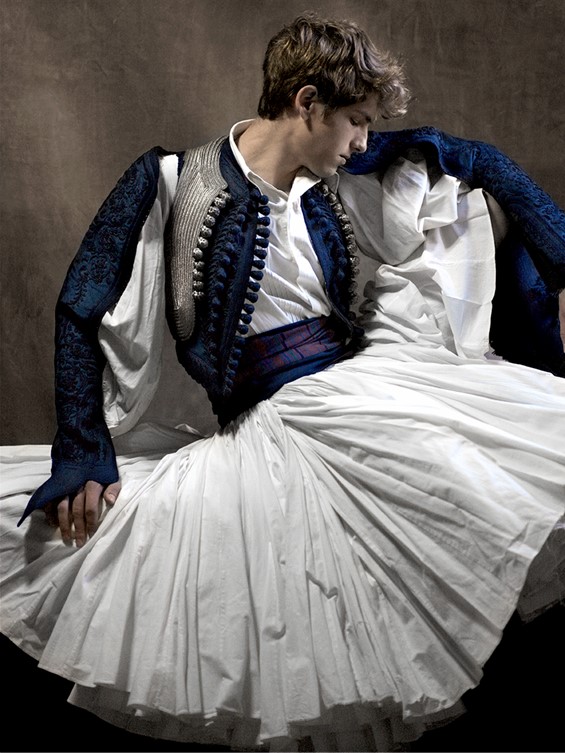
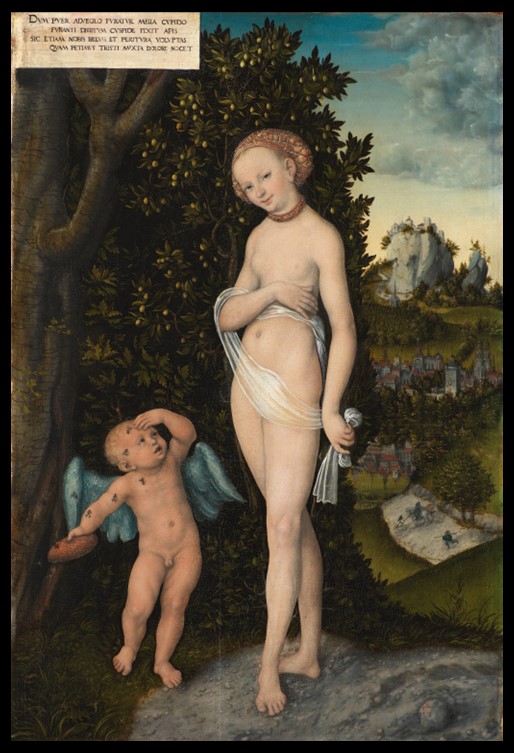
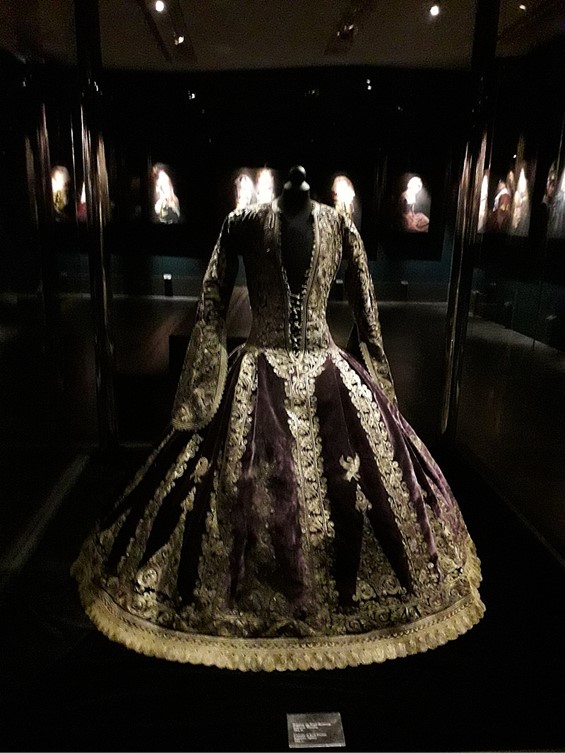
Costume of Dimitrios Mavromichlis, 19th century, Hand finished silver embroidery, using silver stitching carousel and cord, on printed cotton canvas, 126×104 cm. https://gallerykourd.gr/el/raiment-of-the-soul-2/
”The focus of this exhibition is the traditional Greek costume. Simple or more elaborate, everyday or festive, with embroidery and gold decorations, it is not a simple garment. It is a complex semiotic portrait of the person who wears it” said President of the Republic Katerina Sakellaropoulou in her greeting at the opening of the exhibition Raiment of the Soul at the Acropolis Museum (December 20, 2022, until April 2, 2023).https://www.greeknewsagenda.gr/topics/culture-society/7819-raiment-of-the-soul
There are seventy artworks presented in this fine exhibition. They are embroidered photographs of garments and costumes mostly of the 19th century, safeguarded in the past and present with the love and care of people, mainly the personnel of the National Historical Museum of Athens, but also of other Greek Museums. Two artists are responsible for this unique body of work, photographer Vangelis Kyris and artist of embroidery Anatoli Georgiev. They collaborated with Museums holding these precious costumes and chose the ‘right’ contemporary models to wear them. Then, Vangelis Kyris photographed each model capturing the essence of the costume she/he wore. When the photos were printed on large pieces of cotton canvases, majestic like Renaissance paintings, Anatoli Georgiev, using gold or silver thread stitching, silk or cotton threads, cord, sequins, metallic or knitted buttons… embroidered seminal parts of the costume’s original needlework, creating ‘poetry’ through texture. https://www.theacropolismuseum.gr/en/temporary-exhibitions/raiment-soul
The artists see their project, as a journey from the past to the future, with the present as a boat. For Vangelis Kyris beauty is what soothes your gaze and educates your soul, and for Anatoli Georgiev, it is Measure, balance, the feeling that what you see elevates your aesthetics.https://www.ifocus.gr/magazine/editors-choice/3044-xronia-polla-ellada-me-endyma-psyxis and https://www.womantoc.gr/stories/article/afto-pou-anakoufizei-to-vlemma-sou-mia-ksexoristi-ekthesi-gia-tin-oraiotita-ton-pragmaton/
For me, Raiment of the Soul is the best way to Celebrate Greece and its Independence Day!
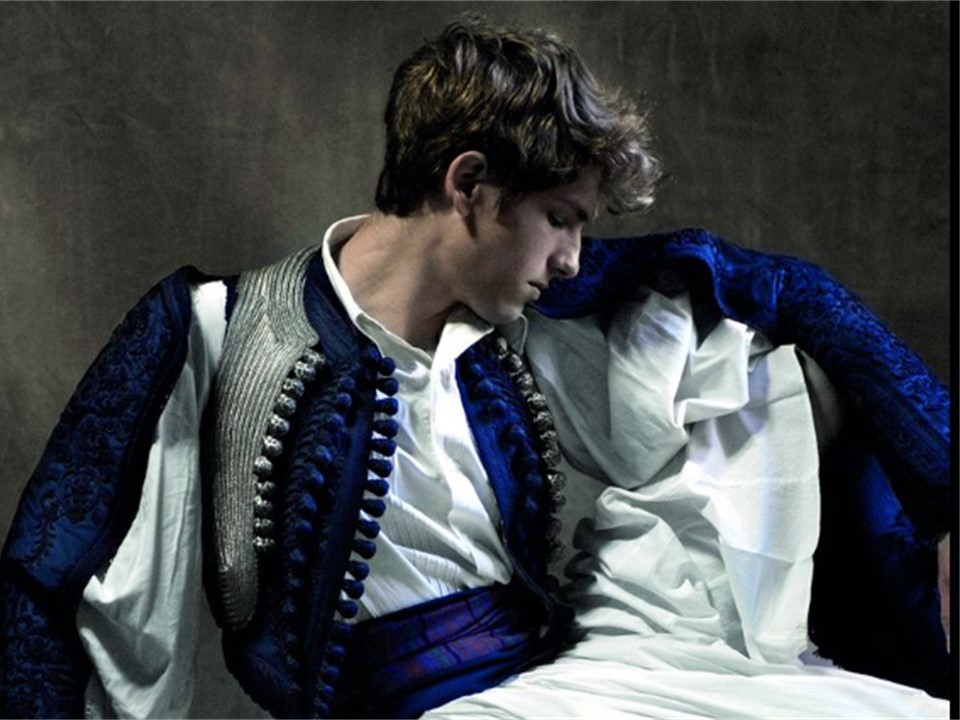

