https://pompeiisites.org/en/comunicati/the-house-of-the-large-fountain-the-house-of-the-anchor-and-the-temple-of-isis-all-reopen-to-the-public/#&gid=1&pid=8
Pompeii is an ancient Roman city located near modern-day Naples, Italy, that was buried under volcanic ash and pumice after the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in AD 79. The eruption preserved much of the city in remarkable detail, offering a unique glimpse into Roman life. Excavations have revealed homes, streets, public baths, markets, and temples, as well as vibrant frescoes and mosaics. One of the notable residences is the House of the Large Fountain, famous for its elaborate garden fountain adorned with mosaics, showcasing the wealth and artistic tastes of its owners. Pompeii is renowned for its archaeological significance, as the site provides valuable insight into the daily routines, social structures, and art of Roman civilization over 2,000 years ago.
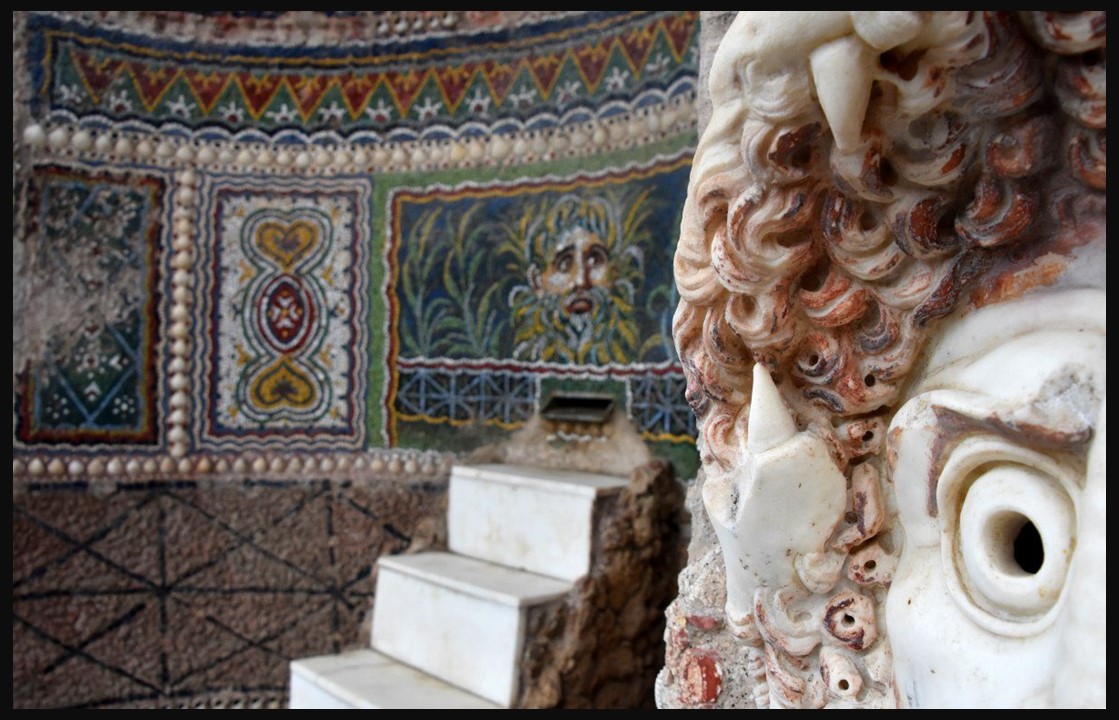
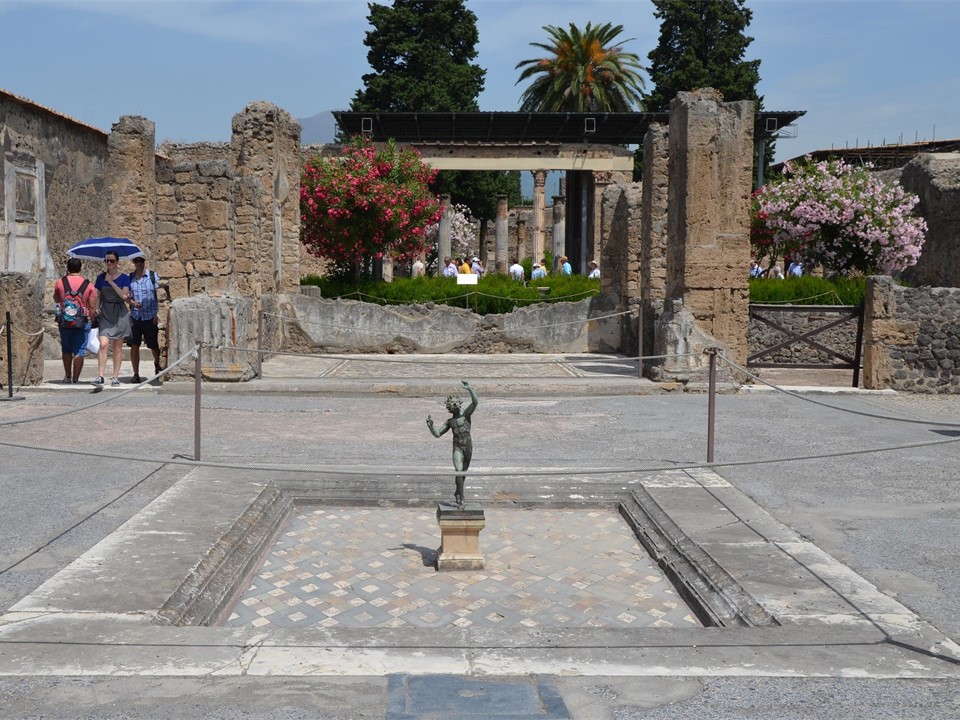
The House of the Large Fountain is one of Pompeii’s most distinctive and luxurious residences, celebrated for its remarkable garden and ornamental water features. Located on Via di Mercurio, the house’s layout dates back to the early 2nd century BC, though it underwent various modifications over time. Originally, the two atria were connected, but later alterations separated them, with the smaller atrium marked by