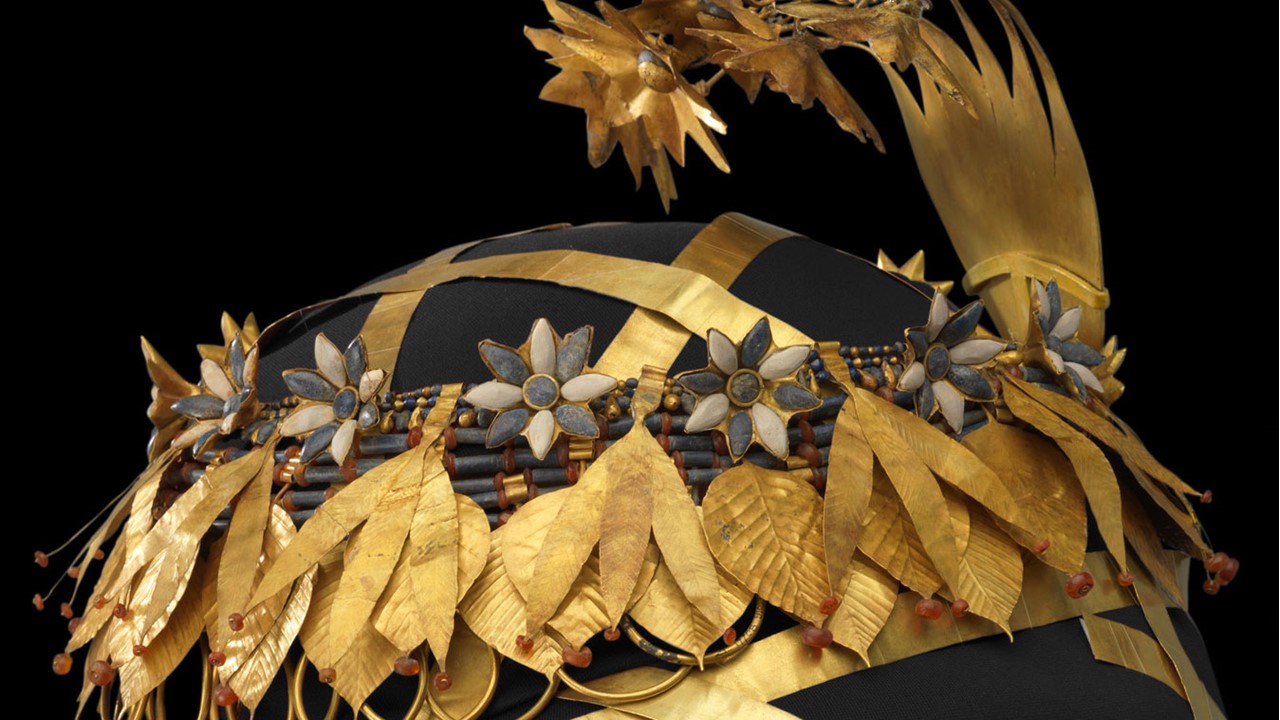
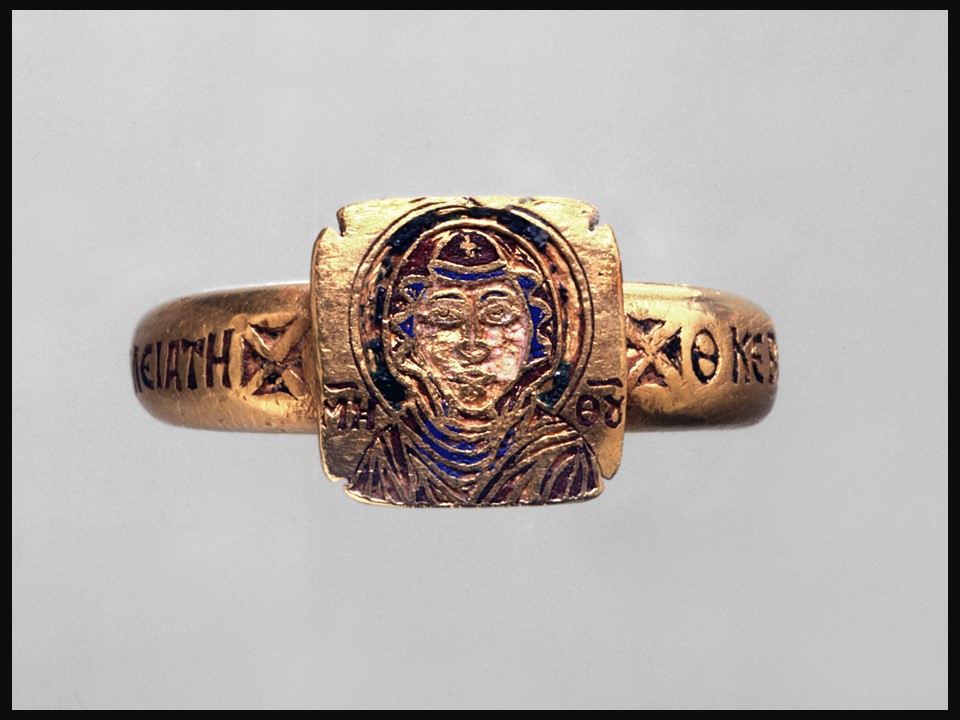
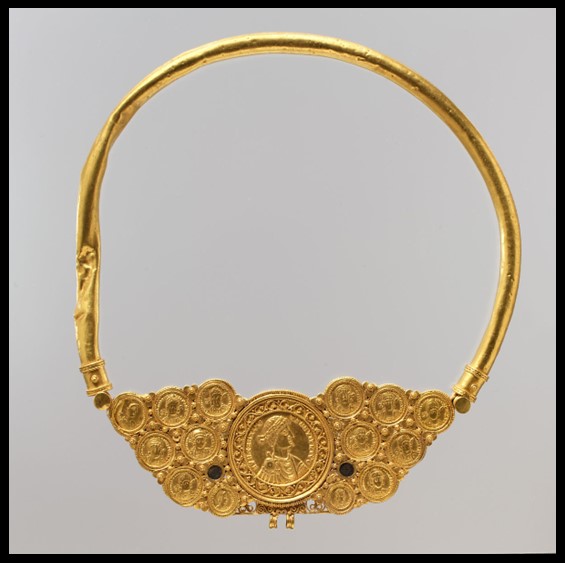
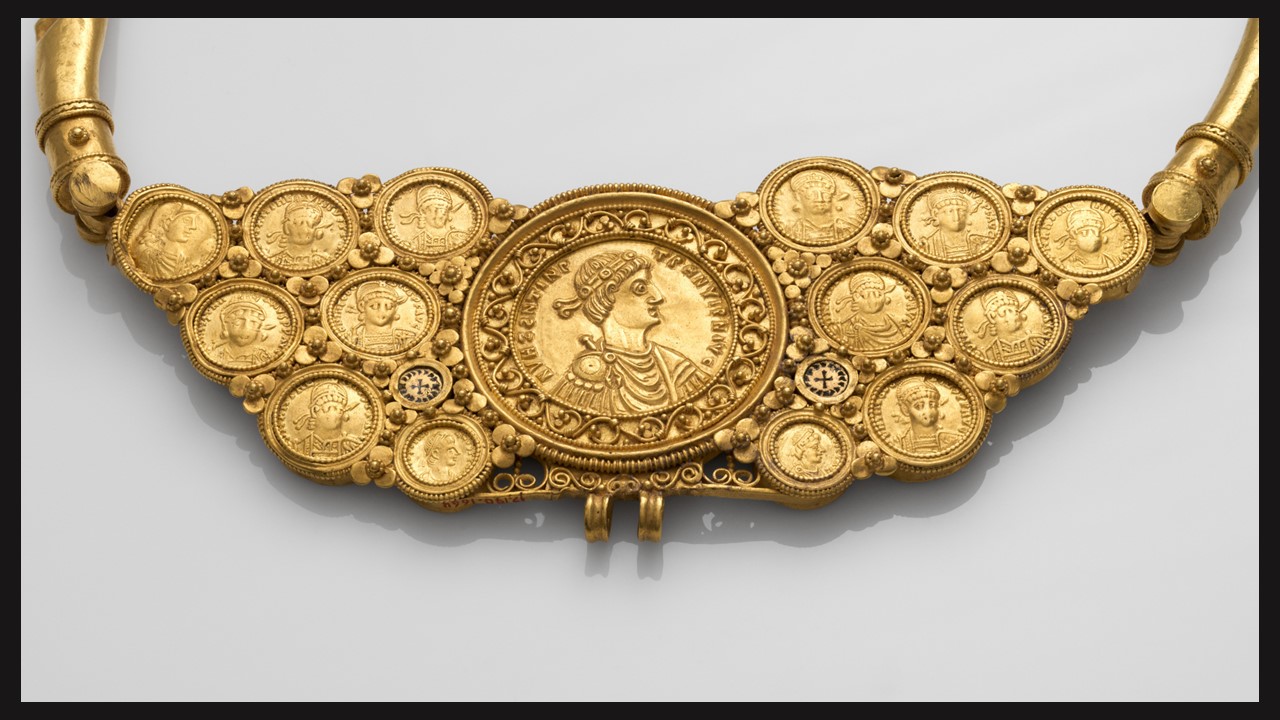
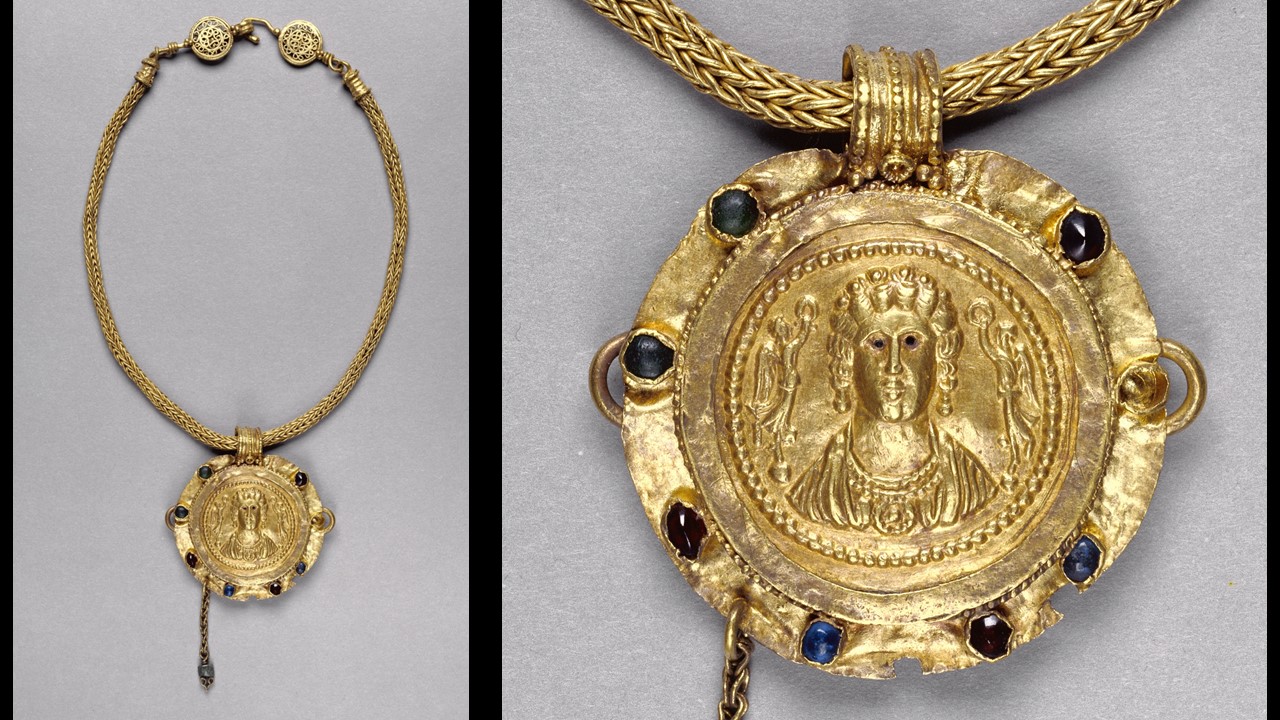
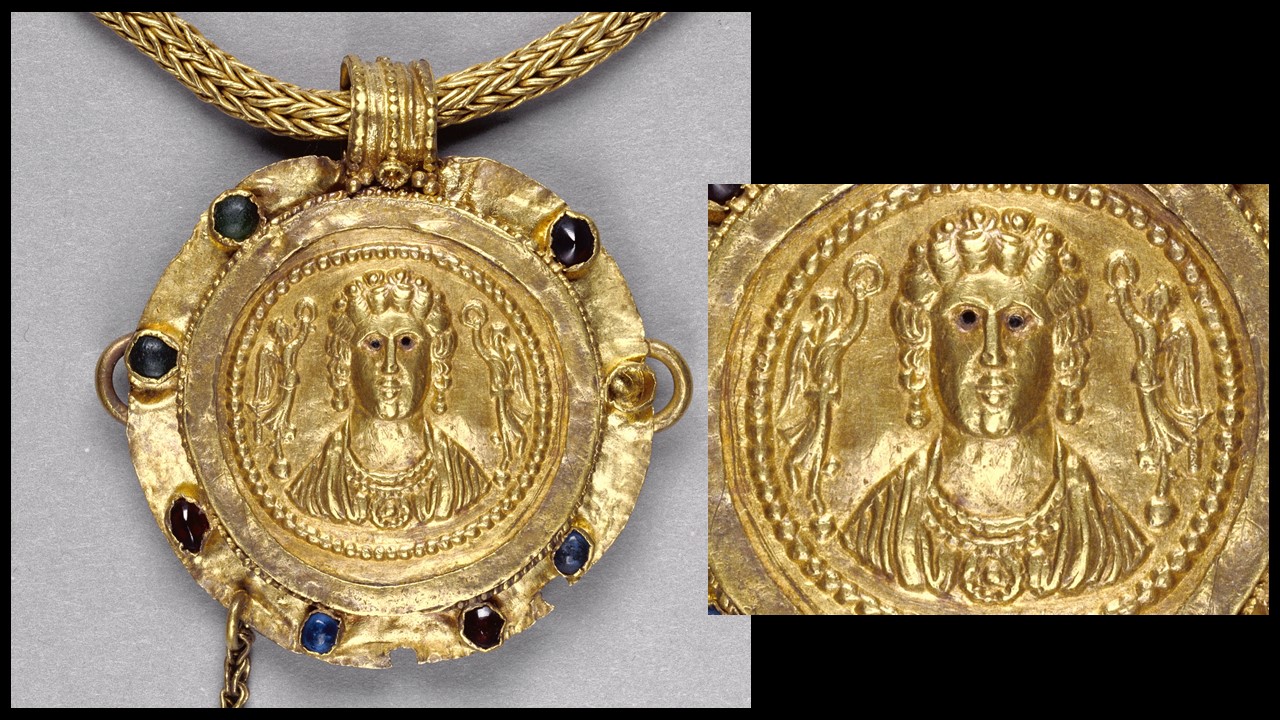
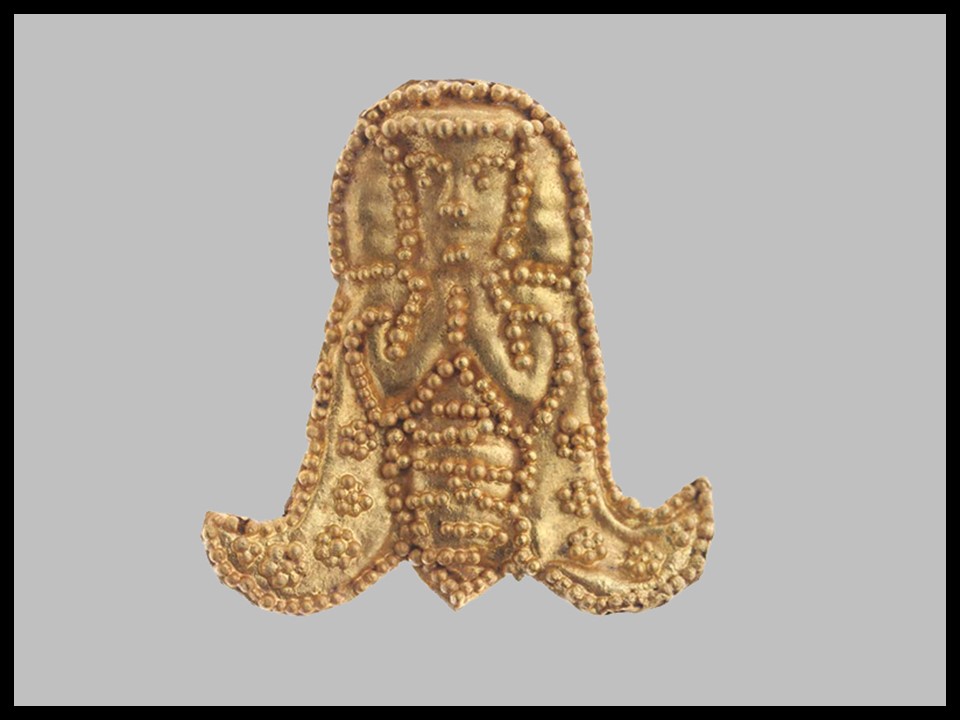
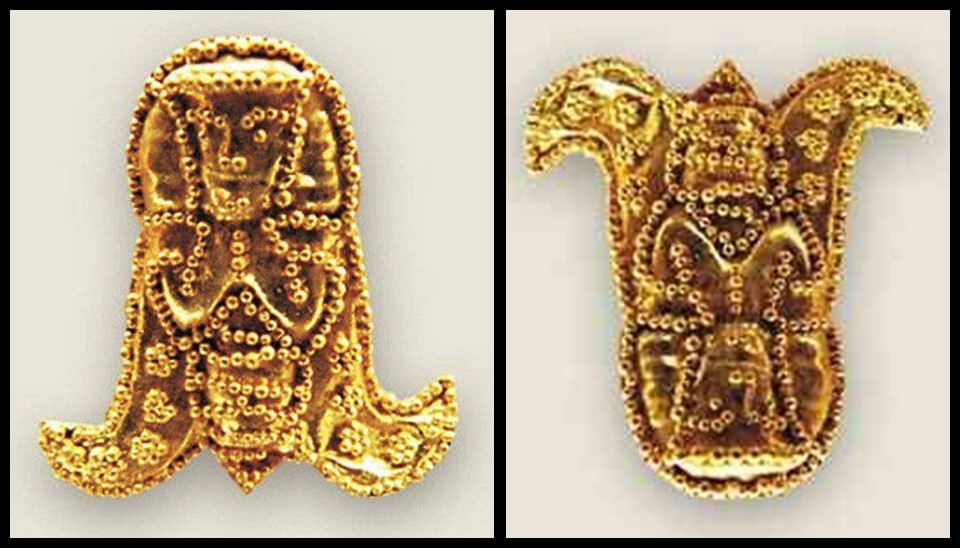
