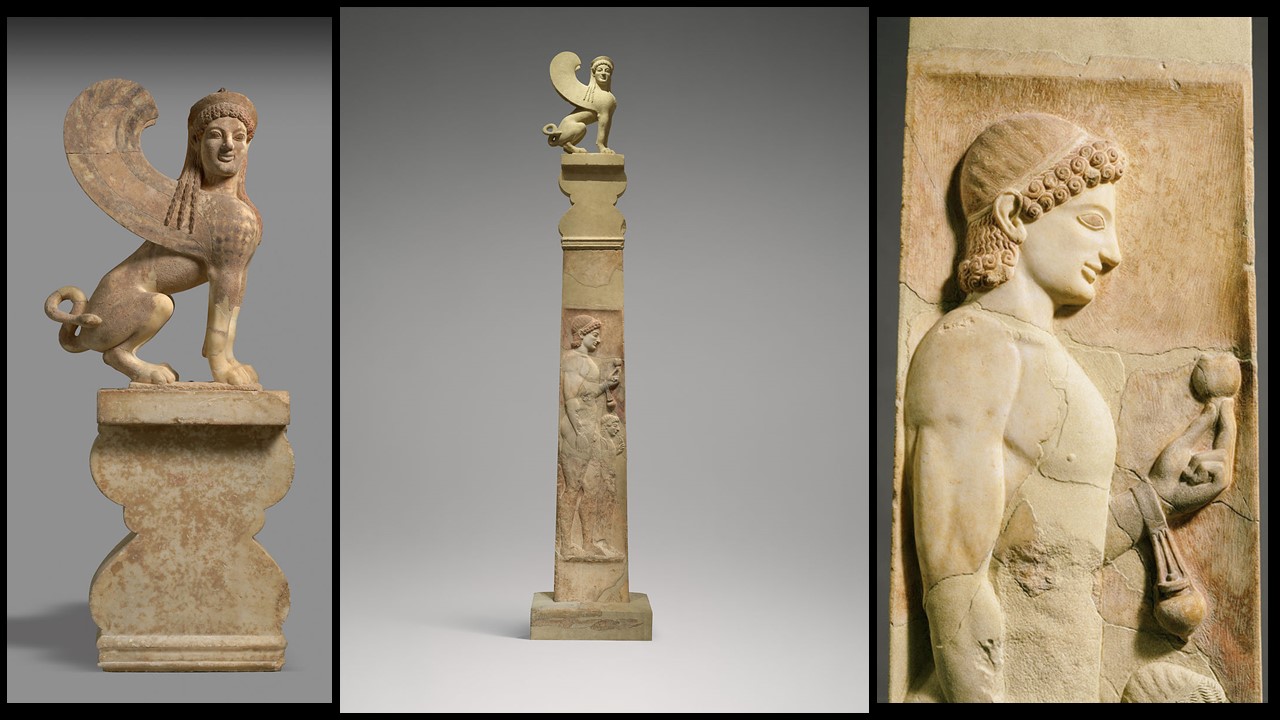
Inscribed on the base of this extraordinary Funerary Stele, we read… To dear Me[gakles], on his death, his father with his dear mother set (me) up as a monument. The ancient Greek marble Grave Stele of a Youth and a little Girl in the Metropolitan Museum of Art, in New York city, is worth exploring…
What is a Stele (for the Ancient Greeks)? A Stele (from ancient Greek στήλη-arrange/stand) is a set upright stone slab used in the ancient world primarily as a grave marker but also for dedication, commemoration, and demarcation. Stelae could be inscribed, carved in relief, or painted. During Greek Antiquity, Grave Stelae (επιτύμβιες στήλες) were usually inscribed and decorated with scenes depicting the deceased, usually alone, but sometimes with a servant or relative. The Early Archaic period Grave Stele in the area of Attica, were often inscribed, decorated in relief, crowned by a capital, which extended upwards and supported a sphinx, a demonic being that protected the tomb, and finally painted! https://www.britannica.com/topic/stela
Is the MET Grave Stele of a Youth and a little Girl special? Yes, it is a very special and unique piece. According to the MET experts… This is the most complete grave monument of its type to have survived from the Archaic period. It is also of high artistic quality and a great source of information on how ancient Greek sculptural pieces were painted. In addition, if the name of the youth in the Stele’s inscription is Megakles, as some scholars believe, then the Stele was erected by the Athenian family of the Alkmeonidai, and it is an archaeological discovery of historical importance. The Alcmaeonidai were a wealthy and powerful noble family of ancient Athens. Cleisthenes, Pericles, and Alkeviades were prominent members of the family. https://www.metmuseum.org/art/collection/search/248500
