https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/a/a6/Jean_Sim%C3%A9on_Chardin%2C_Soap_Bubbles%2C_probably_1733-1734%2C_NGA_994.jpg
https://collections.lacma.org/node/242227
In Jean-Baptiste-Siméon Chardin’s eulogy, he was remembered for having once said, “One makes use of pigments, but one paints with one’s feelings.” And feelings he presents in his Trilogy of Soap Bubbles… three paintings of playful boys and shiny, shimmering, iridescent soap spheres… and a game, suggesting the transience of life. https://www.artsy.net/artwork/jean-simeon-chardin-soap-bubbles-1
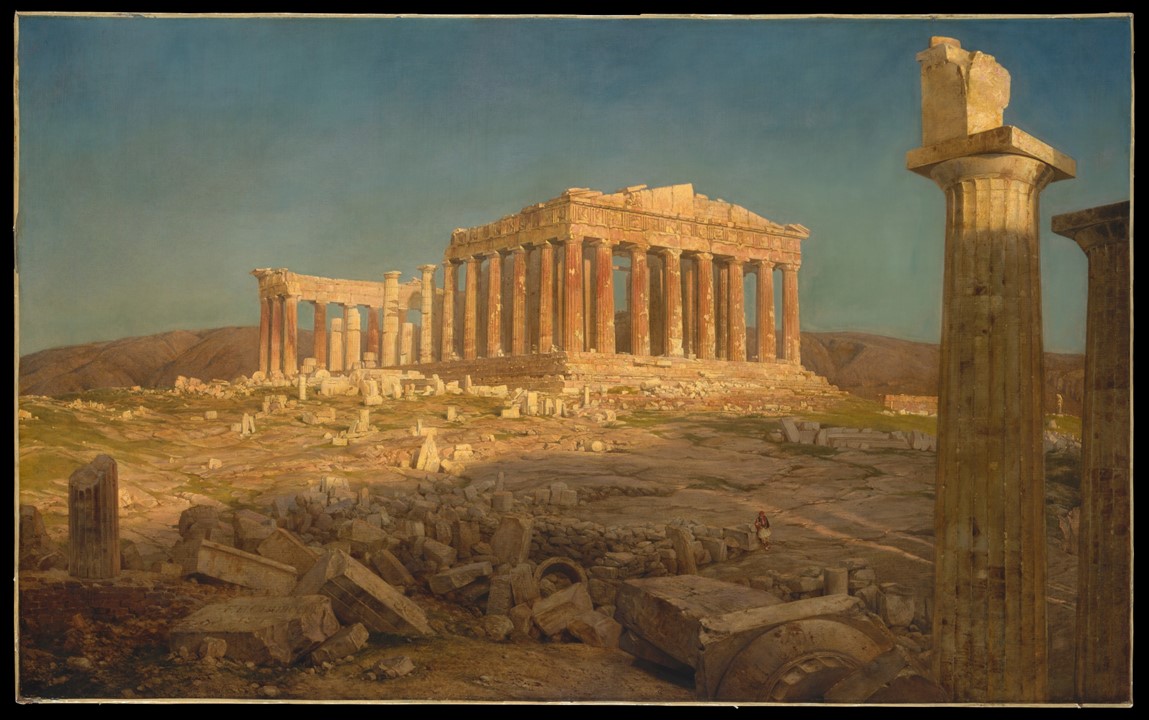
The Metropolitan Museum of New York experts, where my favourite Chardin painting of Soap Bubbles reside, inform us that… The idle play of children was a favorite theme of Chardin, a naturalist among painters. Apparently, the experts continue, he drew inspiration from the seventeenth-century Dutch genre tradition for both the format and the subject, but it is not clear if the artist’s intention was for his painting, understood then to allude to the transience of life, carried such a message. https://www.metmuseum.org/art/collection/search/435888
Jean-Baptiste-Siméon Chardin was the son of a modest cabinetmaker and the student of equally modest artists. Born and raised in Paris, the artist rarely left the city, drawing inspiration from Parisian genre scenes and arrangements of typically French objects and food. He lived on the Left Bank near Saint-Sulpice until 1757, when Louis XV granted him a studio and living quarters in the Louvre. He started his career by painting signposts for tradesmen and details in other artists’ works but in 1728, the Portraitist Nicolas de Largillière “discovered” him at an outdoor show, and Chardin was immediately admitted for membership in the Académie Royale.https://www.getty.edu/art/collection/person/103JYN and https://www.jean-baptiste-simeon-chardin.org/biography.html
Chardin was a frequent participant at the Parisian Salon, a dedicated academician, and, later in life, a pensioner of the French King. He was much admired by Denis Diderot, who would prove to be a great champion of his work. All of his paintings exhibited in the Parisian Salons were outstandingly successful. By 1770 Chardin was the ‘Premiere peintre du roi’, and his pension of 1,400 livres was the highest in the Academy. I am not surprised… even his simple, unassuming Still Lifes are treated with dignity and respect. So much so, that the novelist Marcel Proust wrote… We have learned from Chardin that a pear is as living as a woman, that an ordinary piece of pottery is as beautiful as a precious stone! https://www.getty.edu/art/collection/person/103JYN and https://www.jean-baptiste-simeon-chardin.org/biography.html
According to the dealer and collector Jean Pierre Mariette, writing some fifteen years after the fact, Chardin’s first figural picture, the MET experts inform us, showed a head of a young man blowing bubbles and was studied from a model. Between 1733 and 1739 Chardin painted three paintings, titled Soap Bubbles. It is also known, that in 1739 a version of Soap Bubbles was exhibited at the Paris Salon. The question is… which version? The answer is probably none of the three that have survived, in the Metropolitan Museum, the Los Angeles County Museum of Art, and the National Gallery of Art in Washington. They are definitely similar but not identical, none of them is dated, two of them are horizontals, and one, at the National Gallery, is vertical. https://www.metmuseum.org/art/collection/search/435888
Jean-Baptiste Siméon Chardin’s Trilogy of Soap Bubbles is popular and well-liked! The viewers are absorbed by the depiction of a boy poised on a stone windowsill blowing a big soap bubble and the younger boy next to him, fully absorbed in the activity. Although Chardin gives the illusion of capturing two youths in a candid moment, he has rigorously constructed his composition. Was his intention to present the viewer with an allegorical scene? Does it matter what the artist’s intention was? Are Chardin’s paintings of Soap Bubbles the perfect example of Rococo Art? My answer… I do not know… all I want is to feast my eyes and enjoy a moment of playfulness, and innocence… https://www.nga.gov/collection/art-object-page.994.html
For a PowerPoint on Chardin’s Soap Bubbles, please… Check HERE!
A wonderful Video for Children, prepared by the National Gallery of Art, on Chardin’s Soap Bubbles… https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kaxg6MjjM6g