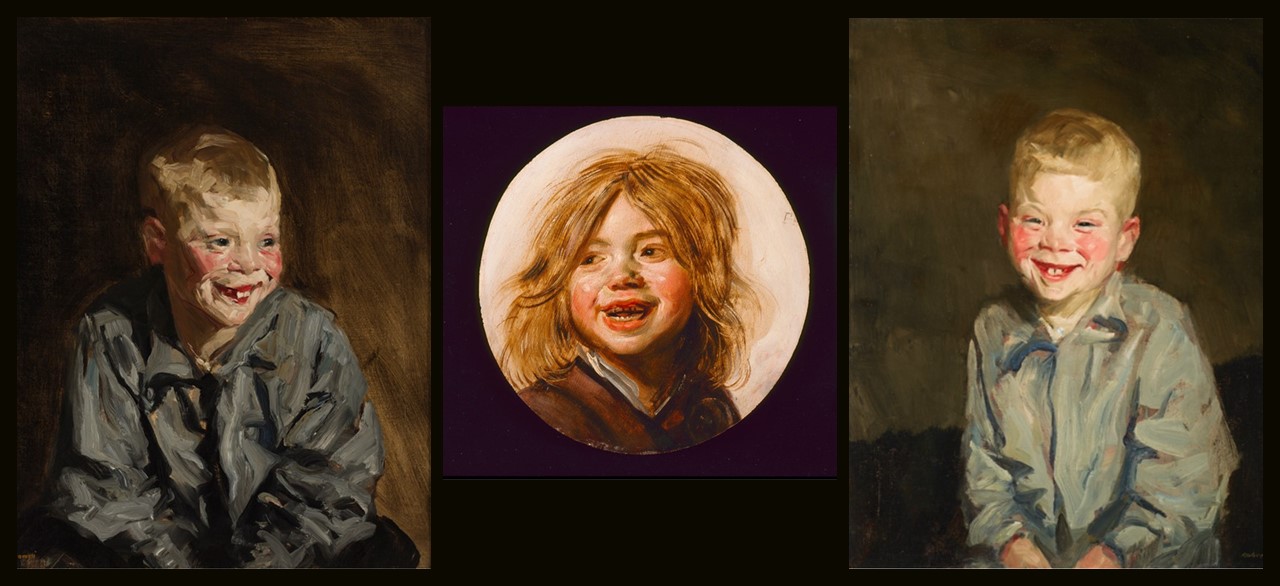
The Dutch Joe (Jopie van Slouten), 1910, oil on canvas, 60.96 × 50.8 cm, Milwaukee Art Museum, WI, USA http://collection.mam.org/details.php?id=13533
Frans Hals, Dutch Artist, 1582/83-1666
Laughing Child, circa 1620-1625, oil on wood, Diameter: 27.94 cm, LACMA (Los Angeles County Museum of Art), CA, USA https://useum.org/artwork/Laughing-boy-Frans-Hals-1625
The Laughing Boy (Jopie van Slouten), 1910, oil on canvas, 61 × 50.8 × 2.5 cm, Birmingham Museum of Art, AL, USA
https://www.artsbma.org/collection/the-laughing-boy-jopie-van-slouten/
Published on October 14, 2018at the Historians of Netherlandish Art Reviews, I read: Frans Hals was rediscovered as a modern idol two hundred years after his death. He was admired, even adored by late 19th-century artists such as Édouard Manet, Max Liebermann… Vincent van Gogh… and American artist Robert Henri, I would like to add. They were all impressed by his loose touch and rough painting style, which came across as ‘Impressionist’… Comparing paintings by Frans Hals to work by the artists whom he inspired gives insight into how modern Frans Hals was in their eye and why they used to say that ‘Frans Hals, c’est un moderne’. The Laughing Boy by Robert Henri is a painting that shows how Frans Hals influenced an American artist of the Ashcan School as well… https://hnanews.org/frans-hals-and-the-moderns/
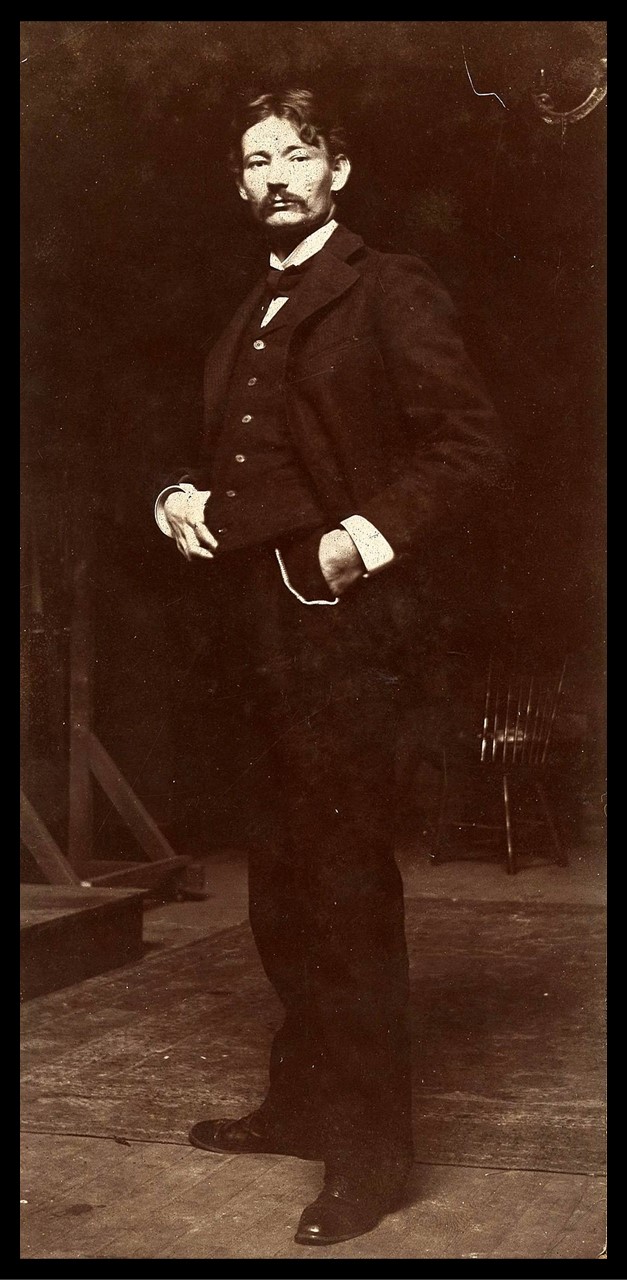