six Doric columns. A portico supported by brick columns was added behind the tablinum, enhancing the house’s architectural complexity. In the final years before Pompeii’s destruction, the large fountain that gives the house its name was erected against the back wall of the small garden, set against a backdrop of vibrant mosaics and decorative stucco that showcases a sense of elegance and refinement. https://pompeiisites.org/en/archaeological-site/house-of-the-large-fountain/
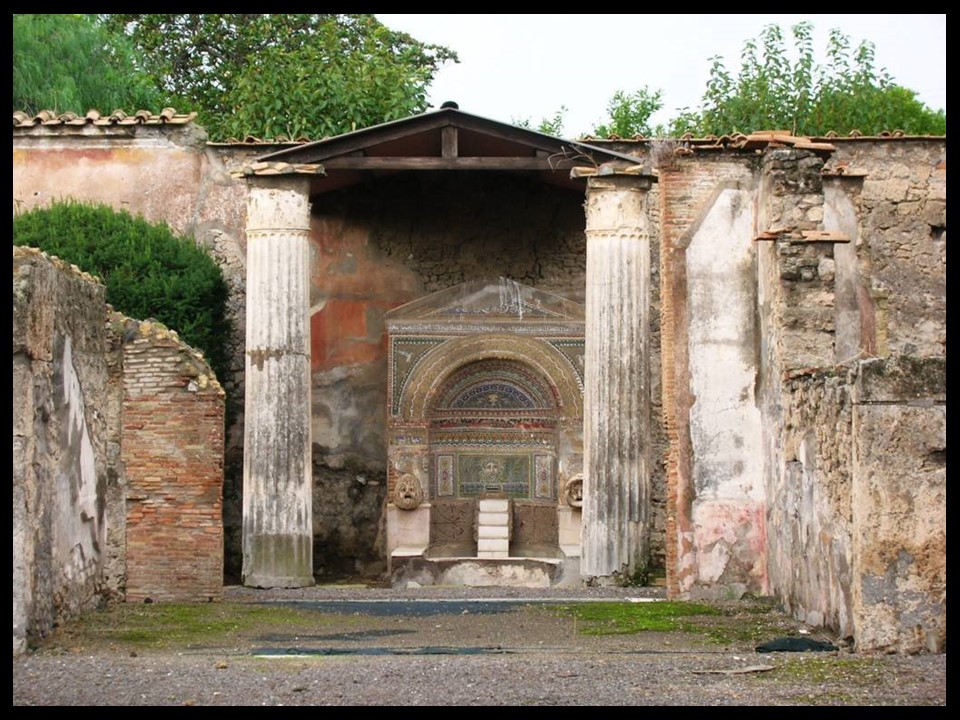

https://www.planetpompeii.com/en/map/the-house-of-large-fountain/524-the-house-of-large-fountain.html
This Pompeiian example of domestic architecture is a stunning blend of artistry and antiquity, rooted in the elegance of the 2nd century BC. The fountain, the house’s most striking feature, dominates the garden space with its intricate design of wall mosaic and sculpture. In front of a colonnaded façade, the fountain consists of a niche which is completely covered with polychrome tesserae and embellished with two marble sculpture theatrical masks, a rare example of non-floor mosaic nympheum made of glass paste and stone. The mosaics, adorned with delicate seashells, and two marble theater masks, reflect the artistic tastes of the Roman aristocracy, offering a glimpse into the luxury and aesthetic values of the time. This lavish display of art and water highlights the owners’ wealth and status in Pompeian society.
