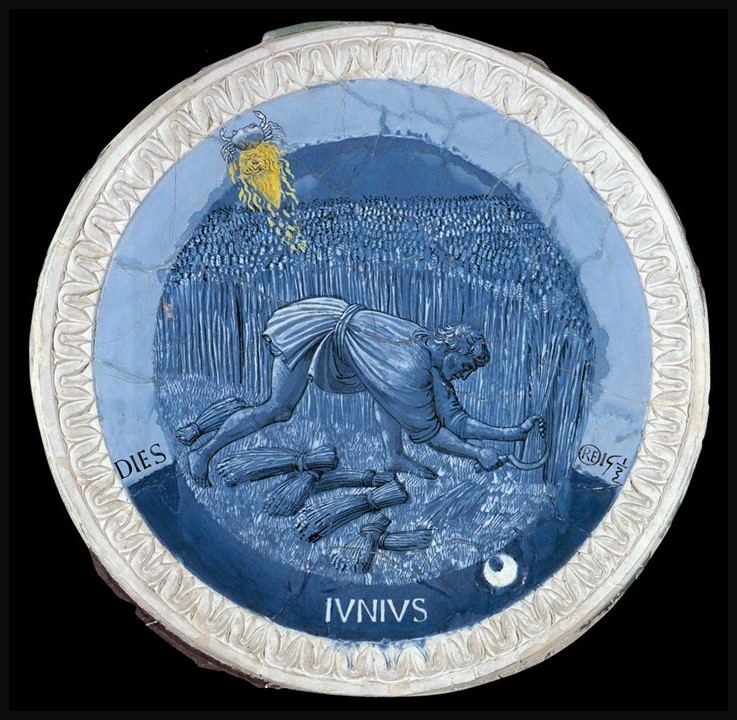
Labours of the Months: June, 1450s, Glazed terracotta, Diameter: 57 cm, Victoria and Albert Museum, London, UK https://www.wga.hu/frames-e.html?/bio/r/robbia/luca/biograph.html
…Which gives into the triumphant and lovely / study, / that has such talent and order and measure / that it represents angelic exultation, / With complete art in inlays and painting, / in perspective and carvings sublime, / and in great mastery of architecture. / There are great numbers of highly ornate books / and vases of alabaster and chalcedony / that are decorated with gold and silver. / And all things there are beautiful and good, / some by nature and others with human talent / made thus with whole perfection… This is how, in Terze Rime, the anonymous Italian 15th-century poet describes the famous studietto, created for Piero de’ Medici in the 1450s. It is the room for which the terracotta roundels of The Labours of the Months by Luca della Robbia were created to adorn the ceiling. https://www.jstor.org/stable/3048729?read-now=1&seq=5#page_scan_tab_contents
In the context of the Renaissance, a studietto or studiolo was a personal space, often elaborately decorated with paintings, sculptures, and frescoes that reflected its owner’s intellectual pursuits and tastes. These rooms were not just private retreats but also places to store and exhibit collections that demonstrated the owner’s wealth, power, and intellectual interests. The decoration and objects within often had symbolic meanings related to virtues, wisdom, and learning. The Medici Palace, a museum since 1974, reflects the grandeur and influence of the Medici family throughout its architecture and the art it houses. Within its walls, in the early 1450s, a studietto was created for Piero de’ Medici, unfortunately destroyed, when the Medici Palace was remodelled in the 17th century. According to Paula Nuttall… the studietto was a small, intimate room intended for study, contemplation, and display. Here were kept the most precious objects in the Medici’s collection: costly illuminated books, classical coins, cameos and vases, medieval ivories and goldsmiths’ work, and a tiny painting by the great Netherlandish master Jan van Eyck. Piero, who suffered from gout and was often confined indoors, is said to have taken great delight in being carried to his studietto, whiling away the hours in contemplating all these objects. https://www.vam.ac.uk/blog/museum-life/twenty-objects-twenty-years-labours-months-florence-c1450