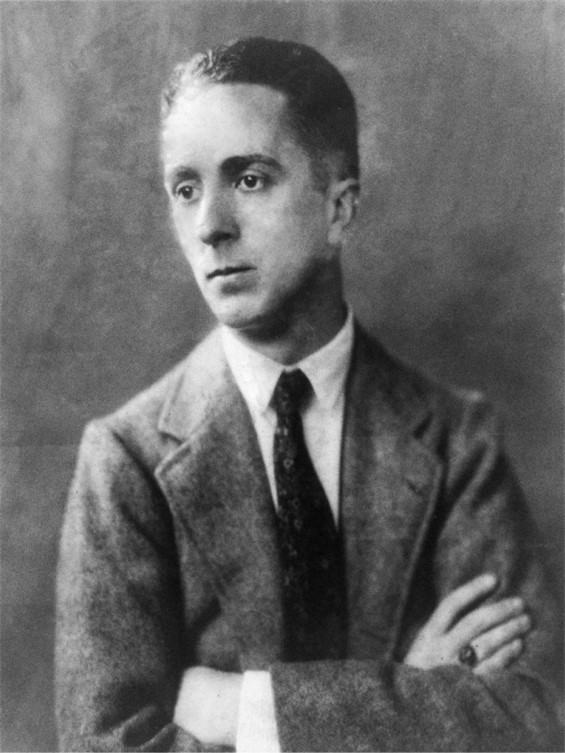
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Robert_Henri_1897.jpg
About 1900, a group of Realist artists set themselves apart from and challenged the American Impressionists and academics. They came to be known as the Ashcan School and Robert Henri was a leading figure among them. The Ashcan School artists selectively documented an unsettling, transitional time in American culture that was marked by confidence and doubt, excitement, and trepidation. Ignoring or registering only gently harsh new realities such as the problems of immigration and urban poverty, they shone a positive light on their era. Along with the American Impressionists, the Ashcan artists defined the avant-garde in the United States until the 1913 Armory Show introduced to the American public the works of true modernists Henri Matisse, Pablo Picasso, Marcel Duchamp, and others. https://www.metmuseum.org/toah/hd/ashc/hd_ashc.htm
Robert Henry Cozad (1865-1929 ) was born in Cincinnati, Ohio, to Theresa Gatewood Cozad and John Jackson Cozad, a gambler and real estate developer. The family, in a true “Wild West” story of land dispute and fatal pistol shooting, fled from Cincinnati to Denver, Colorado where young Robert changed his name to Robert Earl Henri, and in 1883, the family moved to New York City, and then, to Atlantic City in New Jersey. In 1886, a twenty-one years old Robert Henri enrolled at the Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts, one of the finest Art Schools in the US at the time, where he studied under Thomas Anshutz. Later, in Paris, Henri studied at the Académie Julian and the École des Beaux-Arts. From 1888 to 1891, when he returned back to Philadelphia, Robert stayed and traveled in Europe where he came to admire greatly the work of Francois Millet, and embrace Impressionism. Back in the United States, Robert Henri gradually became a fine Art teacher and an acclaimed artist, a leading member of the Ashcan School, an organizer, and a contributor artist of a landmark show entitled “The Eight” in N York. Robert Henri was an avid traveler, an influential Art teacher, and a great mentor to women artists in the United States. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Robert_Henri
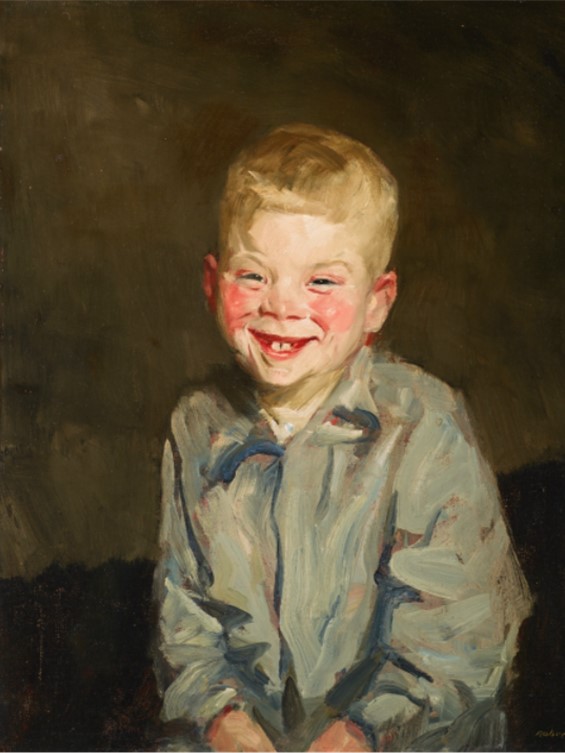

https://www.artsbma.org/collection/the-laughing-boy-jopie-van-slouten/
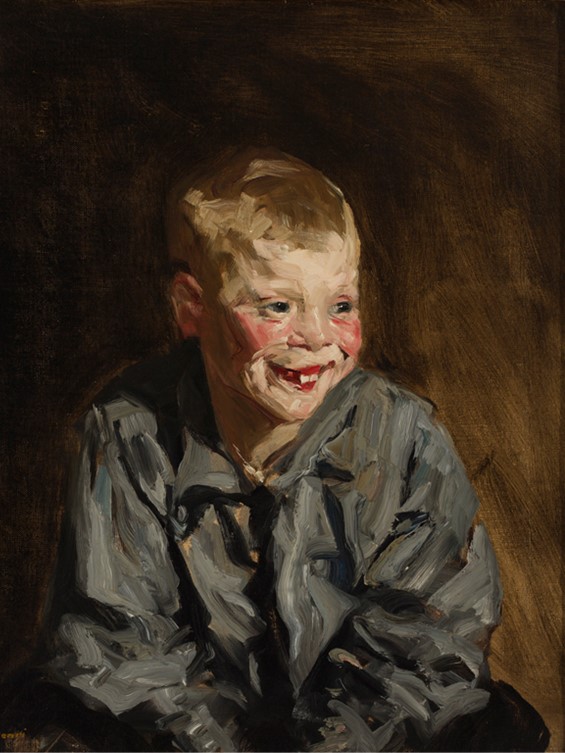

The Dutch Joe (Jopie van Slouten), 1910, oil on canvas, 60.96 × 50.8 cm, Milwaukee Art Museum, WI, USA http://collection.mam.org/details.php?id=13533
During the summers of 1907 and 1910, Henri worked in the Netherlands, where he became captivated with the work of Frans Hals (1580-1666), the Dutch painter known for using lively brushwork to create animated portraits. Hals, according to the Birmingham Museum of Art in the US, made a number of pictures of laughing children, which Henri sought