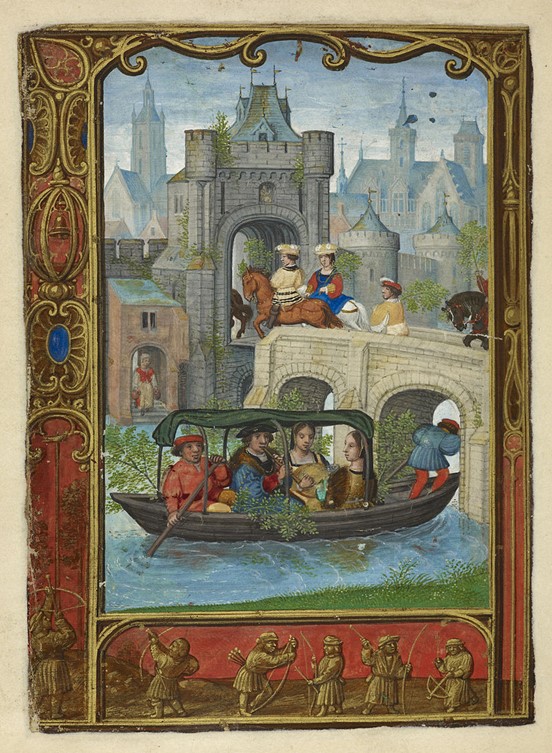
SS Normandie, 1935,lithograph in colours, printed by Alliance Graphique, Paris, 98 x 61cm, Private Collection
https://d2mpxrrcad19ou.cloudfront.net/item_images/1207624/11871155_fullsize.jpg
SS Normandie was the ultimate transatlantic ocean liner – assuredly of the 1930s, but perhaps of the entire 20th century. She had abundance – she was novel, innovative, glittering, exceptionally advanced, truly sensational. Her French creators, designers and decorators sought perfection… SS Normandie Poster by Cassandre says it all! https://www.thehistorypress.co.uk/articles/the-brief-but-glorious-career-of-ss-normandie/
SS Normandie ocean liner was a showcase of French technological prowess and Art Deco design. Her purpose was distinctly threefold: To be the largest liner afloat (the first to exceed 60,000 tons and 1,000 feet in length), to be the fastest ship, and, thirdly, to be an extraordinary floating center of ‘everything French’ – from food to decor to style and fashion. A.M. Cassandre was invited… to create a Poster for her May 29, 1935, inaugural crossing to New York. The artist responded… and created his most iconic work, and the best-known image of the Normandie ocean liner. The simplicity and symmetry of Cassandre’s frontal view of the looming hull of the liner immediately convey its gigantic scale and streamlined elegance. https://www.thehistorypress.co.uk/articles/the-brief-but-glorious-career-of-ss-normandie/ and https://collections.vam.ac.uk/item/O1405126/normandie-poster-cassandre/
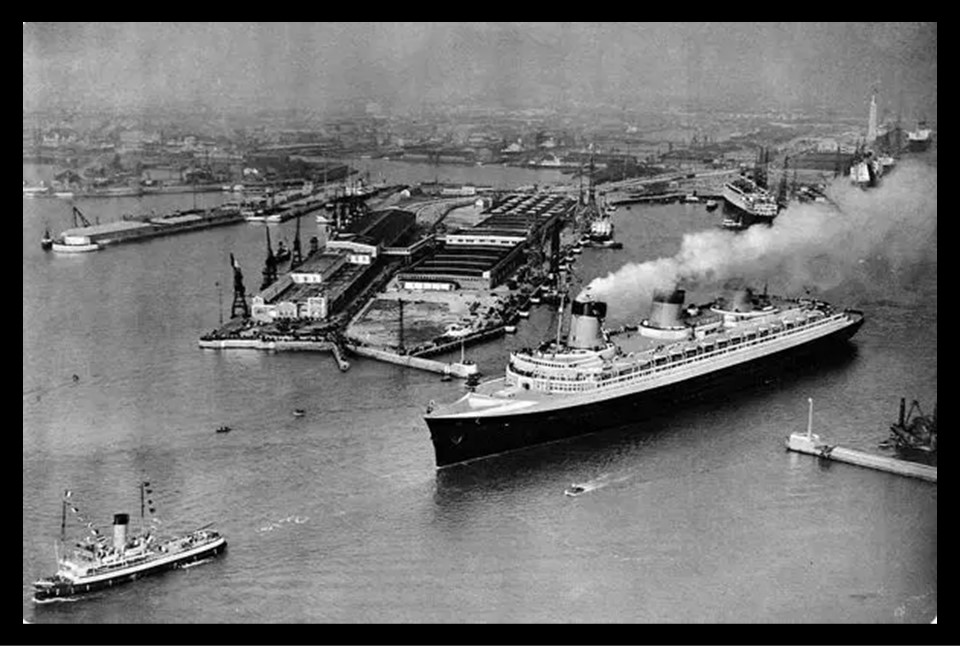

https://www.prints-online.com/french-liner-normandie-leaving-le-havre-may-1935-4383271.html
As Cassandre explained… A Poster unlike a painting, is not, and is not meant to be, a work easily distinguished by its – manner – a unique specimen conceived to satisfy the demanding tastes of a single more or less enlightened art lover. It is meant to be a mass-produced object existing in thousands of copies like a fountain pen or automobile. Like them, it is designed to answer certain strictly material needs. It must have a commercial function. Cassandre’s revolutionary designs introduce a new visual vocabulary, graphic concepts, and challenges that artists found difficult to surpass. http://hogd.pbworks.com/w/page/18698596/am%20Cassandre%20-%20Dubonnet%20poster

https://www.grapheine.com/en/history-of-graphic-design/cassandre-the-magnificient
Cassandre’s work, almost a hundred years later, is still identified as a masterpiece of the Art Deco style… precise and boldly delineated geometric shapes and strong colours. In the SS Normandie poster, Cassandre’s sky is always blue and the sea is always green and the (mechanized) black prow cuts through the (natural) waves, leading a flock of white gulls, as it sets world speed records. What an intimidating, and dramatic composition! This is the first time an artist depicted a ship with an exaggerated and massive bow. This is the first time an artist brilliantly used thirteen white birds, on the left flank of the ship’s prow to further illustrate the massive size of the ocean liner, and give life to his composition. The artist foregrounded the modern technology on the front of the ship, dramatizing the power and speed of its huge engines while allowing the passenger cabins to flare out at the edges. Heralded by the French flag, the ship is tipped with streaks of red, acting as explanation points. https://arthistoryunstuffed.com/the-art-deco-posters-of-cassandre-part-two/
An advertisement for the Normandie and her first arrival in New York City on June 3, 1935, stated that The arrival in New York Harbor of the gigantic superliner Normandie will inaugurate a new era of transatlantic travel. She will set new standards of luxury and speed, steadiness comfort, and safety…not merely the largest liner afloat (79,280 tons)…but in almost every respect a new kind of liner! https://vmfa.museum/piction/6027262-328930764/
For a PowerPoint on Cassandre’s work, please… Check HERE!