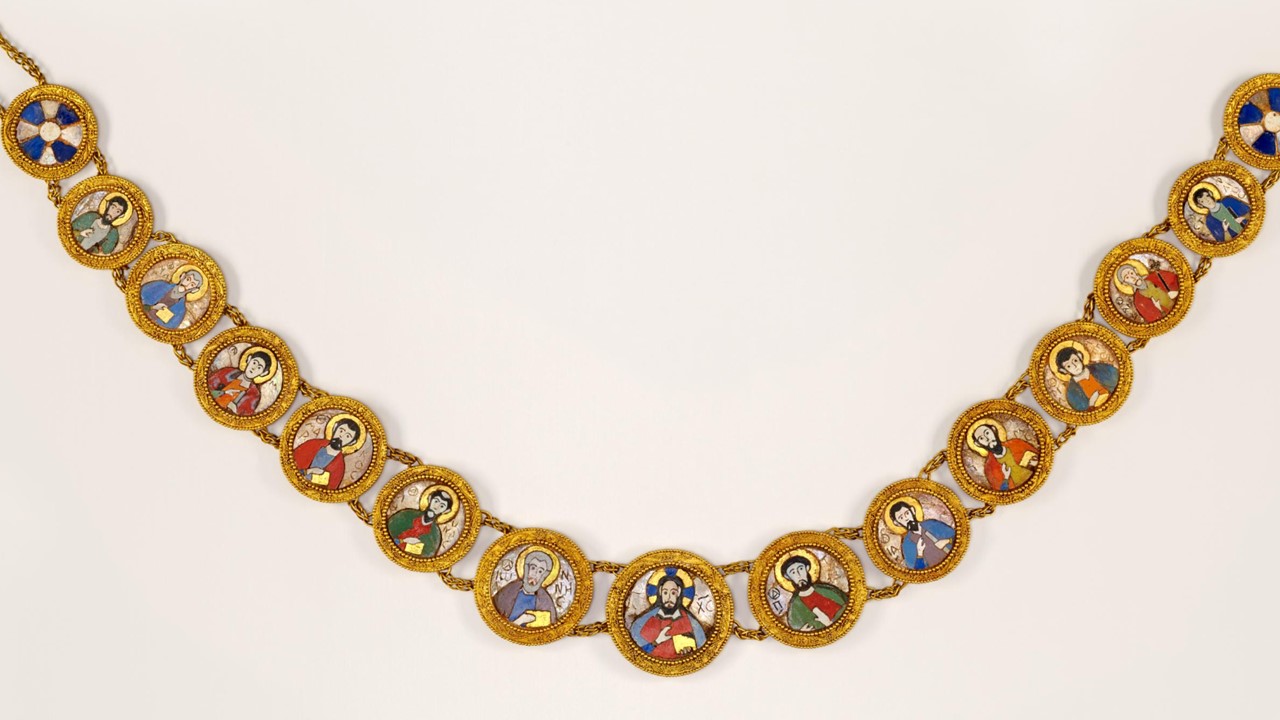
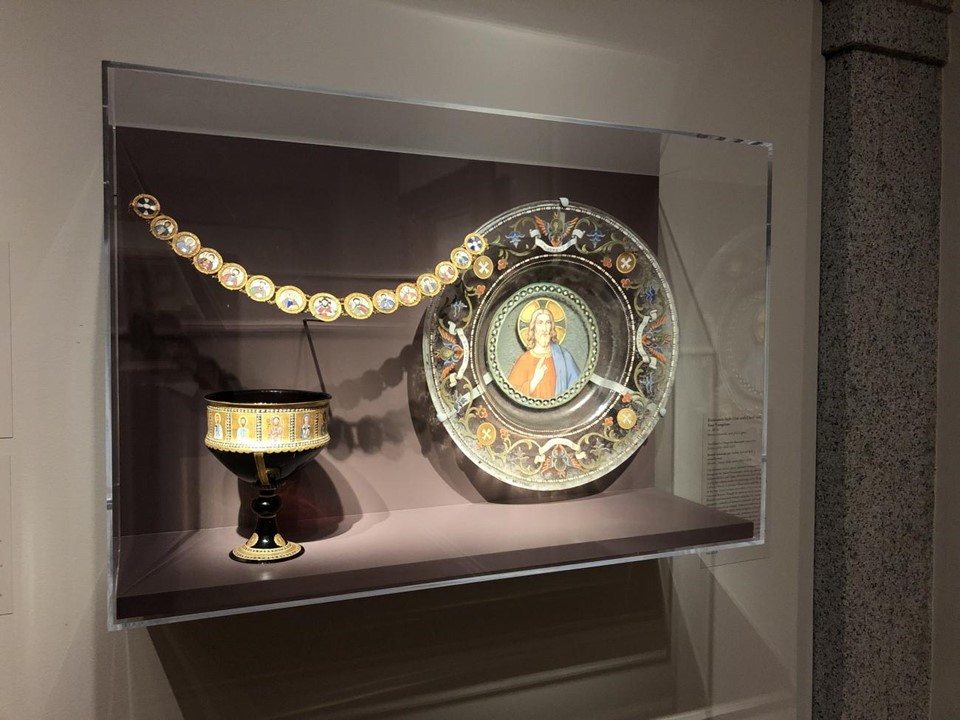
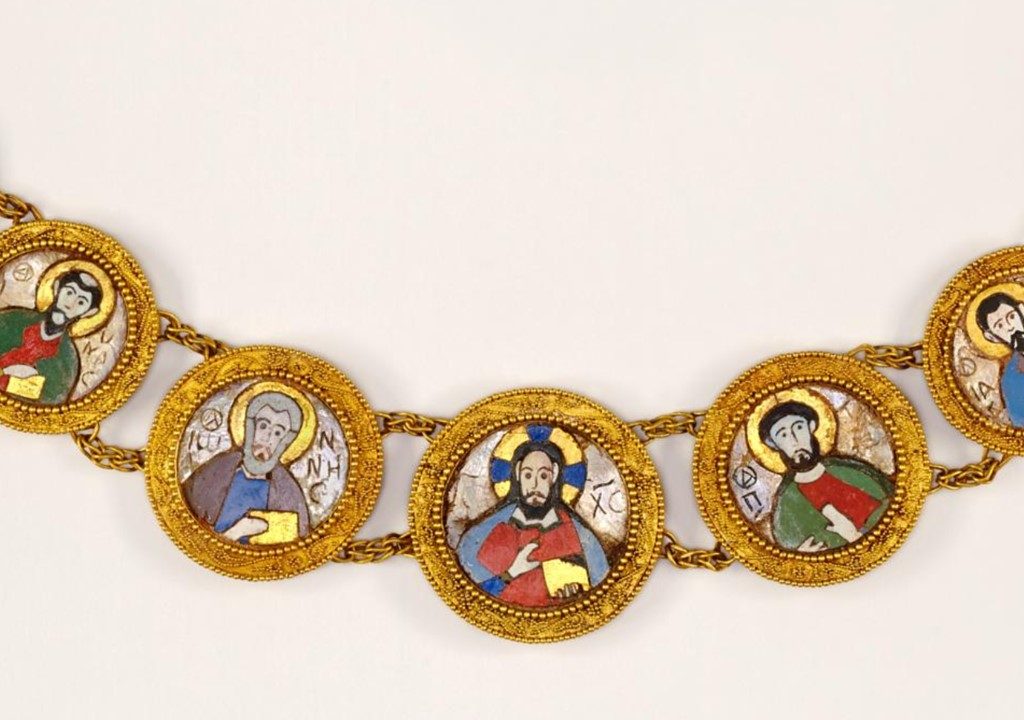
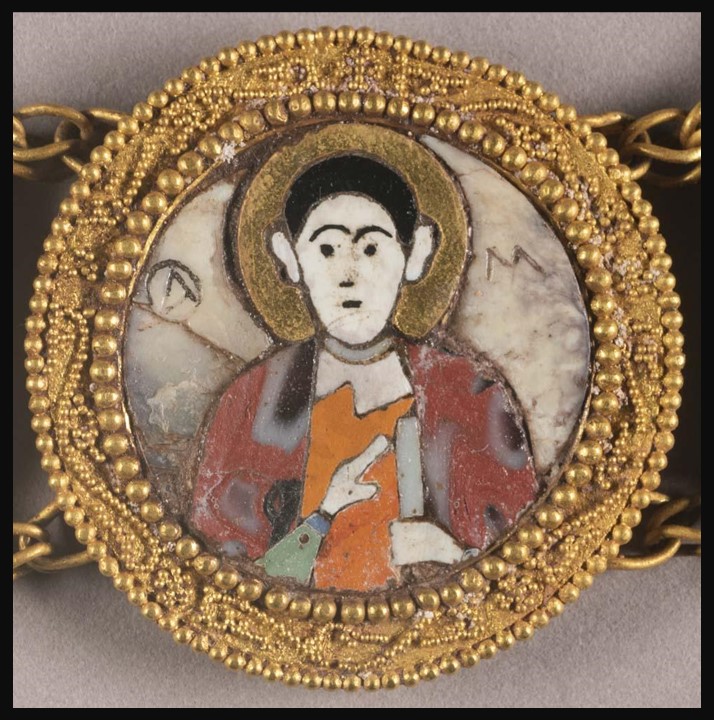
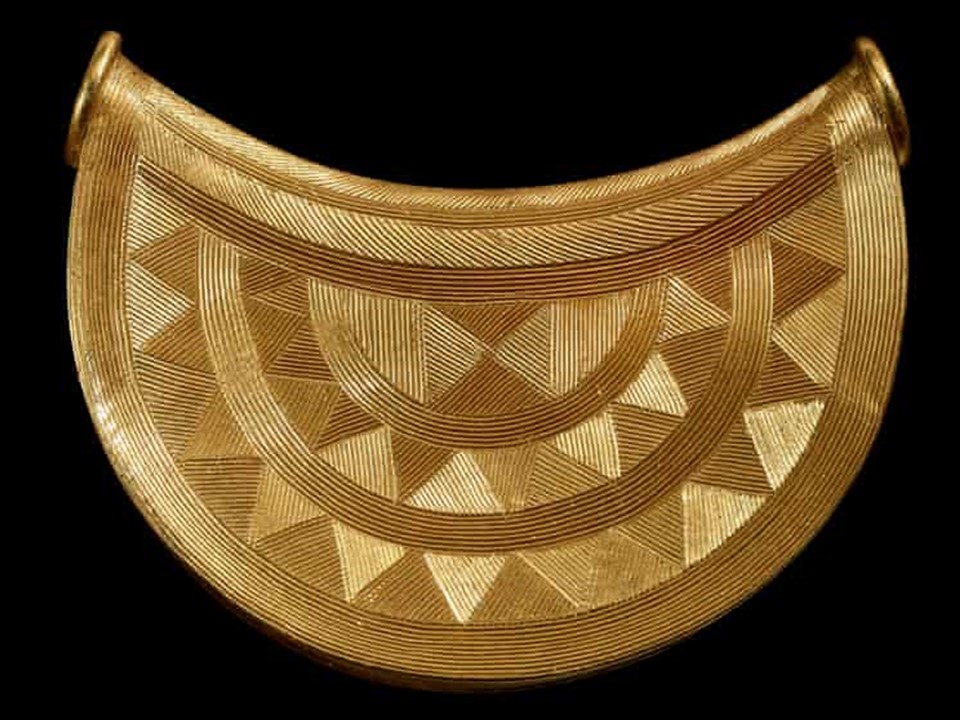
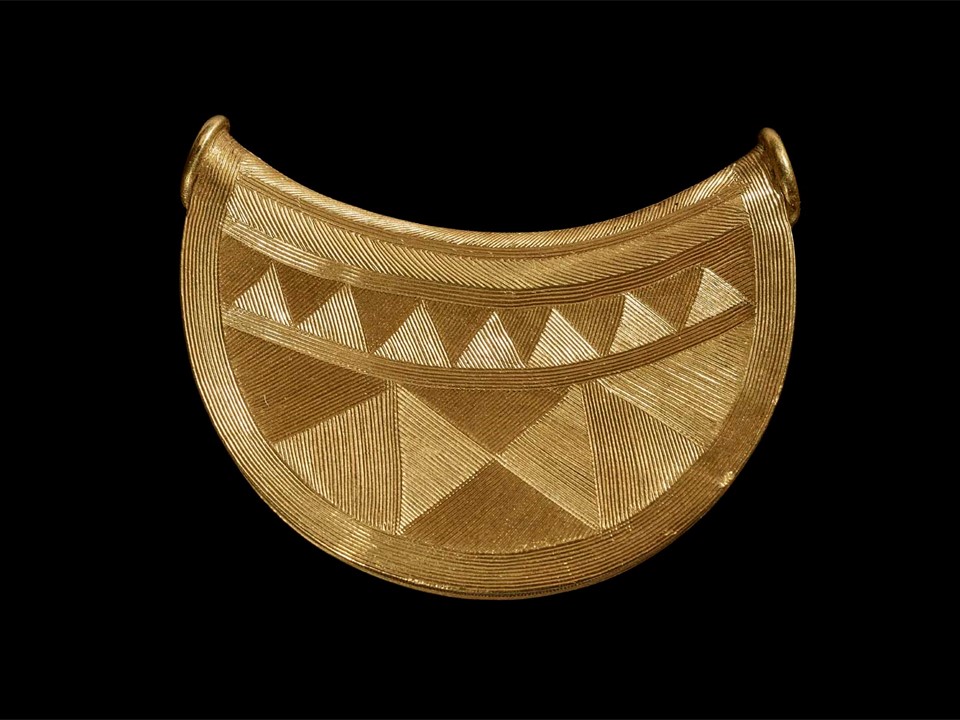
In Byzantine culture, bejewelled perikarpia (wristbands) played a dual role, both