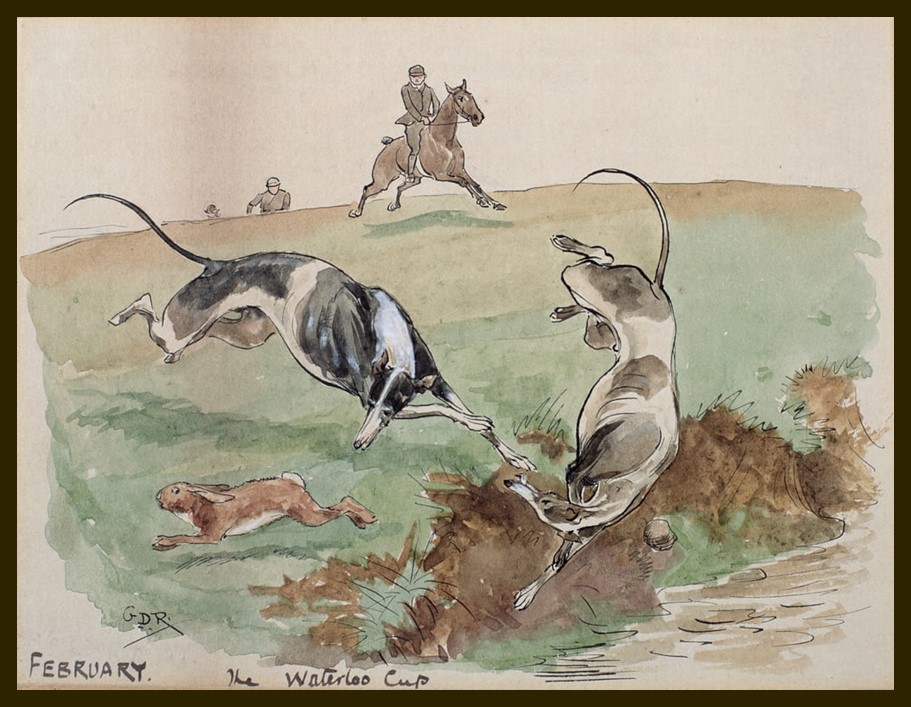
The Month of February: Coursing, the Waterloo Cup, unknown date, pen & ink and w/c on paper, Private Collection https://www.meisterdrucke.uk/fine-art-prints/George-Derville-Rowlandson/179537/The-Month-of-February:-Coursing-%28pen-and-ink-and-wc-on-paper%29.html
I’ll tell of the Magna Charter / As were signed at the Barons’ command / On Runningmead Island in t’ middle of t’ Thames / By King John, as were known as “Lack Land.” / …”We’ll get him a Magna Charter,” / Said Fitz when his face he had freed; / Said the Barons “That’s right and if one’s not enough, / Get a couple and happen they’ll breed.” / So they set about making a Charter, / When at finish they’d got it drawn up, / It looked like a paper on cattle disease, Or the entries for t’ Waterloo Cup… humorously wrote Edgar Marriott, and I think of February and the Waterloo Cup by George Derville Rowlandson. https://allpoetry.com/Magna-Charta
George Derville Rowlandson (1861–1928) was a British artist known for his contributions to the field of illustration and watercolour painting. Rowlandson was born on the 11th of December 1861 in Secunderabad, Madras, India, the son of George Rowlandson an Indian Army colonel, and studied at the Gloucester Art School as well as the Westminster School of Art, London, and in Paris. He was part of the Rowlandson artistic family, his grandfather being the famous caricaturist and satirist Thomas Rowlandson (1757-1827).
His works often depicted charming rural scenes, equestrian portraits, sporting scenes and military subjects as he was one of the first official WWI artists of the UK. At first, that is between 1897 and 1900, Rowlandson worked as an illustrator for The Illustrated London News, and then, from 1899 to 1900, he worked for the English Illustrated Magazine. As a freelance artist, he exhibited oil paintings and watercolours at the British Institution and the Royal Institute of Painters in Watercolours. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/George_Derville_Rowlandson
On the 1st of February, I present you with a lovely watercolour by George Derville Rowlandson, titled February, The Waterloo Cup. It is part of a set of twelve small watercolour paintings depicting a sporting event, one for each month of the year.
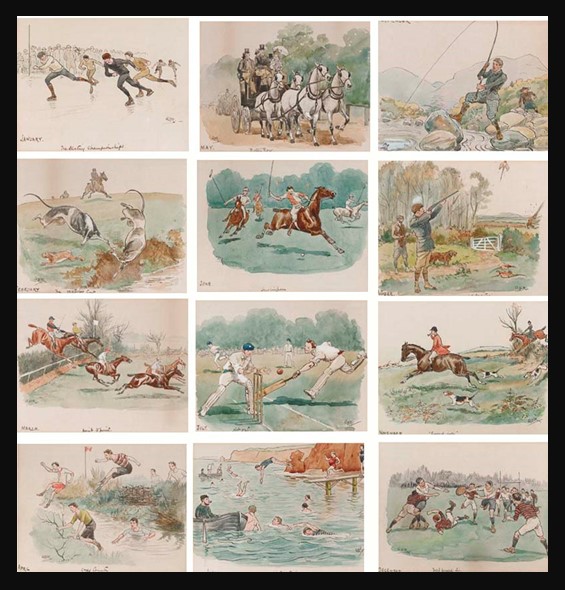

Christie’s experts have identified the Months along with their corresponding sporting events as: January, the skating championships; February, the Waterloo cup; March, point to point; April, cross country; May, Rotten Row; June, Hurlingham; July, not out; August, common objects by the sea; September, his first fish – a fifty pounder at least; October, a rocketer; November, forward away; December, well passed sir all signed with initials ‘G.D.R.’ (seven lower right); and five (lower left) and inscribed ‘January, the skating championships’ (lower centre); ‘February, the Waterloo cup’ (lower centre); ‘March, point to point’ (lower centre); ‘April, cross country’ (lower centre); ‘May, Rotten Row’ (lower centre); ‘June, Hurlingham’ (lower centre); ‘July, not out’ (lower centre); ‘August, common objects by the sea’ (lower centre); ‘September, his first fish -a fifty pounder at least’ (on the reverse); ‘October a rocketer’ (lower centre); ‘November, forward away’ (lower centre); ‘December, well passed Sir’ (lower centre) respectively. https://www.christies.com/en/lot/lot-4210691
Artistically, the scene depicting February and the Waterloo Cup stands out as my favourite, distinct from it being a favoured sporting event. Full of energy and excitement, the scene presents a renowned coursing event organized by the National Coursing Club (NCC). Established in 1836, the competition held a prestigious status in the world of greyhound coursing. The event took place annually at Altcar near Liverpool in England and was named after the Waterloo Hotel, which hosted the inaugural meeting.
Coursing involves setting greyhounds after a hare, and the Waterloo Cup was a prominent fixture attracting participants and spectators alike. The competition’s history spans decades, contributing to the rich tapestry of traditional British sporting events. Not only did it showcase the speed and agility of greyhounds, but it also became a social and cultural phenomenon. The Waterloo Cup held its last meeting in 2005, marking the end of an era in coursing history due to changes in legislation related to animal welfare. Despite its closure, the Waterloo Cup remains a significant historical chapter in the world of coursing and sportsmanship.
For a PowerPoint presentation, please… Check HERE!