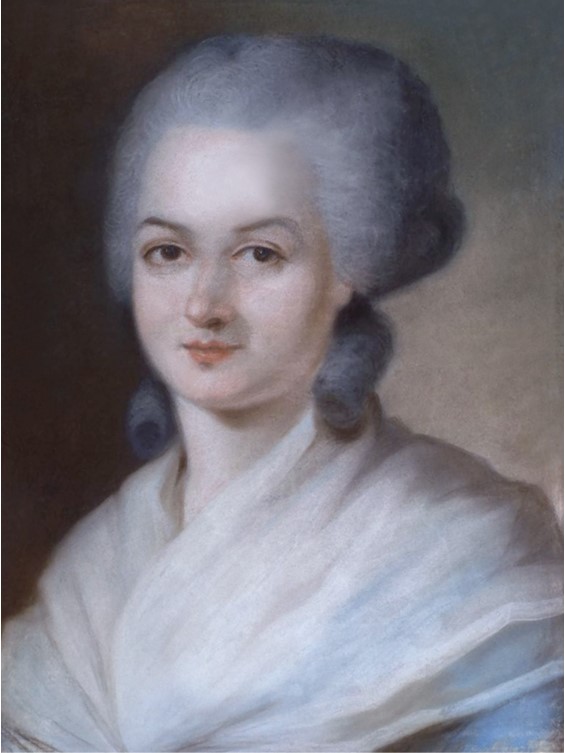
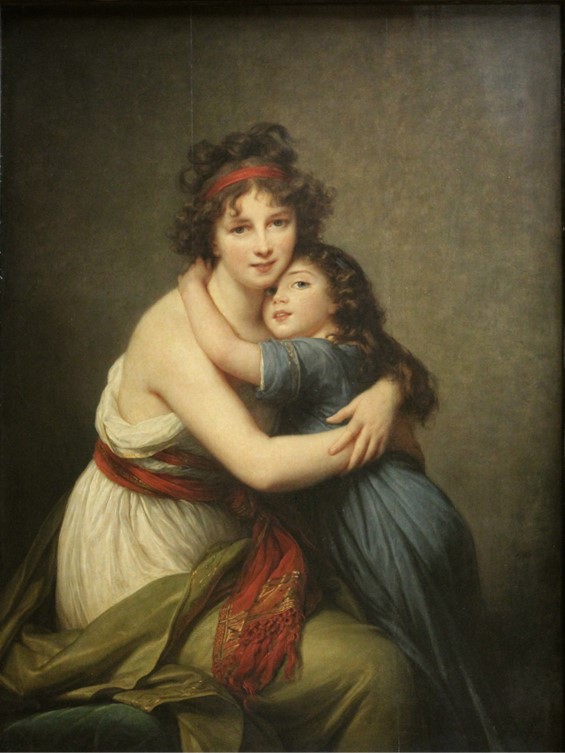
Portrait of Olympe de Gouges, 18th century, pastel on canvas, Private Collection https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Olympe_de_Gouges.png
Yesterday, at seven o’clock in the evening, a most extraordinary person called Olympe de Gouges who held the imposing title of woman of letters, was taken to the scaffold, while all of Paris, while admiring her beauty, knew that she didn’t even know her alphabet… She approached the scaffold with a calm and serene expression on her face and forced the guillotine’s furies, which had driven her to this place of torture, to admit that such courage and beauty had never been seen before… That woman… had thrown herself in the Revolution, body, and soul. But having quickly perceived how atrocious the system adopted by the Jacobins was, she chose to retrace her steps. She attempted to unmask the villains through the literary productions which she had printed and put up. They never forgave her, and she paid for her carelessness with her head… wrote an anonymous Parisian who kept a chronicle of the 1793 events. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Olympe_de_Gouges
Olympe de Gouges was a French playwright, novelist, and political activist who is best known for her writings on women’s rights and social justice. She was born Marie Gouze on May 7, 1748, in Montauban, France. Her mother, Anne Olympe Mouisset Gouze, was the daughter of a bourgeois family, but the identity of her father is ambiguous. Marie Gouze encouraged rumors that Jean-Jacques Lefranc, Marquis de Pompignan was her father, and their relationship is considered plausible but historically unverifiable.
In 1765, Olympe de Gouges married Louis-Yves Aubry, a man much older than her. The marriage was an unhappy one. In 1766 her husband died, and Olympe, funded by her wealthy friend, Jacques Biétrix de Rozières, moved to Paris in 1770 to pursue a career in writing. Described as one of the prettiest women in Paris, de Gouges socialized in fashionable society, attending the most artistic and philosophical salons of Paris. She wrote plays, novels, and pamphlets on a variety of topics, including women’s rights, slavery, and political reform. Her most famous work is the Declaration of the Rights of Woman and the Female Citizen, which she wrote in response to the Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen during the French Revolution.
She was an advocate for women’s suffrage and believed that women should have the same rights as men. She also spoke out against the slave trade and called for the abolition of slavery. De Gouges was an active participant in the French Revolution and supported the Girondists, a moderate political group. However, her views were unpopular with the radical Jacobin faction, and she was arrested and executed by the guillotine on November 3, 1793, during the Reign of Terror. De Gouges’ legacy as a feminist and social justice advocate has been recognized in recent years. Her name is now engraved on the Pantheon in Paris, a mausoleum that honors distinguished French citizens.

https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/3/34/DDFC.jpg
Olympe de Gouges wrote The Declaration of the Rights of Woman and the Female Citizen in 1791, during the French Revolution. The revolution brought about a lot of discussion about individual rights and freedoms, and Gouges saw this as an opportunity to advocate for women’s rights as well. As a feminist writer and activist, who believed in the equality of men and women, Gouges was particularly concerned with the ways in which women were excluded from political and legal rights, and the ways in which they were treated as inferior to men in society. She believed that women were capable of reason and should be granted the same rights and opportunities as men.
The Declaration of the Rights of Woman and the Female Citizen was Gouges’ response to the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen, which was passed by the National Assembly in 1789 and proclaimed the equality of all men. Gouges argued that this declaration did not go far enough and that women were also entitled to the same rights and freedoms. In her declaration, Gouges called for women to have the right to vote, to hold public office, and to receive education. She also argued that marriage should be based on mutual consent and that women should have the right to divorce if they wished. Her declaration was a radical and controversial document at the time, and it was not widely accepted by the French government or society.
Hoping to expose the failures of the French Revolution in the recognition of gender equality.. Houges’ The Declaration of the Rights of Woman starts…
Mothers, daughters, sisters, female representatives of the nation ask to be constituted as a national assembly. Considering that ignorance, neglect, or contempt for the rights of woman are the sole causes of public misfortunes and governmental corruption, they have resolved to set forth in a solemn declaration the natural, inalienable, and sacred rights of woman: so that by being constantly present to all the members of the social body this declaration may always remind them of their rights and duties; so that by being liable at every moment to comparison with the aim of any and all political institutions the acts of women’s and men’s powers may be the more fully respected; and so that by being founded henceforward on simple and incontestable principles the demands of the citizenesses may always tend toward maintaining the constitution, good morals, and the general welfare.
In consequence, the sex that is superior in beauty as in courage, needed in maternal sufferings, recognizes and declares, in the presence and under the auspices of the Supreme Being, the following rights of woman and the citizeness… https://revolution.chnm.org/d/293
For a Student Activity, please… Check HERE!