Where was the Marble Stele found, and how did it reach the MET? According to the MET, the Stele is… said to have come from Kataphygi, Attica. The Museum acquired fragments of the Stele in 1911, 1922, 1936, 1938, and 1951. Two parts of the MET Stele are plaster copies. For example, the Girl’s head is in Berlin, and the youth’s right forearm is in the National Archaeological Museum of Athens. Interestingly, the capital and crowning sphinx, as exhibited in its entirety, are casts of the originals, displayed in a case nearby. https://www.metmuseum.org/art/collection/search/248500
In 1911 the MET acquired a fragmentary shaft, the base, and the acroterion of the Stele from John Marshall in England. A fragment of the youth’s shoulder and arm was acquired in 1922 from M.L. Kambanis in Athens or Paris. The Stele’s marble capital and finial in the form of a sphinx were purchased in 1936 and 1938 through Martin Birnbaum. Fragments of the Stele’s inscription were gifted to the MET in 1951 by Walter C. Baker. https://www.metmuseum.org/art/collection/search/248500 and https://www.metmuseum.org/art/collection/search/248501
First thoughts and impressions… A few ancient Attic Grave Stelae of the Archaic period survived in their entirety. The three-part Grave Stele of a Youth and a little Girl is probably the best example. Exhibited restored, with the help of plaster casts, the MET Stele, shows how imposing and impressive such a monument could be. With considerable height, 4,23 meters, brilliantly painted, the Stele, seen even from afar, dominated the Athenian landscape where it originally stood. https://www.greek-language.gr/digitalResources/ancient_greek/history/art/page_063.html