as functional accessories and symbols of status and protection. They were often worn by emperors, officials, and high-ranking clergy, and were intricately designed with luxurious materials such as precious metals, silk, gold thread, and precious stones. Their aesthetic value lay in the detailed craftsmanship, often reflecting religious and imperial motifs, serving as a visual display of wealth, piety, and power. Additionally, the ornate patterns and vibrant colours used in perikarpia added to the elegance of Byzantine attire, contributing to the overall grandeur of the empire’s visual culture. Today we will focus on a Pair of Byzantine Gold Perikarpia from Thessaloniki that exhibits exceptional beauty!
By asking questions starting with ‘who,’ ‘why,’ ‘when,’ and ‘where’ about the Byzantine Perikarpia from Thessaloniki at the city’s Museum of Byzantine Culture, we can explore the artworks’ historical context, artistic significance, and the story behind their creation.
Where exactly were the perikarpia found, and what does this location tell us about their significance? The perikarpia were discovered under Dodecanesou Street in Thessaloniki, buried about three feet underground. This area was once a busy urban center in Byzantine times, indicating that the wristbands may have belonged to a wealthy or high-status individual living in the city. The location suggests a strong connection to Thessaloniki’s past as a significant cultural and economic hub of the Byzantine Empire. The hiding of these treasure points to periods of conflict and invasion, particularly during the Saracen attack on the city in 904.