Costume of Dimitrios Mavromichlis, 19th century, Hand finished silver embroidery, using silver stitching carousel and cord, on printed cotton canvas, 126×104 cm.
https://gegonota.news/2023/01/25/endyma-psychis-20-dekemvriou-2022-26-martiou-2023/
Demetrios Mavromichalis was the fifth son of Petrobeis Mavromichalis. He was born in Mani, and lived for many years in Paris, upon his return he followed a military career, reaching the rank of lieutenant general. He was a supporter of King Otto I of Greece and took part in the revolution of 1862. As a politician, he participated in the governments of Voulgaris, Kanaris, and Benizelos Roufos. Presented by Kyros and Georgiev in the Acropolis Museum Exhibition, Mavromichalis’s Portrait comes alive and embodies the spirit of Greece through colours, movement, and texture.
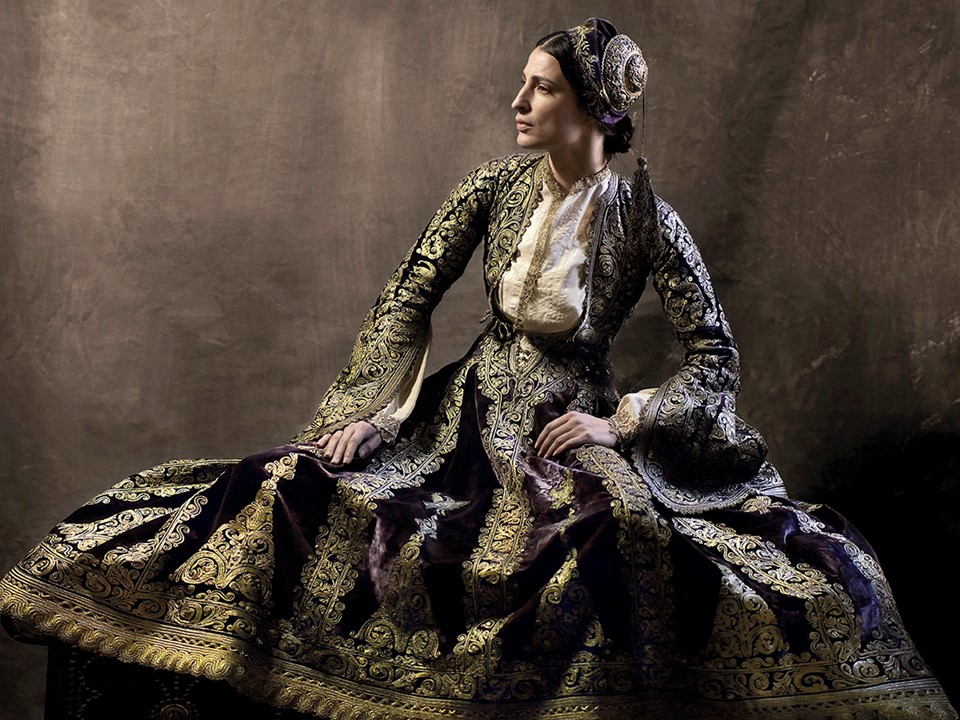