Description… The MET Stele consists of three parts. The lowest part is the Stele’s rectangular base. Inscribed on the base, the unknown artist of the Stele wrote… to dear Me[gakles], on his death, his father with his dear mother set [me] up as a monument. https://www.metmuseum.org/art/collection/search/248500
The middle part of the Stele has a lot to narrate. The front part of the shaft depicts the full-length representation of the deceased, a young man, an athlete, and thee, a παλαιστρίτη (a wrestler or an athlete trained in a παλαίστρα). In heroic nudity, he holds with his left hand a pomegranate, the mythological fruit of death and fertility. Hanging from the left wrist, an aryballos (a small oil flask) reminds us that Megakles, if that was his name, was an active athlete. Little is known of the little, fully clothed, girl, standing before Megakles, holding, with her left hand, an unidentified flower in front of her face. It has been suggested that the girl in the composition might be a younger sister. http://met-guide.blogspot.com/2011/01/grave-stele-of-youth-and-little-girl_28.html
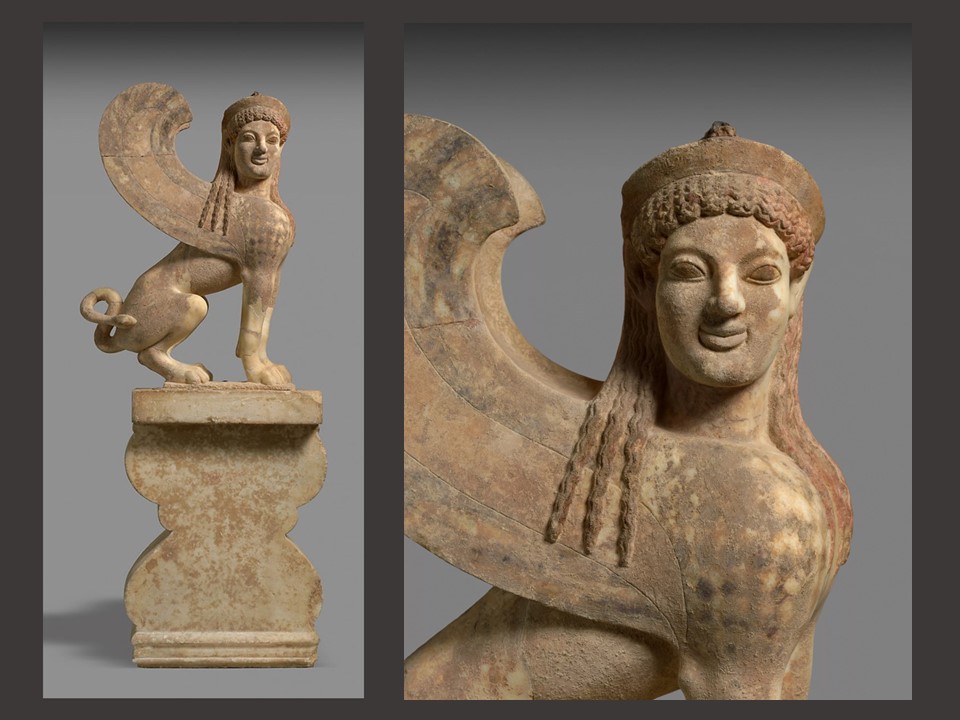
The third, and uppermost part of the Stele, the finial, consists of two members, the lower and the upper. The lower member, in the form of a double capital, was decorated wholly in color, its surface being entirely flat. It is fortunate that enough of the painted decoration survived time, so as to trace the original design… scrolls, making two pairs of volutes, and ‘palmettes’ placed between them. https://www.jstor.org/stable/3252802?seq=3#metadata_info_tab_contents and https://www.metmuseum.org/art/collection/search/248501
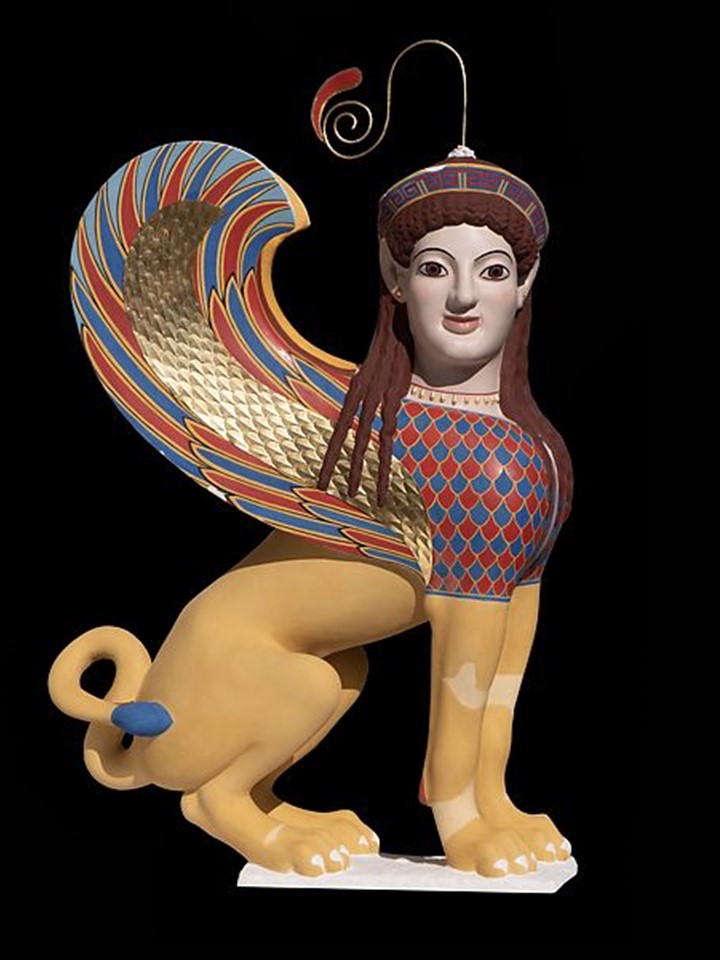