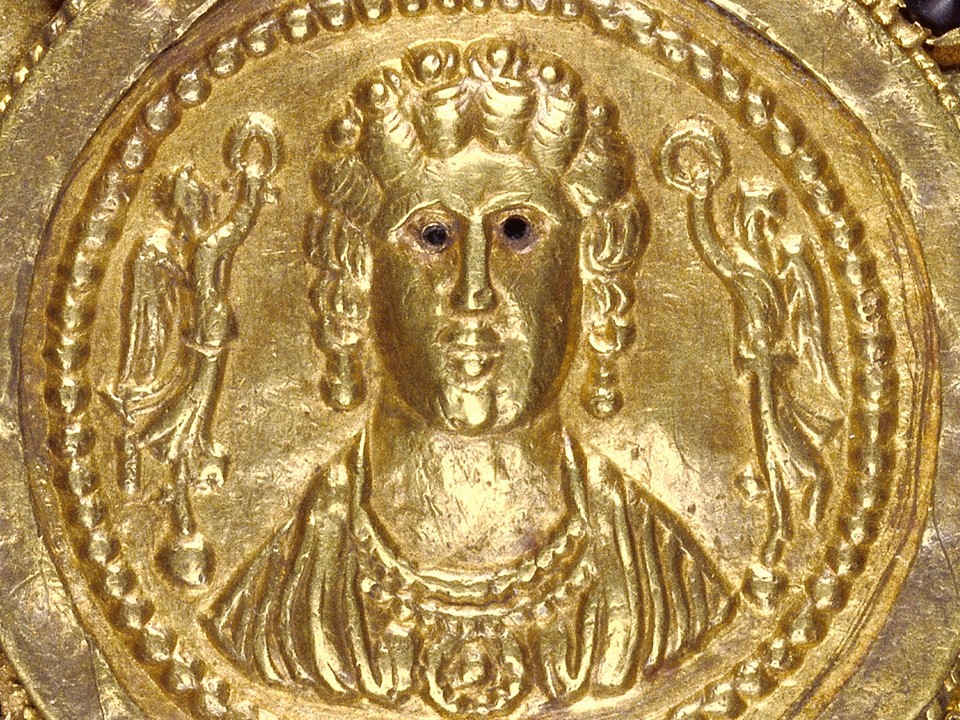
When were they crafted, and how does this fit into Byzantine history? The Byzantine perikarpia were likely crafted during the height of the Byzantine Empire, possibly between the 9th and 10th centuries, based on their artistic style and the period of the Saracen attack on Thessaloniki in 904. This timeframe fits into a period of Byzantine wealth, artistic flourishing, and political challenges, marked by external threats and invasions. The use of gold and enamel on these wristbands reflects the luxurious craftsmanship typical of the empire’s elite, illustrating the fusion of religious symbolism and imperial power in Byzantine art.
Who might have owned or worn these wristbands, and what social or religious role did they play? The perikarpia were likely owned by a wealthy individual or someone of high status, possibly an aristocrat or merchant in Thessaloniki. Given their luxurious design and use of precious materials like gold and enamel, they may have also been worn by someone with religious or imperial connections. In Byzantine society, such items were not only decorative but also served as symbols of wealth, piety, and social rank, possibly even offering spiritual protection. Their burial suggests the owner sought to protect valuable possessions during times of conflict or instability.
Why were they buried twice, and what does their discovery reveal about the history of Thessaloniki during these periods? The perikarpia were buried twice—first during the Saracen attack on Thessaloniki in 904 to protect them from being looted, and then later, possibly in the 1600s, by a wealthy merchant. The double burial reflects the repeated cycles of instability in Thessaloniki’s history, as it faced invasions and upheavals over centuries. Their discovery highlights the city’s historical significance as a center of wealth, commerce, and strategic importance, while also showcasing the lengths individuals went to safeguard valuable possessions during turbulent times.
For a PowerPoint on Byzantine Perikarpia, please… Check HERE!
Bibliography: https://media.ems.gr/ekdoseis/makedonika/makedonika_07/ekd_pemk_07_petsas_2.pdf https://ejournals.epublishing.ekt.gr/index.php/deltion/article/view/4427/4203 σελ 59 Στυλιανός Πελεκανίδης, Τα χρυσά βυζαντινά νομίσματα της Θεσσαλονίκης, Δελτίον XAE 1 (1959), Περίοδος Δ’. Στη μνήμη του ΝίκουΒέη (1883-1958), ΑΘΗΝΑ 1960, Σελ. 55-71, https://www.mbp.gr/sites/default/files/styles/object_images/public/4mikrotexnia.jpg?itok=9xIJgEtP, Dr. Alicia Walker, “Wearable art in Byzantium,” in Smarthistory, July 30, 2021, accessed September 12, 2024, https://smarthistory.org/wearable-art-byzantium/ and https://blogs.getty.edu/iris/uncovering-the-history-of-a-long-buried-byzantine-treasure/