to emulate in his own paintings of Dutch youths. Henri described the subject of this canvas, Jopie van Slouten, as “a great, real human character to paint.” Robert Henri painted a second portrait of the Dutch boy, known as Dutch Joe, and exhibited it in the Milwaukee Art Museum. For his second portrait of young Jopie van Slouten, Henri said: “Jopie thought it was a great joke to pose, and I thought him a great, real character. I consider it one of my successes in an effort to record a boy as he was.” http://collection.mam.org/details.php?id=13533 and https://www.artsbma.org/collection/the-laughing-boy-jopie-van-slouten/
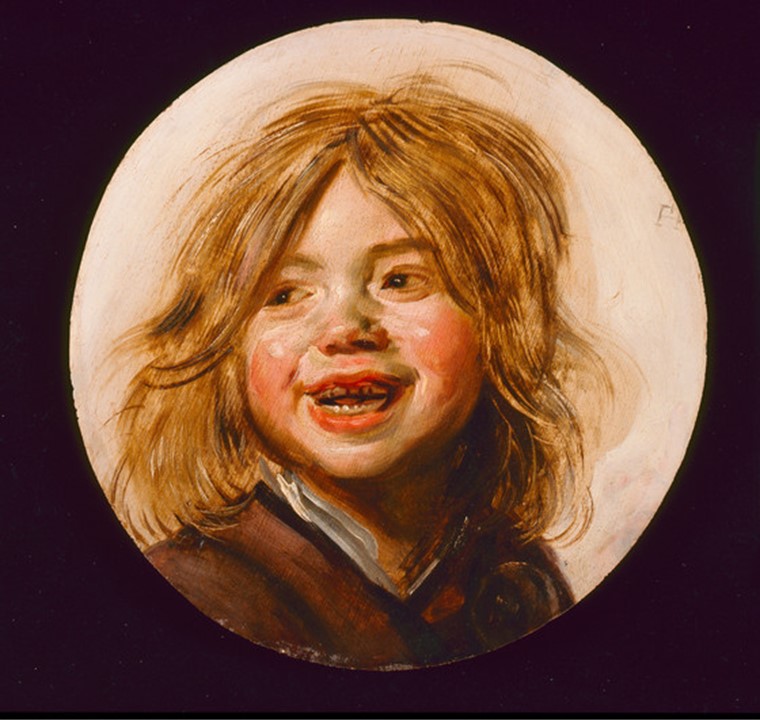

Laughing Child, circa 1620-1625, oil on wood, Diameter: 27.94 cm, LACMA (Los Angeles County Museum of Art), CA, USA https://useum.org/artwork/Laughing-boy-Frans-Hals-1625
For a Student Activity, please… Check HERE!
Between October 13, 2018, to February 24, 2019, in Haarlem, in the Netherlands, a very interesting exhibition took place titled Frans Hals and the Moderns. This exhibition showed the enormous impact of Frans Hals on modern painters. It was for the first time, that portraits of the famous 17th-century Dutch artist were presented alongside modern artistic reactions to his work… like the Laughing Boy by the American Robert Henri. https://www.franshalsmuseum.nl/nl/event/frans-hals-en-de-modernen/

https://www.franshalsmuseum.nl/en/event/frans-hals-and-the-moderns/