The fountain’s centerpiece, a cylindrical base with a central hole, stood bare when first uncovered in the early 19th century. It wasn’t until the late 19th century that a bronze copy of a cherub riding a dolphin, originally discovered in the nearby House of the Arches, was placed at the fountain’s heart. This artistic choice mirrored the style of the House of the Small Fountain, where a similar cherubic figure with a goose serves as the focal point. The display we see today faithfully recreates this historical arrangement, echoing the fountain’s transformation and its lasting legacy over the centuries.
The fountain, positioned at the end of the garden, would have provided a soothing ambiance with its flowing water, contributing to the overall tranquility of the space, offering valuable insight into how water, art, and nature were integrated into daily life. This feature, combined with the house’s other luxuries, points to the social status of its owners, who likely used the space for both private leisure and hosting social gatherings.
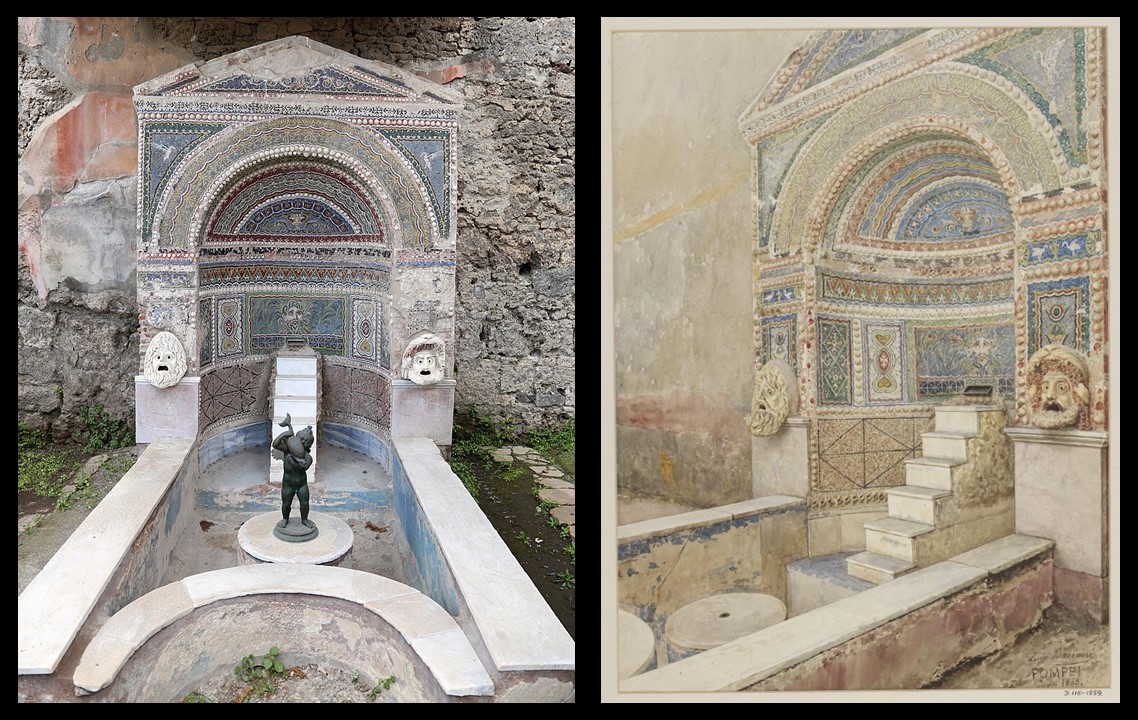

https://www.planetpompeii.com/en/map/the-house-of-large-fountain/524-the-house-of-large-fountain.html and Luigi Bazzani, Italian Artist, 1836–1927
A fountain in Pompeii (House of the Large Fountain, Pompeii), 1888, Watercolour on Paper, 46.35x 35.56 cm, Victoria and Albert Museum, London, UK https://collections.vam.ac.uk/item/O406355/painting-of-pompeii-drawing-luigi-bazzani/#object-details
Today, the house is a key example of Roman domestic art and garden design, offering valuable insight into how water, art, and nature were integrated into daily life. The lavish decorations and grand layout reflect the wealth and aspirations of the Pompeian elite, while the preservation of the site allows modern visitors to step into a world of ancient luxury. The House of the Large Fountain continues to fascinate both archaeologists and visitors for its artistic and architectural significance.
For a PowerPoint Presentation of the House of the Large Fountain in Pompeii, please… Click HERE!
Bibliography: https://collections.vam.ac.uk/search/?page=1&page_size=15&q=Luigi+Bazzani