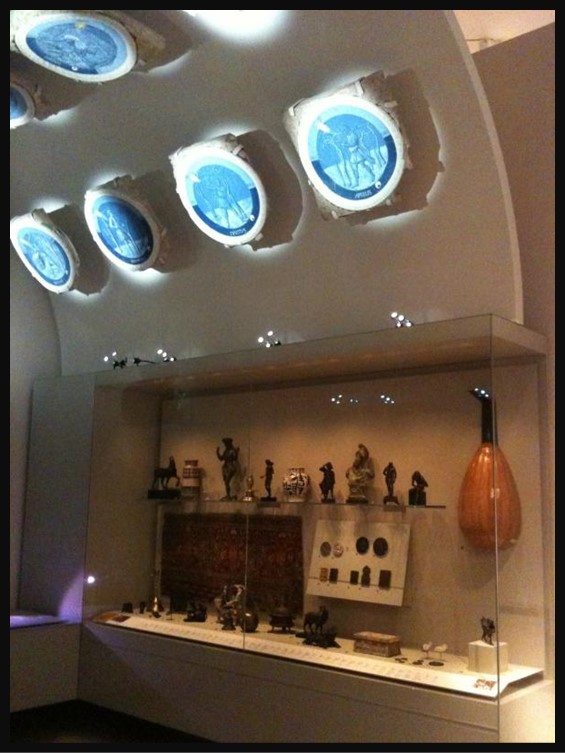

https://umbriaandtuscanyunravelled.blogspot.com/2015/06/object-in-focus-june-2015-june-one-of.html
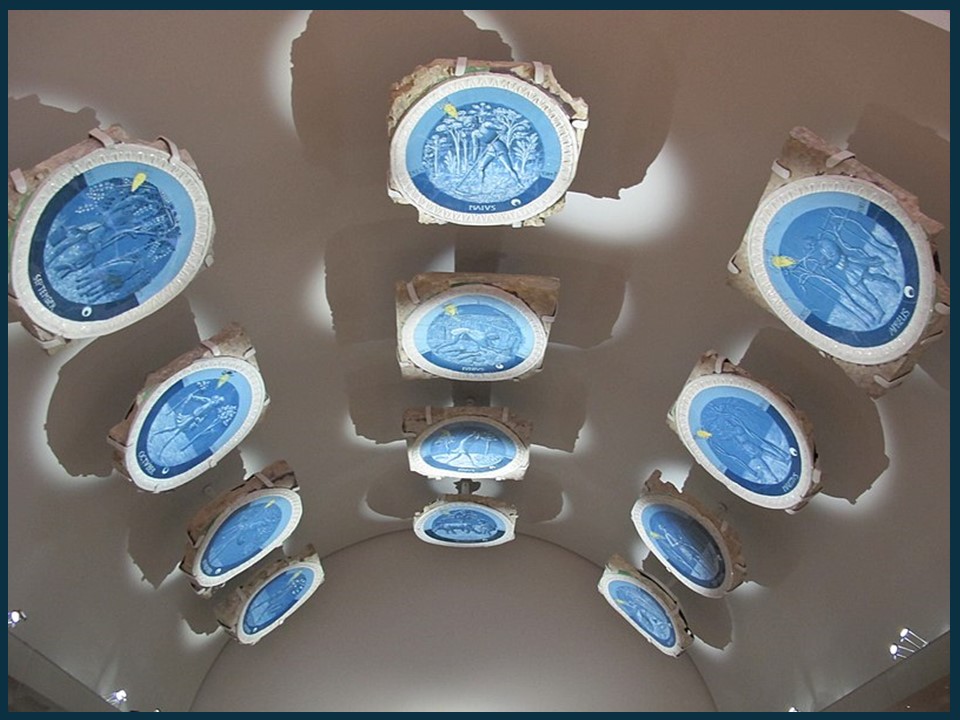
Piero de Medici’s studietto ceiling, crafted by Luca della Robbia, stands as a testament to the innovative spirit of the Renaissance. Employing the much-admired tin-glazed terracotta technique that della Robbia perfected in the early 15th century, the ceiling featured twelve intricately designed roundels, each representing a different Labour of the Month. Unlike popular della Robbia relief sculptures, these roundels boast naturalistic paintings in shades of white and blue, colours achieved through an experimental method seldom replicated. The edges of each roundel are adorned with sculpted leaf patterns, subtly detailed in low relief, offering a textural contrast to the smooth, painted centers. This ceiling, decidedly ornate and uncharacteristically detailed for its time, reflected not only the artistic ambition of della Robbia but also the grandeur of the room it overseed, a fitting canopy for the collection of curiosities and treasures it sheltered.
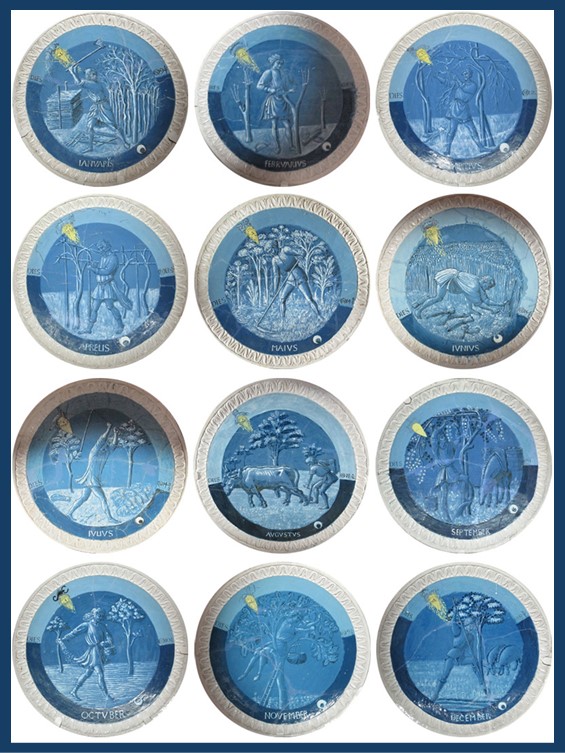

Labours of the Months, 1450s, Glazed terracotta, Diameter: 57 cm, Victoria and Albert Museum, London, UK
https://umbriaandtuscanyunravelled.blogspot.com/2015/06/object-in-focus-june-2015-june-one-of.html
In the mid-15th century, the studietto in the Medici Palace was a marvel of Florentine artistry. These resplendent with the most worthy figures inspired awe in all who entered, as noted by the architect Filarete. This intimate chamber, adorned to stir curiosity and admiration, met an untimely demise during the palace’s 17th-century remodelling. The surviving roundels, treasures of Renaissance art, found their way into a private Italian collection before being acquired by the Victoria and Albert Museum in 1861. Today, these pieces form the heart of a reconstructed space at the V&A, meticulously designed to evoke the original studietto’s ambience!
For a PowerPoint Presentation of the 12 Labours of the Months by Luca della Robbia in the Victoria and Albert Museum in London, please… Check HERE!
Bibliography: https://www.jstor.org/stable/3048729?read-now=1&seq=5#page_scan_tab_contents Some Unknown Descriptions of the Medici Palace in 1459 by Rab Hatfield, The Art Bulletin, Vol. 52, No. 3 (Sep. 1970), pp. 232-249 (18 pages)