Esther Mastrogianni wearing the Epirote Costume of Kyra Frosyni, 18th century, Hand finished gold embroidery using cord, stitching, and metal sequins on printed cotton canvas, 130×170 cm. https://www.theacropolismuseum.gr/en/temporary-exhibitions/raiment-soul

Euphrosyne Vasileiou is better known as Kyra Frosini. She lived in Ioannina, in Epirus and she was famous for her beauty and spirit. Kyra Frosyni was executed for adultery in Ioannina by the Ottoman governor Ali Pasha of Ioannina along with 17 other women. She was allegedly executed for political reasons and was thereby viewed as a national heroine. Her violet-coloured dress represents the finest of 18th century Greek craftsmanship. The Kyros and Georgiev Portrait of Kyra Frosyni is ‘alive’ and stunningly ‘beautiful’ in its regal disposition.
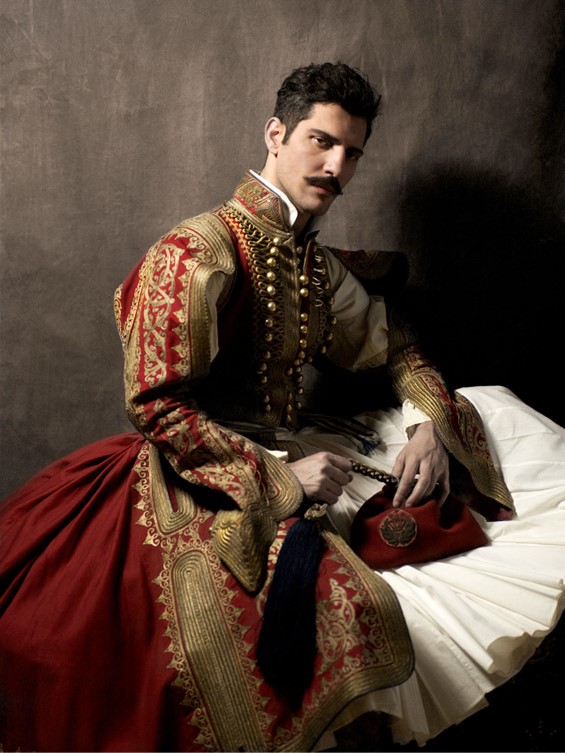

Anatoli Georgiev wearing the attire of Vaso Brajević a Serbian general who became a hero of the Greek War of Independence known by the nickname Mavrovouniotis (“Montenegrin”), 19th century Greek traditional costume, Hand finished gold embroidery using gold metal thread, stitching, cord and metal sequins, on printed cotton canvas, 126×103 cm. https://www.greeknewsagenda.gr/topics/culture-society/7819-raiment-of-the-soul

Vaso Brajević was a Serbian general who became a hero of the Greek War of Independence known by the nickname Mavrovouniotis (“Montenegrin”). His life was adventurous, risk-taking, and bold. Anatoli Georgiev wearing the attire of Vaso Brajević Mavdovouniotis presents a striking and dramatic Portrait of a truly revolutionary personality of a harsh but ‘Romantic’ era.
For Student Activities on the Greek War of Independence, please… Click HERE!
For a short Video on the Exhibition Raiment of the Soul, prepared by the Acropolis Museum, Click… https://www.theacropolismuseum.gr/en/temporary-exhibitions/raiment-soul