The upper member of the finial is a formidable, three-dimensional Sphinx, a mythological creature with a lion’s body and a human head, known in various forms throughout the eastern Mediterranean region from the Bronze Age onward. The Greeks, as in the case of the MET Stele, represented it as a winged female and often placed its image on grave monuments as guardian of the dead. https://www.metmuseum.org/art/collection/search/248501
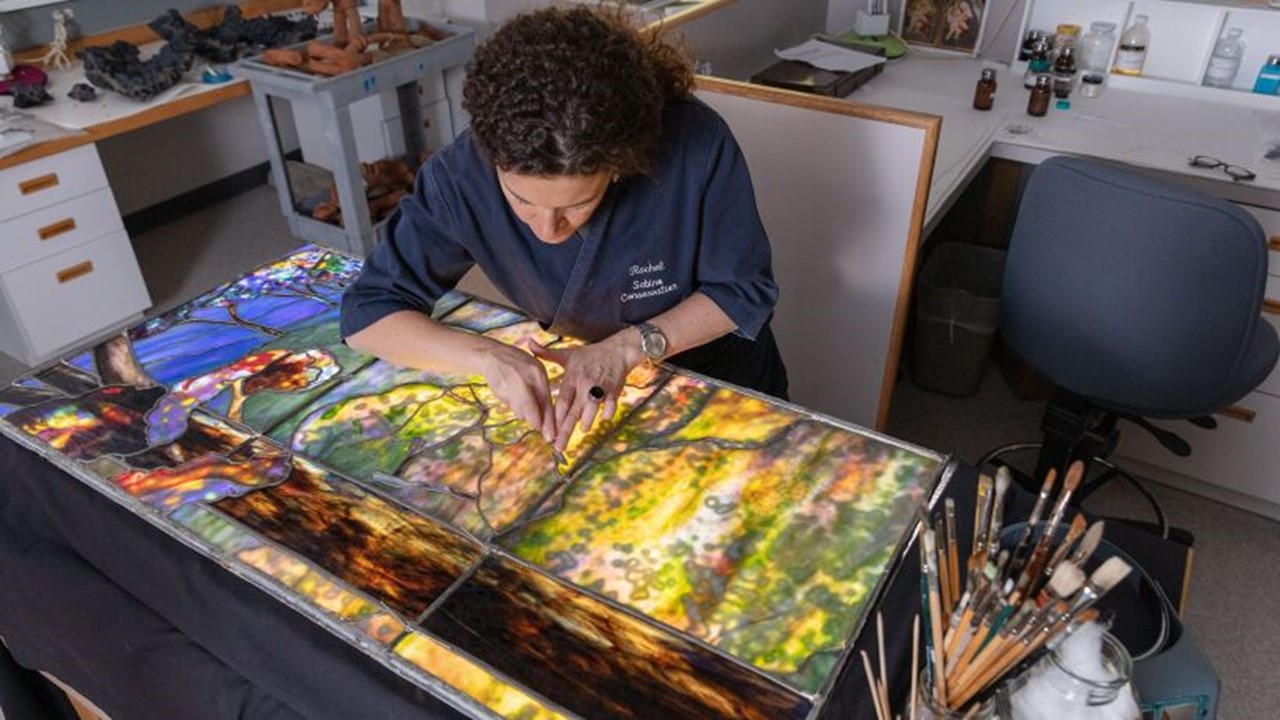
How is the MET Stele related to the Met Chroma: Ancient Sculpture in Color Exhibition? For the decoration of the MET Stele, the unknown artist employed sculpture and painting as well. The original colour on the marble MET Stele is unusually well-preserved, especially the colours of the Sphinx. According to Ulrike Koch-Brinkmann and Vinzenz Brinkmann, scientific analyses, photographs with ultraviolet and infrared light, false-color photographs, and archaeological comparisons allowed an almost complete reconstruction of the elegant designs in luminous and precious natural colors. The new, painted reconstruction of the MET Sphinx is a key display in Chroma: Ancient Sculpture in Color (Through March 26, 2023) Exhibition. https://www.metmuseum.org/exhibitions/listings/2022/chroma/exhibition-objects
For a Student Activity inspired by the Marble stele of a youth and a little girl in the MET, please… Check HERE!
If you are interested in visiting or browsing through the Metropolitan Museum of Art Exhibition Chroma: Ancient Sculpture in Color (Through March 26, 2023), please Check… https://www.metmuseum.org/exhibitions/listings/2022/chroma/visiting-guide and https://www.metmuseum.org/exhibitions/listings/2022/chroma/exhibition-objects For an Exhibition Video prepared by Art Trip (19:37 min), check… https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7LFGtqslZAU